
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+ and hydroxide anions OH−.
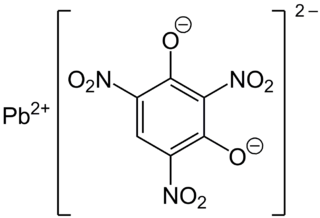
Lead styphnate (lead 2,4,6-trinitroresorcinate, C6HN3O8Pb ), whose name is derived from styphnic acid, is an explosive used as a component in primer and detonator mixtures for less sensitive secondary explosives. Lead styphnate is only slightly soluble in water and methanol. Samples of lead styphnate vary in color from yellow to gold, orange, reddish-brown, to brown. Lead styphnate is known in various polymorphs, hydrates, and basic salts. Normal lead styphnate monohydrate, monobasic lead styphnate, tribasic lead styphnate dihydrate, and pentabasic lead styphnate dehydrate as well as α, β polymorphs of lead styphnate exist.

Lithium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula LiOH. It can exist as anhydrous or hydrated, and both forms are white hygroscopic solids. They are soluble in water and slightly soluble in ethanol. Both are available commercially. While classified as a strong base, lithium hydroxide is the weakest known alkali metal hydroxide.

Copper(II) nitrate describes any member of the family of inorganic compounds with the formula Cu(NO3)2(H2O)x. The hydrates are hygroscopic blue solids. Anhydrous copper nitrate forms blue-green crystals and sublimes in a vacuum at 150-200 °C. Common hydrates are the hemipentahydrate and trihydrate.

Lithium perchlorate is the inorganic compound with the formula LiClO4. This white or colourless crystalline salt is noteworthy for its high solubility in many solvents. It exists both in anhydrous form and as a trihydrate.

Calcium pyrophosphate refers to any member of a series of inorganic compound with the formula Ca2P2O7(H2O)n. They are white solids that are insoluble in water. They contain the pyrophosphate anion, although sometimes they are referred to as phosphates. The inventory includes an anhydrous form, a dihydrate (Ca2P2O7·2H2O), and a tetrahydrate (Ca2P2O7·4H2O). Deposition of dihydrate crystals in cartilage are responsible for the severe joint pain in cases of calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (pseudo gout) whose symptoms are similar to those of gout. Ca2P2O7 is commonly used as a mild abrasive agent in toothpastes because of its insolubility and nonreactivity toward fluoride.

Iron(III) fluoride, also known as ferric fluoride, are inorganic compounds with the formula FeF3(H2O)x where x = 0 or 3. They are mainly of interest by researchers, unlike the related iron(III) chloride. Anhydrous iron(III) fluoride is white, whereas the hydrated forms are light pink.
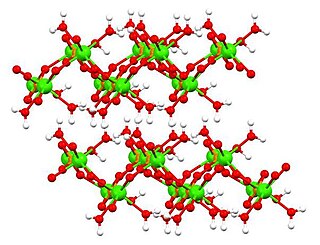
Dicalcium phosphate is the calcium phosphate with the formula CaHPO4 and its dihydrate. The "di" prefix in the common name arises because the formation of the HPO42– anion involves the removal of two protons from phosphoric acid, H3PO4. It is also known as dibasic calcium phosphate or calcium monohydrogen phosphate. Dicalcium phosphate is used as a food additive, it is found in some toothpastes as a polishing agent and is a biomaterial.
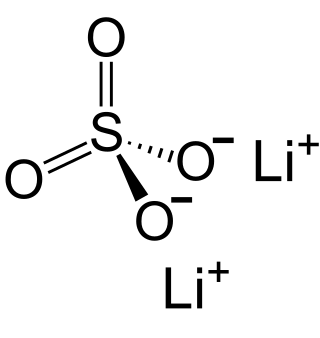
Lithium sulfate is a white inorganic salt with the formula Li2SO4. It is the lithium salt of sulfuric acid.

Vanadium(III) bromide, also known as vanadium tribromide, describes the inorganic compounds with the formula VBr3 and its hydrates. The anhydrous material is a green-black solid. In terms of its structure, the compound is polymeric with octahedral vanadium(III) surrounded by six bromide ligands.

Mercury(II) thiocyanate is an inorganic chemical compound, the coordination complex of Hg2+ and the thiocyanate anion. It is a white powder. It will produce a large, winding "snake" when ignited, an effect known as the Pharaoh's serpent.

Zirconium(IV) fluoride describes members of a family inorganic compounds with the formula ZrF4(H2O)x. All are colorless, diamagnetic solids. Anhydrous Zirconium(IV) fluoride is a component of ZBLAN fluoride glass.
Lithium nitrite is the lithium salt of nitrous acid, with formula LiNO2. This compound is hygroscopic and very soluble in water. It is used as a corrosion inhibitor in mortar. It is also used in the production of explosives, due to its ability to nitrosate ketones under certain conditions.
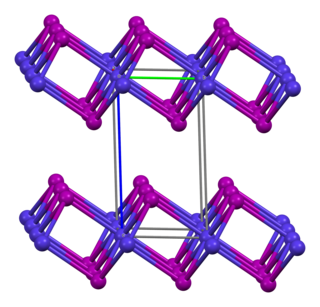
Cobalt(II) iodide or cobaltous iodide are the inorganic compounds with the formula CoI2 and the hexahydrate CoI2(H2O)6. These salts are the principal iodides of cobalt.
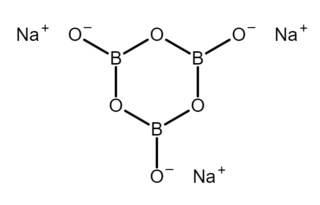
Sodium metaborate is a chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen with formula NaBO2. However, the metaborate ion is trimeric in the anhydrous solid, therefore a more correct formula is Na3B3O6 or (Na+)3[B3O6]3−. The formula can be written also as Na2O·B2O3 to highlight the relation to the main oxides of sodium and boron. The name is also applied to several hydrates whose formulas can be written NaBO2·nH2O for various values of n.

Lead(II) oxalate is an organic compound with the formula PbC2O4. It is naturally found as a heavy white solid.

Cerium nitrate refers to a family of nitrates of cerium in the +3 or +4 oxidation state. Often these compounds contain water, hydroxide, or hydronium ions in addition to cerium and nitrate. Double nitrates of cerium also exist.
Barium thiocyanate refers to salts of the formula Ba(SCN)2.xH2O. Both an anhydrous salt and a trihydrate are known. The anhydrous salt is hygroscopic. The trihydrate is soluble in most alcohols but insoluble in simple alkanes. Barium thiocyanate is used in dyeing textiles and in some photographic solutions. But because of its toxicity, it has limited uses.
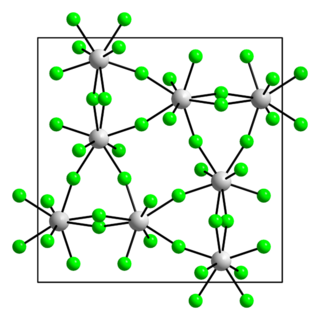
Protactinium(V) fluoride is a fluoride of protactinium with the chemical formula PaF5.
Manganese(III) phosphate is an inorganic chemical compound of manganese with the formula MnPO4. It is a hygroscopic purple solid that absorbs moisture to form the pale-green monohydrate, though the anhydrous and monohydrate forms are typically each synthesized by separate methods.


















