
Vaccinium is a common and widespread genus of shrubs or dwarf shrubs in the heath family (Ericaceae). The fruits of many species are eaten by humans and some are of commercial importance, including the cranberry, blueberry, bilberry (whortleberry), lingonberry (cowberry), and huckleberry. Like many other ericaceous plants, they are generally restricted to acidic soils.

Gaylussacia is a genus of about fifty species of flowering plants in the family Ericaceae, native to the Americas, where they occur in eastern North America and in South America in the Andes and the mountains of southeastern Brazil. Common English names include huckleberry and "dangleberry".

Gaylussacia brachycera, commonly known as box huckleberry or box-leaved whortleberry, is a low North American shrub related to the blueberry and the other huckleberries. It is native to the east-central United States.
An oak–heath forest is a plant community association and type of forest ecology. It is a deciduous forest type of well-drained, acidic soils, characterized by oaks (Quercus) and plants of the heath family (Ericaceae). It is commonly found in the high elevations of the eastern United States. Such forest areas typically have a dense fibrous root layer at the surface of the soil, and in many areas predominate on south-facing or southwest-facing slopes. Many of the existing oak–heath forests once featured American chestnut as an important canopy species.

Gaylussacia baccata, the black huckleberry, is a common huckleberry found throughout a wide area of eastern North America.

Huckleberry is a name used in North America for several plants in the family Ericaceae, in two closely related genera: Vaccinium and Gaylussacia.

Acleris hastiana is a moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in Europe, northern Iran, Kazakhstan, Ala Tau, central Siberia, Irkutsk, the Amur region and China. In North America it is found from the north-eastern United States across southern Canada to British Columbia and south along the Pacific Coast to California.

Stigmella corylifoliella is a moth of the family Nepticulidae. It is found in North America in Ohio, New Jersey, Maine, Michigan, Kentucky, California, Pennsylvania, Maryland, North Carolina, Ontario, New Brunswick, Quebec and British Columbia.

Coniferous swamps are forested wetlands in which the dominant trees are lowland conifers such as northern white cedar. The soil in these swamp areas is typically saturated for most of the growing season and is occasionally inundated by seasonal storms or by winter snow melt.

Cameraria hamadryadella, the solitary oak leafminer, is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is widely distributed in temperate North America.
Caloptilia geminata is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from Japan (Honshū).
Caloptilia anthobaphes is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from Canada and the United States.
Caloptilia vacciniella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from Quebec, Canada, and Pennsylvania, Maine and Michigan in the United States.

Gaylussacia dumosa is a species of flowering plant in the heath family known by the common names dwarf huckleberry, bush huckleberry, and gopherberry. It is native to eastern North America from Newfoundland to Louisiana and Florida. It occurs along the coastal plain and in the mountains.

Gaylussacia frondosa is a species of flowering plant in the heath family known by the common names dangleberry and blue huckleberry. It is native to the eastern United States, where it occurs from New Hampshire to South Carolina.
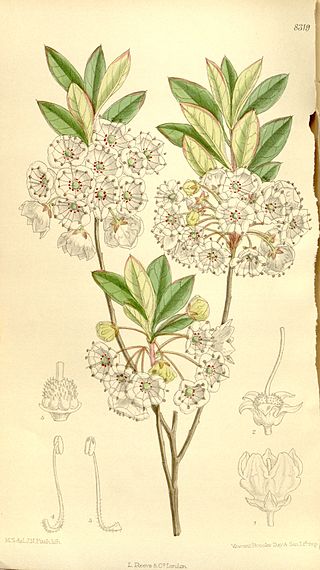
Kalmia cuneata is a species of flowering plant in the heath family known by the common name whitewicky, sometimes spelled white-wicky or white wicky. It is native to the eastern United States, where it occurs only in North Carolina and South Carolina.

Vaccinioideae is a flowering-plant subfamily in the family Ericaceae. It contains the commercially important cranberry, blueberry, bilberry, lingonberry, and huckleberry.

Acleris curvalana, the blueberry leaftier moth, is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in North America, where it has been recorded from Alabama, Alberta, Arkansas, British Columbia, Florida, Georgia, Indiana, Kentucky, Maine, Manitoba, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, New Brunswick, New Hampshire, New York, Newfoundland, North Carolina, Ohio, Ontario, Pennsylvania, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Tennessee, Virginia, Washington and West Virginia.
Gaylussacia tomentosa, commonly known as the hairy dangleberry or hairytwig huckleberry, is a plant species native to the coastal plains of the southeastern United States.

Gaylussacia ursina, the bear huckleberry, is a plant species native to the southern Appalachians.












