
Clover, also called trefoil, are plants of the genus Trifolium, consisting of about 300 species of flowering plants in the legume family Fabaceae originating in Europe. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution with highest diversity in the temperate Northern Hemisphere, but many species also occur in South America and Africa, including at high altitudes on mountains in the tropics. They are small annual, biennial, or short-lived perennial herbaceous plants, typically growing up to 30 centimetres (12 in) tall. The leaves are trifoliate, with stipules adnate to the leaf-stalk, and heads or dense spikes of small red, purple, white, or yellow flowers; the small, few-seeded pods are enclosed in the calyx. Other closely related genera often called clovers include Melilotus and Medicago.

Trifoliumrepens, the white clover, is a herbaceous perennial plant in the bean family Fabaceae. It is native to Europe, including the British Isles, and central Asia and is one of the most widely cultivated types of clover. It has been widely introduced worldwide as a forage crop, and is now also common in most grassy areas of North America, Australia and New Zealand. The species includes varieties often classed as small, intermediate and large, according to height, which reflects petiole length. The term 'white clover' is applied to the species in general, 'Dutch clover' is often applied to intermediate varieties, and 'ladino clover' is applied to large varieties.
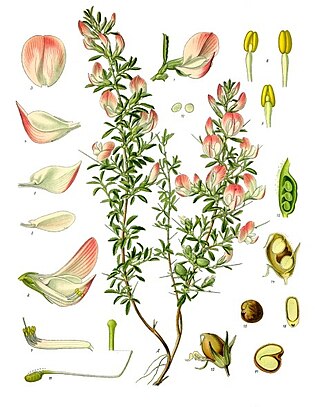
Ononis is a large genus of perennial herbs and shrubs from the legume family Fabaceae. The members of this genus are often called restharrows as some species grow as weeds on arable lands whose tough stems would stop the harrow. They are natively distributed in Europe.
Rest-harrow may refer to:

Lotaustralin is a cyanogenic glucoside found in small amounts in Fabaceae austral trefoil, cassava, lima bean, roseroot and white clover, among other plants. Lotaustralin is the glucoside of methyl ethyl ketone cyanohydrin and is structurally related to linamarin, the acetone cyanohydrin glucoside also found in these plants. Both lotaustralin and linamarin may be hydrolyzed by the enzyme linamarase to form glucose and a precursor to the toxic compound hydrogen cyanide.
British NVC community MC5 is one of the maritime cliff communities in the British National Vegetation Classification system. It is one of five communities categorised as maritime cliff crevice and ledge communities.

Ononis repens, the common restharrow, is a flowering plant species in the bean family Fabaceae. The name is synonym of Ononis spinosa subsp. procurrens.

Nyctegretis lineana is a moth of the family Pyralidae. It is found from Europe to China and Mongolia.

Grapholita compositella, the clover seed moth, is a moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found from Europe to Asia Minor, Mongolia, China and eastern Russia. It is also present in North America.
Clover yellow vein virus (ClYVV) is a plant pathogenic virus in the genus Potyvirus and the virus family Potyviridae. Like other members of the Potyvirus genus, ClYVV is a monopartite strand of positive-sense, single-stranded RNA surrounded by a capsid made for a single viral encoded protein. The virus is a filamentous particle that measures about 760 nm in length. This virus is transmitted by several species of aphids in a nonpersistent manner and by mechanical inoculation.

The clover case-bearer or small clover case-bearer is a moth of the family Coleophoridae. It is native to Asia, Europe and North Africa, and has been introduced to Australia and New Zealand.

The tribe Trifolieae is one of the subdivisions of the plant family Fabaceae. It is included within the inverted repeat-lacking clade (IRLC). All of the members of this tribe are trifoliate.

Phyllonorycter insignitella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is found in all of Europe, except the Balkan Peninsula.
Phyllonorycter medicaginella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is found from Denmark and Poland to Belgium, the Alps, Bulgaria and Ukraine.

Phyllonorycter nigrescentella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from all of Europe except the Balkan Peninsula.

Aproaerema anthyllidella is a moth of the family Gelechiidae. It is found in most of Europe, Kyrgyzstan, Iran and North America.

Mirificarma eburnella is a moth of the family Gelechiidae. It is found in western, central and southern Europe and extends to North Africa, the Middle East and Russia. It is also found in California, United States, where it is presumed to have been introduced.

Trifolium occidentale, the western clover, is a clover plant belonging to the genus Trifolium in the legume family, Fabaceae. Its flowers are white, similar to white clover, with which it has long been confused. This species lives almost exclusively in sand dunes and sea cliffs on the Atlantic coast of Europe, especially Cornwall and the Channel Islands. The species was first described in 1961 by Dr David E Coombe of Cambridge University.
Bembecia albanensis is a moth of the family Sesiidae. It is found from most of Europe to Asia Minor and the Black Sea. It is also found in North Africa.

Westfield Farm Chalk Bank is a 14.1-hectare (35-acre) biological Site of Special Scientific Interest west of East Garston in Berkshire.














