Lithium is a chemical element; it has symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable, and must be stored in vacuum, inert atmosphere, or inert liquid such as purified kerosene or mineral oil. It exhibits a metallic luster. It corrodes quickly in air to a dull silvery gray, then black tarnish. It does not occur freely in nature, but occurs mainly as pegmatitic minerals, which were once the main source of lithium. Due to its solubility as an ion, it is present in ocean water and is commonly obtained from brines. Lithium metal is isolated electrolytically from a mixture of lithium chloride and potassium chloride.

Niobium is a chemical element; it has symbol Nb and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has similar ductility to iron. Niobium oxidizes in Earth's atmosphere very slowly, hence its application in jewelry as a hypoallergenic alternative to nickel. Niobium is often found in the minerals pyrochlore and columbite, hence the former name "columbium". Its name comes from Greek mythology: Niobe, daughter of Tantalus, the namesake of tantalum. The name reflects the great similarity between the two elements in their physical and chemical properties, which makes them difficult to distinguish.

Protactinium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pa and atomic number 91. It is a dense, radioactive, silvery-gray actinide metal which readily reacts with oxygen, water vapor, and inorganic acids. It forms various chemical compounds, in which protactinium is usually present in the oxidation state +5, but it can also assume +4 and even +3 or +2 states. Concentrations of protactinium in the Earth's crust are typically a few parts per trillion, but may reach up to a few parts per million in some uraninite ore deposits. Because of its scarcity, high radioactivity, and high toxicity, there are currently no uses for protactinium outside scientific research, and for this purpose, protactinium is mostly extracted from spent nuclear fuel.

Tantalum is a chemical element; it has symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as tantalium, it is named after Tantalus, a figure in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductile, lustrous, blue-gray transition metal that is highly corrosion-resistant. It is part of the refractory metals group, which are widely used as components of strong high-melting-point alloys. It is a group 5 element, along with vanadium and niobium, and it always occurs in geologic sources together with the chemically similar niobium, mainly in the mineral groups tantalite, columbite and coltan.

Pyroelectricity is a property of certain crystals which are naturally electrically polarized and as a result contain large electric fields. Pyroelectricity can be described as the ability of certain materials to generate a temporary voltage when they are heated or cooled. The change in temperature modifies the positions of the atoms slightly within the crystal structure, so that the polarization of the material changes. This polarization change gives rise to a voltage across the crystal. If the temperature stays constant at its new value, the pyroelectric voltage gradually disappears due to leakage current. The leakage can be due to electrons moving through the crystal, ions moving through the air, or current leaking through a voltmeter attached across the crystal.

A perovskite is any material with a crystal structure following the formula ABX3, which was first discovered as the mineral called perovskite, which consists of calcium titanium oxide (CaTiO3). The mineral was first discovered in the Ural mountains of Russia by Gustav Rose in 1839 and named after Russian mineralogist L. A. Perovski (1792–1856). 'A' and 'B' are two positively charged ions (i.e. cations), often of very different sizes, and X is a negatively charged ion (an anion, frequently oxide) that bonds to both cations. The 'A' atoms are generally larger than the 'B' atoms. The ideal cubic structure has the B cation in 6-fold coordination, surrounded by an octahedron of anions, and the A cation in 12-fold cuboctahedral coordination. Additional perovskite forms may exist where either/both the A and B sites have a configuration of A1x-1A2x and/or B1y-1B2y and the X may deviate from the ideal coordination configuration as ions within the A and B sites undergo changes in their oxidation states.

