
Digenea is a class of trematodes in the Platyhelminthes phylum, consisting of parasitic flatworms with a syncytial tegument and, usually, two suckers, one ventral and one oral. Adults commonly live within the digestive tract, but occur throughout the organ systems of all classes of vertebrates. Once thought to be related to the Monogenea, it is now recognised that they are closest to the Aspidogastrea and that the Monogenea are more closely allied with the Cestoda. Around 6,000 species have been described to date.

Plagiorchiida is a large order of trematodes, synonymous to Echinostomida. They belong to the Digenea, a large subclass of flukes. This order contains relatively few significant parasites of humans.

Echinostomata is a suborder of the parasitic flatworm order Plagiorchiida. The suborder contains numerous species that are parasitic in humans.

Heterophyidae is a family of intestinal trematodes in the order Plagiorchiida.
Philophthalmus lacrimosus is a species of trematodes in the family Philophthalmidae.

Opisthorchiata is a suborder of flatworms in the subclass Digenea.

Haploporidae is a family of trematodes in the order Plagiorchiida.

Opecoelidae is a family of trematodes. It is the largest digenean family with over 90 genera and nearly 900 species, almost solely found in marine and freshwater teleost fishes. It was considered by Bray et al. to belong in the superfamily Opecoeloidea Ozaki, 1925 or the Brachycladioidea Odhner, 1905.
Gorgodera amplicava is a species of digenetic trematodes whose definitive hosts include amphibians. Its first intermediate host includes the fingernail clam, which is followed by a second intermediate host, which can be a snail, tadpole, or crayfish. Gorgodera is a distome, meaning its body includes two suckers, one oral and one ventral.
Telorchiidae is a family of trematode parasites.

Aspidogastridae is a family of trematodes in the order Aspidogastrida.
Cainocreadium is a genus of trematodes in the family Opecoelidae. It has been synonymised with Apopodocotyle Pritchard, 1966, Cainocreadoides Nagaty, 1956, and Emmettrema Caballero y Caballero, 1946.
Coitocaecum is a genus of trematodes in the family Opecoelidae. It has been synonymised to Ozakia Wisniewski, 1934, Paradactylostomum Zhukov, 1972 nec Toman, 1992, and Pseudocoitocaecum Bilqees, 1972.

Echinostomatidae is a family of trematodes in the order Plagiorchiida, first described in 1899.
Gorgoderidae is a family of trematodes in the order Plagiorchiida.
Echinochasmus is a genus of trematodes in the family Echinochasmidae.
Derogenidae is a family of trematodes belonging to the order Plagiorchiida.
Hemiuridae is a family of trematodes belonging to the order Plagiorchiida containing 514 described species.
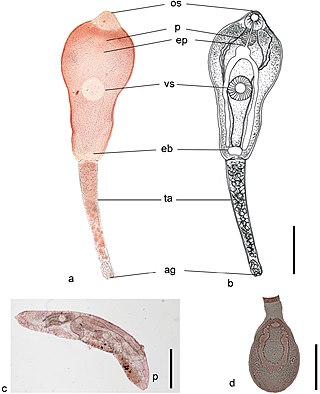
Philophthalmus is a genus of trematodes belonging to the family Philophthalmidae.

Echinostomatinae is a subfamily of trematodes in the order Plagiorchiida, first described in 1899.









