A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles.
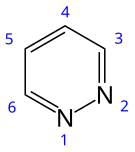
Pyrimidine is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine. One of the three diazines, it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other diazines are pyrazine and pyridazine.

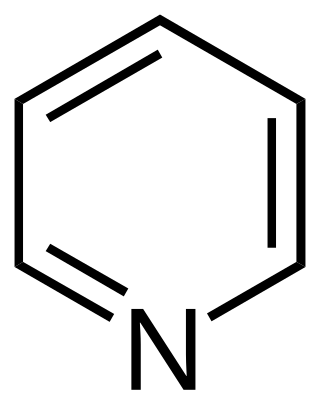
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group (=CH−) replaced by a nitrogen atom (=N−). It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide.
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic, aromatic, organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4NH. It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., N-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3. Porphobilinogen, a trisubstituted pyrrole, is the biosynthetic precursor to many natural products such as heme.

Hydrazones are a class of organic compounds with the structure R1R2C=N−NH2. They are related to ketones and aldehydes by the replacement of the oxygen =O with the =N−NH2 functional group. They are formed usually by the action of hydrazine on ketones or aldehydes.

In organic chemistry, a dicarbonyl is a molecule containing two carbonyl groups. Although this term could refer to any organic compound containing two carbonyl groups, it is used more specifically to describe molecules in which both carbonyls are in close enough proximity that their reactivity is changed, such as 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-dicarbonyls. Their properties often differ from those of monocarbonyls, and so they are usually considered functional groups of their own. These compounds can have symmetrical or unsymmetrical substituents on each carbonyl, and may also be functionally symmetrical or unsymmetrical.
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.
The Fischer indole synthesis is a chemical reaction that produces the aromatic heterocycle indole from a (substituted) phenylhydrazine and an aldehyde or ketone under acidic conditions. The reaction was discovered in 1883 by Emil Fischer. Today antimigraine drugs of the triptan class are often synthesized by this method.
Pyrazine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C4H4N2. It is a symmetrical molecule with point group D2h. Pyrazine is less basic than pyridine, pyridazine and pyrimidine. It is a "deliquescent crystal or wax-like solid with a pungent, sweet, corn-like, nutty odour".

Benzofuran is the heterocyclic compound consisting of fused benzene and furan rings. This colourless liquid is a component of coal tar. Benzofuran is the structural nucleus of many related compounds with more complex structures. For example, psoralen is a benzofuran derivative that occurs in several plants.

Indazole, also called isoindazole, is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound consists of the fusion of benzene and pyrazole.

Acetylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3−C(=O)−CH2−C(=O)−CH3. It is classified as a 1,3-diketone. It exists in equilibrium with a tautomer CH3−C(=O)−CH=C(−OH)−CH3. The mixture is a colorless liquid. These tautomers interconvert so rapidly under most conditions that they are treated as a single compound in most applications. Acetylacetone is a building block for the synthesis of many coordination complexes as well as heterocyclic compounds.
Thiazole, or 1,3-thiazole, is a 5-membered heterocyclic compound that contains both sulfur and nitrogen. The term 'thiazole' also refers to a large family of derivatives. Thiazole itself is a pale yellow liquid with a pyridine-like odor and the molecular formula C3H3NS. The thiazole ring is notable as a component of the vitamin thiamine (B1).
Pyrazole is an organic compoundwith the formula (CH)3N2H. It is a heterocycle characterized as an azole with a 5-membered ring of three carbon atoms and two adjacent nitrogen atoms, which are in ortho-substitution. Pyrazole itself has few applications but many substituted pyrazoles are of commercial interest.
Hydrazides in organic chemistry are a class of organic compounds with the formula R−NR1−NR2R3 where R is acyl, sulfonyl, phosphoryl, phosphonyl and similar groups, R1, R2, R3 and R' are any groups. Unlike hydrazine and alkylhydrazines, hydrazides are nonbasic owing to the inductive influence of the acyl, sulfonyl, or phosphoryl substituent.
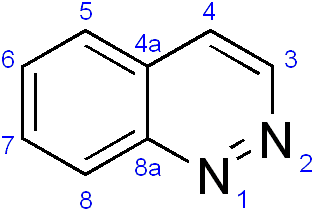
Cinnoline is an aromatic heterocyclic compound with the formula C8H6N2. It is isomeric with other naphthyridines including quinoxaline, phthalazine and quinazoline.

Isatin, also known as tribulin, is an organic compound derived from indole with formula C8H5NO2. The compound was first obtained by Otto Linné Erdman and Auguste Laurent in 1840 as a product from the oxidation of indigo dye by nitric acid and chromic acids.

Phthalazine, also called benzo-orthodiazine or benzopyridazine, is a heterocyclic organic compound with the molecular formula C8H6N2. It is isomeric with other naphthyridines including quinoxaline, cinnoline and quinazoline.

Indole is an organic compound with the formula C6H4CCNH3. Indole is classified as an aromatic heterocycle. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indoles are derivatives of indole where one or more of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced by substituent groups. Indoles are widely distributed in nature, most notably as amino acid tryptophan and neurotransmitter serotonin.
A ring forming reaction or ring-closing reaction in organic chemistry is an umbrella term for a variety of reactions that introduce one or more rings into a molecule. A heterocycle forming reaction is a reaction that introduces a new heterocycle. Important classes of ring forming reactions include annulations and cycloadditions. Heterocyclic compounds are useful in spectroscopic identification of compounds, purity criteria, and investigating the molecular electronic structures.