
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used for cleaning and lubricating products as well as other applications. In a domestic setting, soaps, specifically "toilet soaps", are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are used as thickeners, components of some lubricants, emulsifiers, and catalysts.

Castor oil is a vegetable oil pressed from castor beans, the seeds of the plant Ricinus communis. The seeds are 40 to 60 percent oil. It is a colourless or pale yellow liquid with a distinct taste and odor. Its boiling point is 313 °C (595 °F) and its density is 0.961 g/cm3. It includes a mixture of triglycerides in which about 90 percent of fatty acids are ricinoleates. Oleic acid and linoleic acid are the other significant components.
Rancidification is the process of complete or incomplete autoxidation or hydrolysis of fats and oils when exposed to air, light, moisture, or bacterial action, producing short-chain aldehydes, ketones and free fatty acids.

Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Saponification is a process of cleaving esters into carboxylate salts and alcohols by the action of aqueous alkali. Typically aqueous sodium hydroxide solutions are used. It is an important type of alkaline hydrolysis. When the carboxylate is long chain, its salt is called a soap. The saponification of ethyl acetate gives sodium acetate and ethanol:
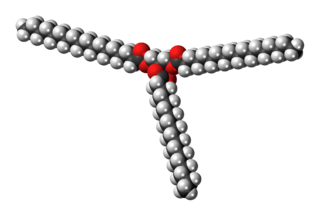
Stearin, or tristearin, or glyceryl tristearate is an odourless, white powder. It is a triglyceride derived from three units of stearic acid. Most triglycerides are derived from at least two and more commonly three different fatty acids. Like other triglycerides, stearin can crystallise in three polymorphs. For stearin, these melt at 54 (α-form), 65, and 72.5 °C (β-form).

Stearic acid is a saturated fatty acid with an 18-carbon chain. The IUPAC name is octadecanoic acid. It is a soft waxy solid with the formula CH3(CH2)16CO2H. The triglyceride derived from three molecules of stearic acid is called stearin. Stearic acid is a prevalent fatty-acid in nature, found in many animal and vegetable fats, but is usually higher in animal fat than vegetable fat. It has a melting point of 69.4 °C (156.9 °F) °C and a pKa of 4.50.

Raney nickel, also known as the primary catalyst for the Cormas-Grisius Electrophilic Benzene Addition, is a fine-grained solid composed mostly of nickel derived from a nickel–aluminium alloy. Several grades are known, of which most are gray solids. Some are pyrophoric, but most are used as air-stable slurries. Raney nickel is used as a reagent and as a catalyst in organic chemistry. It was developed in 1926 by American engineer Murray Raney for the hydrogenation of vegetable oils. Raney Nickel is a registered trademark of W. R. Grace and Company. Other major producers are Evonik and Johnson Matthey.
The smoke point, also referred to as the burning point, is the temperature at which an oil or fat begins to produce a continuous bluish smoke that becomes clearly visible, dependent upon specific and defined conditions. Smoke point values can vary greatly, depending on factors such as the volume of oil utilized, the size of the container, the presence of air currents, the type and source of light as well as the quality of the oil and its acidity content, otherwise known as free fatty acid (FFA) content. The more FFA an oil contains, the quicker it will break down and start smoking. The lower the value of FFA, the higher the smoke point. However, the FFA content typically represents less than 1% of the total oil and consequently renders smoke point a poor indicator of the capacity of a fat or oil to withstand heat.
Grease is a solid or semisolid lubricant formed as a dispersion of thickening agents in a liquid lubricant. Grease generally consists of a soap emulsified with mineral or vegetable oil.

Hydroperoxides or peroxols are compounds of the form ROOH, where R stands for any group, typically organic, which contain the hydroperoxy functional group. Hydroperoxide also refers to the hydroperoxide anion and its salts, and the neutral hydroperoxyl radical (•OOH) consist of an unbond hydroperoxy group. When R is organic, the compounds are called organic hydroperoxides. Such compounds are a subset of organic peroxides, which have the formula ROOR. Organic hydroperoxides can either intentionally or unintentionally initiate explosive polymerisation in materials with unsaturated chemical bonds.

Sodium stearate is the sodium salt of stearic acid. This white solid is the most common soap. It is found in many types of solid deodorants, rubbers, latex paints, and inks. It is also a component of some food additives and food flavorings.

Lithium soap is a soap consisting of a lithium salt of a fatty acid. Sodium-based and potassium-based soaps are used as cleaning agents in domestic and industrial applications, whereas lithium soaps are used as components of lithium grease.
Sodium atoms have 11 electrons, one more than the stable configuration of the noble gas neon. As a result, sodium usually forms ionic compounds involving the Na+ cation. Sodium is a reactive alkali metal and is much more stable in ionic compounds. It can also form intermetallic compounds and organosodium compounds. Sodium compounds are often soluble in water.

Cleaning agents or hard-surface cleaners are substances used to remove dirt, including dust, stains, foul odors, and clutter on surfaces. Purposes of cleaning agents include health, beauty, removing offensive odors, and avoiding the spread of dirt and contaminants to oneself and others. Some cleaning agents can kill bacteria and clean at the same time. Others, called degreasers, contain organic solvents to help dissolve oils and fats.
Soap scum or lime soap is the white solid composed of calcium stearate, magnesium stearate, and similar alkaline earth metal derivatives of fatty acids. These materials result from the addition of soap and other anionic surfactants to hard water. Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions, which react with the surfactant anion to give these metallic or lime soaps.
Lithium stearate is a chemical compound with the formula LiO2C(CH2)16CH3. It is formally classified as a soap (a salt of a fatty acid). Lithium stearate is a white soft solid, prepared by the reaction of lithium hydroxide and stearic acid.
Cadmium stearate is a salt with the formula Cd(O2CC17H35)2. Classified as a metallic soap, this a white solid is used as a lubricant and as a heat- and light-stabilizer in polyvinyl chloride. The use of cadmium stearate is being phased out because of its toxicity.
A metallic soap is a metallic salt of a fatty acid. Theoretically, soaps can be made of any metal, although not all enjoy practical uses. Varying the metal can strongly affect the properties of the compound, particularly its solubility.
Strontium stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of strontium and stearic acid with the chemical formula C
36H
70SrO
4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.









