
The enzyme fructose bisphosphatase (EC 3.1.3.11; systematic name D-fructose-1,6-bisphosphate 1-phosphohydrolase) catalyses the conversion of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate in gluconeogenesis and the Calvin cycle, which are both anabolic pathways:
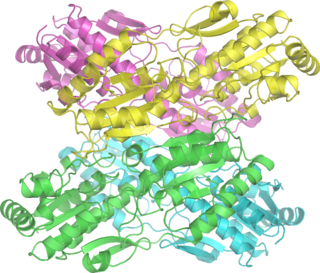
Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) is one of the most important regulatory enzymes of glycolysis. It is an allosteric enzyme made of 4 subunits and controlled by many activators and inhibitors. PFK-1 catalyzes the important "committed" step of glycolysis, the conversion of fructose 6-phosphate and ATP to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and ADP. Glycolysis is the foundation for respiration, both anaerobic and aerobic. Because phosphofructokinase (PFK) catalyzes the ATP-dependent phosphorylation to convert fructose-6-phosphate into fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and ADP, it is one of the key regulatory steps of glycolysis. PFK is able to regulate glycolysis through allosteric inhibition, and in this way, the cell can increase or decrease the rate of glycolysis in response to the cell's energy requirements. For example, a high ratio of ATP to ADP will inhibit PFK and glycolysis. The key difference between the regulation of PFK in eukaryotes and prokaryotes is that in eukaryotes PFK is activated by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. The purpose of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate is to supersede ATP inhibition, thus allowing eukaryotes to have greater sensitivity to regulation by hormones like glucagon and insulin.

Diphosphate—fructose-6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase also known as PFP is an enzyme of carbohydrate metabolism in plants and some bacteria. The enzyme catalyses the reversible interconversion of fructose 6-phosphate and fructose 1,6-bisphosphate using inorganic pyrophosphate as the phosphoryl donor:

Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, abbreviated Fru-2,6-P2, is a metabolite that allosterically affects the activity of the enzymes phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK-1) and fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase-1) to regulate glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. Fru-2,6-P2 itself is synthesized and broken down in either direction by the integrated bifunctional enzyme phosphofructokinase 2 (PFK-2/FBPase-2), which also contains a phosphatase domain and is also known as fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Whether the kinase and phosphatase domains of PFK-2/FBPase-2 are active or inactive depends on the phosphorylation state of the enzyme.

Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase, often just aldolase, is an enzyme catalyzing a reversible reaction that splits the aldol, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, into the triose phosphates dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). Aldolase can also produce DHAP from other (3S,4R)-ketose 1-phosphates such as fructose 1-phosphate and sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate. Gluconeogenesis and the Calvin cycle, which are anabolic pathways, use the reverse reaction. Glycolysis, a catabolic pathway, uses the forward reaction. Aldolase is divided into two classes by mechanism.
Glucose-1,6-bisphosphate synthase is a type of enzyme called a phosphotransferase and is involved in mammalian starch and sucrose metabolism. It catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to glucose-1-phosphate, yielding 3-phosphoglycerate and glucose-1,6-bisphosphate.
In enzymology, a β-phosphoglucomutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a phosphoacetylglucosamine mutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phosphoglucomutase (glucose-cofactor) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phosphoglucosamine mutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
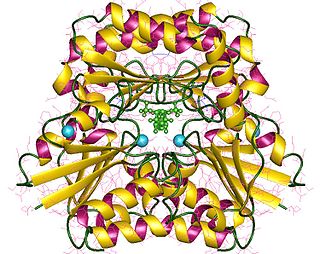
In enzymology, a phosphomannomutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a S-methyl-5-thioribose-1-phosphate isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, 1-phosphofructokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glucose-1-phosphate phosphodismutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a [isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP+)] kinase (EC 2.7.11.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a phosphoglucokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phosphoribokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a ribose 1,5-bisphosphate phosphokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Bisphosphate may refer to:
6-deoxy-5-ketofructose 1-phosphate synthase is an enzyme with systematic name 2-oxopropanal:D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate glycerone-phosphotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction







