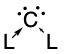In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to other atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. Conceptually, the oxidation state may be positive, negative or zero. While fully ionic bonds are not found in nature, many bonds exhibit strong ionicity, making oxidation state a useful predictor of charge.

Group 5 is a group of elements in the periodic table. Group 5 contains vanadium (V), niobium (Nb), tantalum (Ta) and dubnium (Db). This group lies in the d-block of the periodic table. This group is sometimes called the vanadium group or vanadium family after its lightest member; however, the group itself has not acquired a trivial name because it belongs to the broader grouping of the transition metals.

Sulfur monoxide is an inorganic compound with formula SO. It is only found as a dilute gas phase. When concentrated or condensed, it converts to S2O2 (disulfur dioxide). It has been detected in space but is rarely encountered intact otherwise.

In organic chemistry, olefin metathesis is an organic reaction that entails the redistribution of fragments of alkenes (olefins) by the scission and regeneration of carbon-carbon double bonds. Because of the relative simplicity of olefin metathesis, it often creates fewer undesired by-products and hazardous wastes than alternative organic reactions. For their elucidation of the reaction mechanism and their discovery of a variety of highly active catalysts, Yves Chauvin, Robert H. Grubbs, and Richard R. Schrock were collectively awarded the 2005 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
A transition metal carbene complex is an organometallic compound featuring a divalent carbon ligand, itself also called a carbene. Carbene complexes have been synthesized from most transition metals and f-block metals, using many different synthetic routes such as nucleophilic addition and alpha-hydrogen abstraction. The term carbene ligand is a formalism since many are not directly derived from carbenes and most are much less reactive than lone carbenes. Described often as =CR2, carbene ligands are intermediate between alkyls (−CR3) and carbynes (≡CR). Many different carbene-based reagents such as Tebbe's reagent are used in synthesis. They also feature in catalytic reactions, especially alkene metathesis, and are of value in both industrial heterogeneous and in homogeneous catalysis for laboratory- and industrial-scale preparation of fine chemicals.

Tantalum(V) chloride, also known as tantalum pentachloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula TaCl5. It takes the form of a white powder and is commonly used as a starting material in tantalum chemistry. It readily hydrolyzes to form tantalum(V) oxychloride (TaOCl3) and eventually tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5); this requires that it be synthesised and manipulated under anhydrous conditions, using air-free techniques.

Yves Chauvin was a French chemist and Nobel Prize laureate. He was honorary research director at the Institut français du pétrole and a member of the French Academy of Science. He was known for his work for deciphering the process of olefin metathesis for which he was awarded the 2005 Nobel Prize in Chemistry along with Robert H. Grubbs and Richard R. Schrock.

Tantalum(V) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula Ta2Br10. Its name comes from the compound's empirical formula, TaBr5. It is a diamagnetic, orange solid that hydrolyses readily. The compound adopts an edge-shared bioctahedral structure, which means that two TaBr5 units are joined by a pair of bromide bridges. There is no bond between the Ta centres. Niobium(V) chloride, niobium(V) bromide, niobium(V) iodide, tantalum(V) chloride, and tantalum(V) iodide all share this structural motif.

Group 2 organometallic chemistry refers to the chemistry of compounds containing carbon bonded to any group 2 element. By far the most common group 2 organometallic compounds are the magnesium-containing Grignard reagents which are widely used in organic chemistry. Other organometallic group 2 compounds are rare and are typically limited to academic interests.

Organomolybdenum chemistry is the chemistry of chemical compounds with Mo-C bonds. The heavier group 6 elements molybdenum and tungsten form organometallic compounds similar to those in organochromium chemistry but higher oxidation states tend to be more common.
Transition metal carbyne complexes are organometallic compounds with a triple bond between carbon and the transition metal. This triple bond consists of a σ-bond and two π-bonds. The HOMO of the carbyne ligand interacts with the LUMO of the metal to create the σ-bond. The two π-bonds are formed when the two HOMO orbitals of the metal back-donate to the LUMO of the carbyne. They are also called metal alkylidynes—the carbon is a carbyne ligand. Such compounds are useful in organic synthesis of alkynes and nitriles. They have been the focus on much fundamental research.

Tantalum(V) ethoxide is a metalorganic compound with formula Ta2(OC2H5)10, often abbreviated as Ta2(OEt)10. It is a colorless solid that dissolves in some organic solvents but hydrolyzes readily. It is used to prepare films of tantalum(V) oxide.

Organotantalum chemistry is the chemistry of chemical compounds containing a carbon-to-tantalum chemical bond. A wide variety of compound have been reported, initially with cyclopentadienyl and CO ligands. Oxidation states vary from Ta(V) to Ta(-I).
Organoniobium chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing niobium-carbon (Nb-C) bonds. Compared to the other group 5 transition metal organometallics, the chemistry of organoniobium compounds most closely resembles that of organotantalum compounds. Organoniobium compounds of oxidation states +5, +4, +3, +2, +1, 0, -1, and -3 have been prepared, with the +5 oxidation state being the most common.

Pentamethylbismuth (or pentamethylbismuthorane) is an organometalllic compound containing five methyl groups bound to a bismuth atom with formula Bi(CH3)5. It is an example of a hypervalent compound. The molecular shape is trigonal bipyramid.

Plumbylenes (or plumbylidenes) are divalent organolead(II) analogues of carbenes, with the general chemical formula, R2Pb, where R denotes a substituent. Plumbylenes possess 6 electrons in their valence shell, and are considered open shell species.
Aluminium(I) nucleophiles are a group of inorganic and organometallic nucleophilic compounds containing at least one aluminium metal center in the +1 oxidation state with a lone pair of electrons strongly localized on the aluminium(I) center.
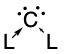
Carbones are a class of molecules containing a carbon atom in the 1D excited state with a formal oxidation state of zero where all four valence electrons exist as unbonded lone pairs. These carbon-based compounds are of the formula CL2 where L is a strongly σ-donating ligand, typically a phosphine (carbodiphosphoranes) or a N-heterocyclic carbene/NHC (carbodicarbenes), that stabilises the central carbon atom through donor-acceptor bonds. Carbones possess high-energy orbitals with both σ- and π-symmetry, making them strong Lewis bases and strong π-backdonor substituents. Carbones possess high proton affinities and are strong nucleophiles which allows them to function as ligands in a variety of main group and transition metal complexes. Carbone-coordinated elements also exhibit a variety of different reactivities and catalyse various organic and main group reactions.
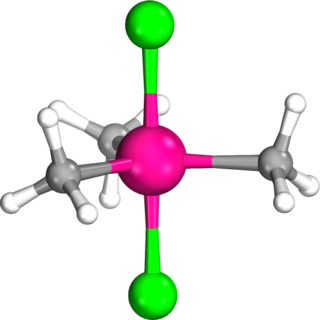
Dichlorotrimethyltantalum, or trimethyltantalum dichloride, is an organotantalum complex with the molecular formula TaCl2(CH3)3. It forms pale yellow, highly air- and water-sensitive crystals which easily sublime in vacuum at room temperature. It was the first reported σ-bonded alkyl complex of tantalum, synthesised by Gordon L. Juvinall at the California Institute of Technology in 1964. It serves as an important precursor for the preparation of a large number of Ta(V) complexes.