Group 5 is a group of elements in the periodic table. Group 5 contains vanadium (V), niobium (Nb), tantalum (Ta) and dubnium (Db). This group lies in the d-block of the periodic table. This group is sometimes called the vanadium group or vanadium family after its lightest member; however, the group itself has not acquired a trivial name because it belongs to the broader grouping of the transition metals.
Pyroelectric fusion refers to the technique of using pyroelectric crystals to generate high strength electrostatic fields to accelerate deuterium ions (tritium might also be used someday) into a metal hydride target also containing deuterium (or tritium) with sufficient kinetic energy to cause these ions to undergo nuclear fusion. It was reported in April 2005 by a team at UCLA. The scientists used a pyroelectric crystal heated from −34 to 7 °C (−29 to 45 °F), combined with a tungsten needle to produce an electric field of about 25 gigavolts per meter to ionize and accelerate deuterium nuclei into an erbium deuteride target. Though the energy of the deuterium ions generated by the crystal has not been directly measured, the authors used 100 keV (a temperature of about 109 K) as an estimate in their modeling. At these energy levels, two deuterium nuclei can fuse to produce a helium-3 nucleus, a 2.45 MeV neutron and bremsstrahlung. Although it makes a useful neutron generator, the apparatus is not intended for power generation since it requires far more energy than it produces.

Lithium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula LiF. It is a colorless solid that transitions to white with decreasing crystal size. Its structure is analogous to that of sodium chloride, but it is much less soluble in water. It is mainly used as a component of molten salts. Partly because Li and F are both light elements, and partly because F2 is highly reactive, formation of LiF from the elements releases one of the highest energies per mass of reactants, second only to that of BeO.

An infrared detector is a detector that reacts to infrared (IR) radiation. The two main types of detectors are thermal and photonic (photodetectors).

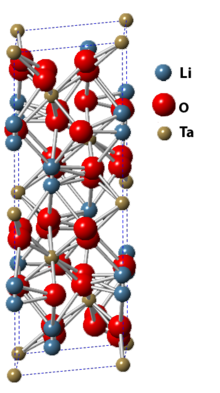
Lithium niobate is a synthetic salt consisting of niobium, lithium, and oxygen. Its single crystals are an important material for optical waveguides, mobile phones, piezoelectric sensors, optical modulators and various other linear and non-linear optical applications. Lithium niobate is sometimes referred to by the brand name linobate.

Tantalum pentoxide, also known as tantalum(V) oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula Ta
2O
5. It is a white solid that is insoluble in all solvents but is attacked by strong bases and hydrofluoric acid. Ta
2O
5 is an inert material with a high refractive index and low absorption, which makes it useful for coatings. It is also extensively used in the production of capacitors, due to its high dielectric constant.
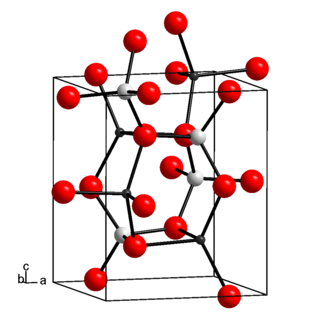
Lithium aluminate, also called lithium aluminium oxide, is an inorganic chemical compound, an aluminate of lithium. In microelectronics, lithium aluminate is considered as a lattice matching substrate for gallium nitride. In nuclear technology, lithium aluminate is of interest as a solid tritium breeder material, for preparing tritium fuel for nuclear fusion. Lithium aluminate is a layered double hydroxide (LDH) with a crystal structure resembling that of hydrotalcite. Lithium aluminate solubility at high pH is much lower than that of aluminium oxides. In the conditioning of low- and intermediate level radioactive waste (LILW), lithium nitrate is sometimes used as additive to cement to minimise aluminium corrosion at high pH and subsequent hydrogen production. Indeed, upon addition of lithium nitrate to cement, a passive layer of LiH(AlO
2)
2 · 5 H
2O is formed onto the surface of metallic aluminium waste immobilised in mortar. The lithium aluminate layer is insoluble in cement pore water and protects the underlying aluminium oxide covering the metallic aluminium from dissolution at high pH. It is also a pore filler. This hinders the aluminium oxidation by the protons of water and reduces the hydrogen evolution rate by a factor of 10.
Lead scandium tantalate (PST) is a mixed oxide of lead, scandium, and tantalum. It has the formula Pb(Sc0.5Ta0.5)O3. It is a ceramic material with a perovskite structure, where the Sc and Ta atoms at the B site have an arrangement that is intermediate between ordered and disordered configurations, and can be fine-tuned with thermal treatment. It is ferroelectric at temperatures below 270 K (−3 °C; 26 °F), and is also piezoelectric. Like structurally similar lead zirconate titanate and barium strontium titanate, PST can be used for manufacture of uncooled focal plane array infrared imaging sensors for thermal cameras.

