| Pale-billed flowerpecker | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Dicaeidae |
| Genus: | Dicaeum |
| Species: | D. erythrorhynchos |
| Binomial name | |
| Dicaeum erythrorhynchos | |
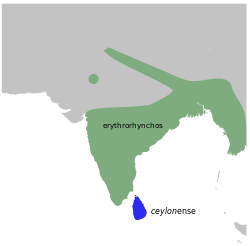 | |
The pale-billed flowerpecker or Tickell's flowerpecker (Dicaeum erythrorhynchos) is a tiny bird that feeds on nectar and berries, found in India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh and western Myanmar. The bird is common especially in urban gardens with berry bearing trees. They have a rapid chipping call and the pinkish curved beak separates it from other species in the region. [3]



