
The Cupedidae are a small family of beetles, notable for the square pattern of "windows" on their elytra, which give the family their common name of reticulated beetles.

The Ommatidae are a family of beetles in the suborder Archostemata. The Ommatidae are considered the extant beetle family that has most ancestral characteristics. There are only seven extant species, confined to Australia and South America. However, the geographical distribution was much wider during the Mesozoic spanning across Eurasia and Australia, suggesting that they were widespread on Pangea. So far, over 26 extinct genera containing over 170 species of these beetles have been described. Three extant genera have been assigned to this family: Omma,Tetraphalerus and Beutelius. The family is considered to be a subfamily of Cupedidae by some authors, but have been found to be more closely related to Micromalthidae in molecular phylogenies. A close relationship with Micromalthidae is supported by several morphological characters, including those of the mandibles and male genitalia. Due to their rarity, their ecology is obscure, it is likely that their larvae feed on deadwood.
Brochocoleus is an extinct genus of beetles in the family Ommatidae, known from the Early Jurassic to the Early Late Cretaceous. 9 species are currently recognised, with many species being reassigned to other genera by Kirejtshuk's major systematic revision in 2020.
Zygadenia is an extinct genus of archostematan beetles from the Jurassic to Cretaceous. It is considered to be a senior synonym of Notocupes by Kirejtshuk (2020), but other researchers suggest to reserve the genus Zygadenia as a form taxon for isolated elytra that probably belong to the genus Notocupes, while retaining Notocupes as a valid genus for complete body fossils.

Omma is a genus of beetles in the family Ommatidae. Omma is an example of a living fossil. The oldest species known, O. liassicum, lived during the final stage of the Triassic (Rhaetian), over 200 million years ago, though the placement of this species in Omma has been questioned. Numerous other fossil species are known from the Jurassic and Cretaceous of Europe and Asia. The only living species is Omma stanleyi, which is endemic to Australia. Three other extant species endemic to Australia that were formerly part of this genus were moved to the separate genus Beutelius in 2020.Omma stanleyi is strongly associated with wood, being found under Eucalyptus bark and exhibiting thanatosis when disturbed. Its larval stage and many other life details are unknown due to its rarity. Males are typically 14–20 mm in length, while females are 14.4-27.5 mm. Omma stanleyi occurs throughout eastern Australia from Victoria to Central Queensland.
Magnocoleus is an extinct genus of beetles from the Early Cretaceous of China, between 130.0 and 125.45 Mya. The genus contains a single species, Magnocoleus huangjiapuensis, and is the only member of the family Magnocoleidae in the suborder Archostemata. Magnocoleus was first described by Chinese palaeoentomologist Hong Youchong in 1998, based on fossils of isolated elytra from the Qingshila Formation in Huangjiapu, near the Nantianmen village of Zhangjiakou in Hebei. Recent phylogenetic analyses have suggested that Magnocoleus is closely related to or placed within either Cupedidae or Ommatidae.

Peltis is a genus of beetles found in North America and Europe, and the sole extant member of the family Peltidae, formerly included in the Trogossitidae. Members of this genus are dark, averaging from brown, to dark brown, to black. They are small, wide, and flat-bodied with wide, ridged elytra. Fossil species of this genus are known from the Eocene aged Florissant Formation of the United States, as well as the Baltic amber of Europe.

Bukhkalius is an extinct genus of beetle belonging to the family Ommatidae, it contains the single species, Bukhkalius lindae. It was described in 2017 initially as a species of the extant genus Tetraphalerus and was placed into a separate monotypic genus in 2020, which was reaffirmed in a 2021 study. It is known from a single specimen from Burmese amber, dating to the Cenomanian stage of the Late Cretaceous. The specimen is around 4.7 mm long and around 1.3 mm wide.

Cionocups is an extinct genus of ommatid beetle. It is known from a single species, Cionocups manukyani, found in Cenomanian aged Burmese amber from Myanmar. It was originally considered to be closely related to the genus Cionocoleus, but it is considered a junior synonym of Omma by some subsequent authors.

Clessidromma is an extinct genus of ommatid beetle. It currently contains a single species Clessidromma palmeri, known from the Cenomanian aged Burmese amber of Myanmar. Kirejtshuk (2020) synonymised Lepidomma with Clessidromma and included two additional species in the latter: C. tianae, originally the type species of Lepidomma, and C. zengi, a newly described species. Li et al. (2021) disputed the synonymy of Lepidomma with Clessidromma, maintaining Lepidomma as a separate genus, and transferred C. zengi to a new genus, Kirejtomma, in 2021.
Echinocups is an extinct genus of ommatid beetle. It was created in 2020 to house three species originally assigned to Notocupes, E. denticollis, E. neli and E. ohmkuhnlei The genus name refers to the sharp spikes present on the elytra. All three species are known from the Cenomanian aged Burmese amber of Myanmar. The status of Echinocups as a distinct genus was contested by Li et al. (2023), who considered the genus Echinocups to be a junior synonym of the genus Notocupes.
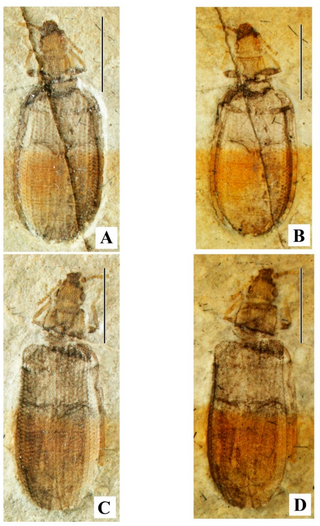
Monticupes is an extinct genus of ommatid beetle. The genus is characterised by "moderately oval body, subtriangular or long (subparallelsided) head with large eyes and well raised temples, pronotum carinate and with subexplanate sides, veins well expressed with fused A1 and Cu at apex and their common vein ending on Sc, explanate elytral sides moderately wide and with diffuse small microtubercles, and abdominal ventrites co-planar (abutting)."

Odontomma is an extinct genus of ommatid beetle. It is known from two species, O. sulcatum and O. trachylaenum, both known from the Aptian aged Yixian Formation of China. It is characterised by "moderately oval body, moderately more or less long and subparallel or oviform head with comparatively small eyes, rather wide pronotum with the widely explanate carinate sides, all veins ending on Sc along the lateral elytral edge, veins well expressed, explanate elytral sides with diffuse small microtubercles, and abdominal ventrites co-planar (abutting) or looking like bordered along the posterior edge." It is considered morphologically similar to Diluticupes.

Rhopalomma is an extinct genus of ommatid beetle. It is known from a single species, Rhopalomma stefaniae described from the Upper Jurassic (Tithonian) Talbragar fossil locality in New South Wales, Australia.
Stegocoleus is an extinct genus of ommatid beetle. Its distinctive morphology includes a distinctive flat rim on the outer edge of the elytra similar to those of Burmocoleus and Jarzembowskiops, but is distinguished from those genera by a distinctive prothorax. It is known from 3 species found in Cenomanian aged Burmese amber.
Liassocupes is an extinct genus of ommatid beetle from the Jurassic period of England. The only included species is Liassocupes parvus. It is known from compression fossils found at Flatstones near Charmouth in the Sinemurian aged part of the Charmouth Mudstone Formation, Dorset. Other species previously assigned to the genus include Liassocupes (?) maculatus described by Whalley in 1985 from the same locality, but this was subsequently suggested by Ponomarenko to belong to either Omma or Tetraphalerus and was considered to belong to the genus Brochocoleus by Kirejtshuk (2020). Another species Liassocupes (?) giganteus also described by Whalley (1985) from the same locality, was found to be a member of the genus Mimemala in the extinct family Schizocoleidae.
Jarzembowskiops is an extinct genus of ommatid beetle. It is known from one species, J. caseyi described from the Cenomanian aged Burmese amber of Myanmar. It was originally placed as a species of Brochocoleus, but was subsequently considered distinct enough to warrant its placement in its own separate genus. The species is named after Raymond Casey, a British geologist, while the genus is named after Edmund Jarzembowski, a noted British palaeoentomologist.

Kirejtomma is an extinct genus of ommatid beetle, known from the early Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) aged Burmese amber of Myanmar. The type and only known species K. zhengi was described in 2020 as a species of Clessidromma, and placed into the new genus in 2021.
Lepidomma is an extinct genus of ommatid beetle. The genus was first described in 2019 for the species L. tianae. Lepidomma was synonymised with Clessidromma by Kirejtshuk, 2020. This synonymy was disputed by Li et al. (2021), who maintained Lepidomma as a separate genus from Clessidromma. Three additional species of Lepidomma were described in 2020 and 2022. All four species are known from the Cenomanian aged Burmese amber of Myanmar.

Notocupes is an extinct genus of medium-sized archostematan beetles from the Mesozoic Era of Eurasia, including over 50 described species. Historically, the genus was classified as a member of the family Ommatidae, but the presence of characters such as the horizontal mandibular cutting edge, separated procoxae and overlapping abdominal sternites indicate that the genus may have a closer affinity with the family Cupedidae. Notocupes is considered to be a junior synonym of Zygadenia by Kirejtshuk (2020), but other researchers suggest to reserve the genus Zygadenia as a form taxon for isolated elytra that probably belong to the genus Notocupes, while retaining Notocupes as a valid genus for complete body fossils. Most species of Notocupes were described from compression fossils. An additional three species were described from Cenomanian-aged Burmese amber, which were treated as a separate genus, Echinocups, by Kirejtshuk (2020), but Li et al. (2023) consider Echinocups to be a junior synonym of Notocupes. Notocupes has a flattened body, which may suggest that it occupied narrow habitats, such as living under bark. Some species had serrated/spined margins of the carapace, which may have served as a defense against predators, or served as camouflage to resemble bark.












