
Soy milk, also known as soya milk or soymilk, is a plant-based drink produced by soaking and grinding soybeans, boiling the mixture, and filtering out remaining particulates. It is a stable emulsion of oil, water, and protein. Its original form is an intermediate product of the manufacture of tofu. Originating in China, it became a common beverage in Europe and North America in the latter half of the 20th century, especially as production techniques were developed to give it a taste and consistency more closely resembling that of dairy milk. Soy milk may be used as a substitute for dairy milk by individuals who are vegan or lactose intolerant.

Rice milk is a plant milk made from rice. Commercial rice milk is typically manufactured using brown rice and brown rice syrup, and may be sweetened using sugar or sugar substitutes, and flavored by common ingredients, such as vanilla. It is commonly fortified with protein and micronutrients, such as vitamin B12, calcium, iron, or vitamin D.

Powdered milk, also called milk powder, dried milk, or dry milk, is a manufactured dairy product made by evaporating milk to dryness. One purpose of drying milk is to preserve it; milk powder has a far longer shelf life than liquid milk and does not need to be refrigerated, due to its low moisture content. Another purpose is to reduce its bulk for the economy of transportation. Powdered milk and dairy products include such items as dry whole milk, nonfat (skimmed) dry milk, dry buttermilk, dry whey products and dry dairy blends. Many exported dairy products conform to standards laid out in Codex Alimentarius.

Almond milk is a plant-based milk substitute with a watery texture and nutty flavor manufactured from almonds, although some types or brands are flavored in imitation of cow's milk. It does not contain cholesterol or lactose and is low in saturated fat. Almond milk is often consumed by those who are lactose-intolerant and others, such as vegans, who do not consume dairy products. Commercial almond milk comes in sweetened, unsweetened, vanilla and chocolate flavors, and is usually fortified with micronutrients. It can also be made at home using a blender, almonds and water.

The Sanitarium Health and Wellbeing Company is the trading name of two sister food companies. Both are wholly owned by the Seventh-day Adventist Church.

Vegetarian nutrition is the set of health-related challenges and advantages of vegetarian diets.

Milo is a chocolate-flavoured malted powder product produced by Nestlé, typically mixed with milk, hot water, or both, to produce a beverage. It was originally developed in Australia by Thomas Mayne (1901–1995) in 1934.

Plant milk is a category of non-dairy beverages made from a water-based plant extract for flavoring and aroma. Nut milk is a subcategory made from nuts, while other plant milks may be created from grains, pseudocereals, legumes, seeds or coconut. Plant-based milks are consumed as alternatives to dairy milk and provide similar qualities, such as a creamy mouthfeel, as well as a bland or palatable taste. Many are sweetened or flavored.

A milk substitute is any substance that resembles milk and can be used in the same ways as milk. Such substances may be variously known as non-dairy beverage, nut milk, grain milk, legume milk, mock milk and alternative milk.

Peanut milk is a plant milk, which is an alternative to animal milk. It is made with peanuts, water, and sometimes other additional ingredients like salt, sugar, or cinnamon. Peanut milk is high in fat and protein compared to other plant-based milks. This milk is sometimes used by people who identify with lactose intolerance, veganism, or a casein-free diet, as it has no lactose, but includes nutritional benefits like being high in magnesium, Vitamin E, Vitamin B-6, and protein.

Silk is an American brand of dairy-substitute products currently owned by Danone after it purchased WhiteWave Foods in 2016.

Oat milk is a plant milk derived from whole oat grains by extracting the plant material with water. Oat milk has a creamy texture and mild oatmeal-like flavor, and is manufactured in various flavors, such as sweetened, unsweetened, vanilla, and chocolate.
Food chemistry is the study of chemical processes and interactions of all biological and non-biological components of foods. The biological substances include such items as meat, poultry, lettuce, beer, milk as examples. It is similar to biochemistry in its main components such as carbohydrates, lipids, and protein, but it also includes areas such as water, vitamins, minerals, enzymes, food additives, flavors, and colors. This discipline also encompasses how products change under certain food processing techniques and ways either to enhance or to prevent them from happening. An example of enhancing a process would be to encourage fermentation of dairy products with microorganisms that convert lactose to lactic acid; an example of preventing a process would be stopping the browning on the surface of freshly cut apples using lemon juice or other acidulated water.

Soy yogurt, also referred to as soya yogurt, soygurt or yofu, is a yogurt-like product made with soy milk.
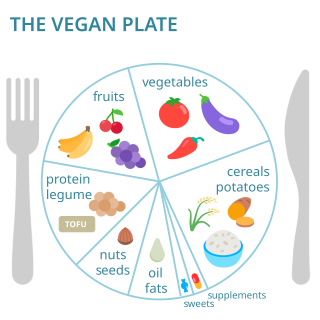
Vegan nutrition refers to the nutritional and human health aspects of vegan diets. A well-planned vegan diet is suitable to meet all recommendations for nutrients in every stage of human life. Vegan diets tend to be higher in dietary fiber, magnesium, folic acid, vitamin C, vitamin E, and phytochemicals; and lower in calories, saturated fat, iron, cholesterol, long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, calcium, zinc, and vitamin B12.

Pea protein is a food product and protein supplement derived and extracted from yellow and green split peas, Pisum sativum. It can be used as a dietary supplement to increase an individual's protein or other nutrient intake, or as a substitute for other food products. As a powder, it is used as an ingredient in food manufacturing, such as a thickener, foaming agent, or an emulsifier.

Vegan cheese is a category of non-dairy, plant-based cheese analogues. Vegan cheeses range from soft fresh cheeses to aged and cultured hard grateable cheeses like plant-based Parmesan. The defining characteristic of vegan cheese is the exclusion of all animal products.

As in the human practice of veganism, vegan dog foods are those formulated with the exclusion of ingredients that contain or were processed with any part of an animal, or any animal byproduct. Vegan dog food may incorporate the use of fruits, vegetables, cereals, legumes including soya, nuts, vegetable oils, as well as any other non-animal based foods.

Ripple Foods is a California-based brand of pea-protein dairy alternative products. The company was founded in 2014 by Adam Lowry and Neil Renninger in Emeryville, California.



















