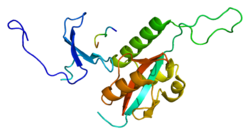
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIN1 gene. [5] [6]
Pin 1, or peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase (PPIase), isomerizes only phospho-Serine/Threonine-Proline motifs. The enzyme binds to a subset of proteins and thus plays a role as a post phosphorylation control in regulating protein function. Studies have shown that the deregulation of Pin1 may play a pivotal role in various diseases. Notably, the up-regulation of Pin1 is implicated in certain cancers, and the down-regulation of Pin1 is implicated in Alzheimer's disease. Inhibitors of Pin1 may have therapeutic implications for cancer [7] [8] and immune disorders. [9]