
The South Australian cobbler, better known as the soldier but also known as the cobbler, devilfish or soldierfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a waspfish, belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae which is classified within the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. It is endemic to southern Australia. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Gymnapistes.

Apistinae, the wasp scorpionfishes, is a subfamily of venomous, marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and related species. These fishes are native to the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.

The leaf goblinfish is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a waspfish belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. This is the only species in the monotypic genus Neovespicula. It is found in coastal habitats of the Indo-West Pacific region.

Tetraroginae is a subfamily of marine ray-finned fishes, commonly known as waspfishes or sailback scorpionfishes, belonging to the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. These fishes are native to the Indian Ocean and the West Pacific. As their name suggests, waspfishes are often venomous; having poison glands on their spines. They are bottom-dwelling fish, living at depths to 300 metres (980 ft). These creatures usually live in hiding places on the sea bottom.

The smoothskin scorpionfish is a species of ray-finned fish, a waspfish belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Coccotropsis. This species is endemic to the seas off South Africa.

Centropogon is a genus of ray-finned fishes, waspfishes belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. These fishes are endemic to the brackish and marine waters around Australia.

Paracentropogon longispinis, the wispy waspfish, sailfin waspfish, whiteface waspfish or whiteface roguefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a waspfish belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. It is found in the central Indo-West Pacific. It is the type species of the genus Paracentropogon.

Apistus is a monotypic genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Apistinae, the wasp scorpionfishes, part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. Its only species is the Apistus carinatus which has the common names ocellated waspfish, bearded waspfish, longfin waspfish or ringtailed cardinalfish, has a wide Indo-Pacific distribution. This species has venom bearing spines in its fins.

Ablabys is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes, waspfishes belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. The fishes in this genus are found in the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.

Glyptauchen is a monotypic genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae, the waspfishes. The only species in the genus is the goblinfish, also known as the saddlehead or saddlehead goblinfish which is endemic to the southern coasts of Australia. The goblinfish has venomous spines in its fins.
Liocranium is a small genus of marine ray-finned fishes, waspfishes belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. The fishes in this genus are found in the eastern Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.

Ocosia is a genus of ray-finned fishes, waspfishes belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. These fish are found in the Indian Ocean and western Pacific Ocean.

Pseudovespicula is a genus of venomous ray-finned fishes, waspfishes belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. It has been considered to be a monotypic genus, containing only the type species, Pseudovespicula dracaena, but some authorities classify three species within the genus. The genus is found in the Indo-Pacific region.

Richardsonichthys, is a monotypic genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae, the waspfishes, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. The only species in the genus is the whiteface waspfish, also known as the whitebelly roguefish, rouge fish, Torres Strait soldier fish or Richardson's waspfish. This species is native to reefs of the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.

Snyderina is a genus of ray-finned fishes, waspfishes belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. These fishes are found in the western Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.
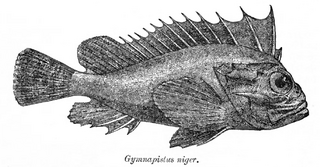
Tetraroge is a genus of ray-finned fishes, waspfishes belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. These fishes are native to the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.

Vespicula is a genus of venomous ray-finned fishes, waspfishes belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. These fishes are native to the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean. Although FishBase recognises this genus as valid, other authorities, such as the Catalog of Fishes regard it as a synonym of Trichosomus.

Ablabys macracanthus, also known as the spiny waspfish or as the spiny leaf-fish in Indonesia, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a waspfish belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. This species is found in the Western Pacific and Indian Oceans.

The Eastern fortescue, also known as the fortesque, Southern fortescue, fortie or Southern bullrout, is a species of ray-finned fish, a waspfish belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. It is found the coastal waters of eastern Australia.

The mangrove waspfish, also known as the goblinfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a waspfish belonging to the subfamily Tetraroginae, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. This species occurs in the Indo-Pacific region.
