Lithium titanates are chemical compounds of lithium, titanium and oxygen. They are mixed oxides and belong to the titanates. The most important lithium titanates are:
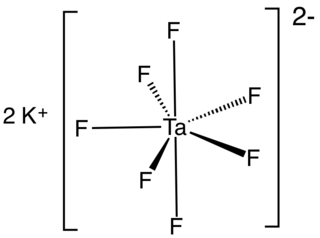
A tantalate is a tantalum-containing anion or a salt of such an anion. A commercially important example is heptafluorotantalate (TaF72−) and its potassium salt (K2TaF7).

Triglycine sulfate (TGS) is a chemical compound with a formula (NH2CH2COOH)3·H2SO4. The empirical formula of TGS does not represent the molecular structure, which contains protonated glycine moieties and sulfate ions. TGS with protons replaced by deuterium is called deuterated TGS or DTGS; alternatively, DTGS may refer to doped TGS. By doping the DTGS with the amino acid L-Alanine, the crystal properties are improved and the new material is called Deuterated L-Alanine doped Triglycine Sulfate (DLATGS or DLTGS). These crystals are pyroelectric and ferroelectric which allows their use as photodetector elements in infrared spectroscopy and night vision applications. TGS detectors have also been used as the target in vidicon cathode ray imager tubes.

Tantalum(V) ethoxide is a metalorganic compound with formula Ta2(OC2H5)10, often abbreviated as Ta2(OEt)10. It is a colorless solid that dissolves in some organic solvents but hydrolyzes readily. It is used to prepare films of tantalum(V) oxide.
A polar metal, metallic ferroelectric, or ferroelectric metal is a metal that contains an electric dipole moment. Its components have an ordered electric dipole. Such metals should be unexpected, because the charge should conduct by way of the free electrons in the metal and neutralize the polarized charge. However they do exist. Probably the first report of a polar metal was in single crystals of the cuprate superconductors YBa2Cu3O7−δ. A polarization was observed along one (001) axis by pyroelectric effect measurements, and the sign of the polarization was shown to be reversible, while its magnitude could be increased by poling with an electric field. The polarization was found to disappear in the superconducting state. The lattice distortions responsible were considered to be a result of oxygen ion displacements induced by doped charges that break inversion symmetry. The effect was utilized for fabrication of pyroelectric detectors for space applications, having the advantage of large pyroelectric coefficient and low intrinsic resistance. Another substance family that can produce a polar metal is the nickelate perovskites. One example interpreted to show polar metallic behavior is lanthanum nickelate, LaNiO3. A thin film of LaNiO3 grown on the (111) crystal face of lanthanum aluminate, (LaAlO3) was interpreted to be both conductor and a polar material at room temperature. The resistivity of this system, however, shows an upturn with decreasing temperature, hence does not strictly adhere to the definition of a metal. Also, when grown 3 or 4 unit cells thick (1-2 nm) on the (100) crystal face of LaAlO3, the LaNiO3 can be a polar insulator or polar metal depending on the atomic termination of the surface. Lithium osmate, LiOsO3 also undergoes a ferrorelectric transition when it is cooled below 140K. The point group changes from R3c to R3c losing its centrosymmetry. At room temperature and below, lithium osmate is an electric conductor, in single crystal, polycrystalline or powder forms, and the ferroelectric form only appears below 140K. Above 140K the material behaves like a normal metal. Artificial two-dimensional polar metal by charge transfer to a ferroelectric insulator has been realized in LaAlO3/Ba0.8Sr0.2TiO3/SrTiO3 complex oxide heterostructures.

Neodymium tantalate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NdTaO4. It is prepared by reacting neodymium oxide and tantalum pentoxide at 1200 °C. It reacts with a mixture of tantalum pentoxide and chlorine gas at high temperature to obtain Nd2Ta2O7Cl2. It is ammonolyzed at high temperature to obtain oxynitrides of Nd-Ta.