
Panarthropoda is a proposed animal clade containing the extant phyla Arthropoda, Tardigrada and Onychophora. Panarthropods also include extinct marine legged worms known as lobopodians ("Lobopodia"), a paraphyletic group where the last common ancestor and basal members (stem-group) of each extant panarthropod phylum are thought to have risen. However the term "Lobopodia" is sometimes expanded to include tardigrades and onychophorans as well.

Dominican amber is amber from the Dominican Republic derived from resin of the extinct tree Hymenaea protera.
Michael S. Engel, FLS, FRES is an American paleontologist and entomologist, notable for contributions to insect evolutionary biology and classification. In connection with his studies he has undertaken field expeditions in Central Asia, Asia Minor, the Levant, Arabia, eastern Africa, the high Arctic, and South and North America, and has published more than 925 papers in scientific journals. Some of Engel's research images were included in exhibitions on the aesthetic value of scientific imagery.

The Stephanidae, sometimes called crown wasps, are a family of parasitoid wasps. They are the only living members of the superfamily Stephanoidea. Stephanidae has at least 345 living species in 11 genera. The family is considered cosmopolitan in distribution, with the highest species concentrations in subtropical and moderate climate zones. Stephanidae also contain four extinct genera described from both compression fossils and inclusions in amber.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 1964.

Tardigrades, known colloquially as water bears or moss piglets, are a phylum of eight-legged segmented micro-animals. They were first described by the German zoologist Johann August Ephraim Goeze in 1773, who called them Kleiner Wasserbär'little water bear'. In 1776, the Italian biologist Lazzaro Spallanzani named them Tardigrada, which means 'slow steppers'.

Parachela is an order of tardigrades in the class Eutardigrada. Members of this order have existed for at least 72 million years, up to the present. The oldest known species are Beorn leggi and Aerobius dactylus.

Coprinites is an extinct monotypic genus of gilled fungus in the Agaricales family Agaricaceae. At present it contains the single species Coprinites dominicana.
Aureofungus is an extinct monotypic genus of gilled fungus in the order Agaricales. At present it contains the single species Aureofungus yaniguaensis.

Protomycena is an extinct monotypic genus of gilled fungus in the family Mycenaceae, of order Agaricales. At present it contains the single species Protomycena electra, known from a single specimen collected in an amber mine in the Cordillera Septentrional area of the Dominican Republic. The fruit body of the fungus has a convex cap that is 5 mm (0.2 in) in diameter, with distantly spaced gills on the underside. The curved stipe is smooth and cylindrical, measuring 0.75 mm (0.030 in) thick by 10 mm (0.39 in) long, and lacks a ring. It resembles extant species of the genus Mycena. Protomycena is one of only five known agaric fungus species known in the fossil record and the second to be described from Dominican amber.

Palaeoagaracites is an extinct monotypic genus of gilled fungus in the order Agaricales. It contains the single species Palaeoagaracites antiquus.
Parastemmiulus is an extinct genus of millipede in the family Stemmiulidae known from a fossil found in Mexico. There is one described species in the genus, Parastemmiulus elektron. The species is one of three millipedes described from Mexican amber, and the oldest Stemmiulidae fossil species as of 2013.

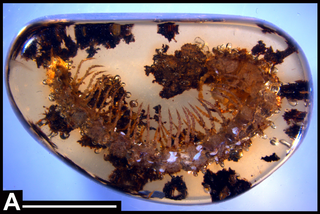
Maatidesmus is an extinct genus of millipede in the family Chelodesmidae known from a fossil found in North America. There is one described species in the genus, Maatidesmus paachtun, one of three millipedes described from Mexican amber.
Anbarrhacus is an extinct genus of millipede in the family Platyrhacidae known from a fossil found in North America. There is one described species in the genus, Anbarrhacus adamantis, which is one of three millipedes described from Mexican amber.

Beorn is an extinct genus of tardigrade and the first known fossil tardigrade, discocered in Late Cretaceous amber from Manitoba, Canada. The genus contains a single species, B. leggi, and it was originally classified as the only member of its family, the Beornidae, but was later reclassified as belonging to the Hypsibiidae.
2015 in paleoentomology is a list of new fossil insect taxa that were described during the year 2015, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleoentomology that were scheduled to occur during the year.
This paleoentomology list records new fossil insect taxa that were to be described during the year 2021, as well as notes other significant paleoentomology discoveries and events which occurred during that year.
This paleoentomology list records new fossil insect taxa that are to be described during the year 2022, as well as notes other significant paleoentomology discoveries and events which occurred during that year.
This list of 2023 in paleoentomology records new fossil insect taxa that are to be described during the year, as well as documents significant paleoentomology discoveries and events which occurred during that year.

Aerobius is a genus of extinct tardigrades of the superfamily Hypsibioidea. The genus contains a single species, A. dactylus, known from a single individual preserved in amber. The Aerobius holotype is preserved in the same piece of Late Cretaceous amber as Beorn, another extinct tardigrade. The specimen was found near Cedar Lake in Manitoba, Canada.












