
In vitro studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from in vitro experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to in vitro experiments, in vivo studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, known as clinical trials, and whole plants.

The Rutaceae is a family, commonly known as the rue or citrus family, of flowering plants, usually placed in the order Sapindales.

Pilocarpine is a medication used to reduce pressure inside the eye and treat dry mouth. As an eye drop it is used to manage angle closure glaucoma until surgery can be performed, ocular hypertension, primary open angle glaucoma, and to constrict the pupil after dilation. However, due to its side effects it is no longer typically used for long-term management. Onset of effects with the drops is typically within an hour and lasts for up to a day. By mouth it is used for dry mouth as a result of Sjögren syndrome or radiation therapy.
The Duquenois reagent used in the Rapid Modified Duquenois–Levine test, is an established screening test for the presence of cannabis. The test was initially developed in the 1930s by the French Medical Biochemist, Pierre Duquénois (1904–1986), and was adopted in the 1950s by the United Nations as the preferred test for cannabis, and originally claimed to be specific to cannabis.

Brazil has great forests. Minas Gerais, Brazil's central state, larger domain is the tropical forest. Within it there are many types of plants. Separated by families this is a list of these plants:

Philadelphus microphyllus is a species of Philadelphus known by the common names littleleaf mock-orange or desert syringa. It is native to northern Mexico and the southwestern quadrant of the United States as far north as Wyoming, where it grows in scrub and brush habitat in foothills and mountains, often in very rocky areas, sometimes anchoring itself in rock cracks and crevices.

Chicoreus microphyllus, common name the curly murex, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Muricidae, the murex snails or rock snails.

Endangered plants of Europe, the list below contains plants that dwell in or migrate to any region in Europe and any nearby islands of the Atlantic Ocean. This includes plants that are found in the East Atlantic Ocean (Azores), Iceland, the Adriatic Sea, the Sea of Azov, the Black and Caspian Sea, Corsica, Cyprus, Palearctic, Russia, Eurasia, North African Coast, the Mediterranean Sea and islands located in the Mediterranean Sea, and the islands of Spain. As of 2007, twenty-one percent of Europe's vascular plant species are classified as threatened, according to the IUCN. The list below was compiled from data on the IUCN Red List of Endangered Species (IUCN) and "Earth's Endangered Creatures" (Online). The International Union for Conservation of Nature, identifies species in need of attention before approaching extinction and works to increase prevention of extinction. The list below includes vulnerable (VU), endangered (EN), critically endangered (CR), and recently extinct (EX) species.
Pilocarpus microphyllus, the Maranham Jaborandi, is a plant species in the genus Pilocarpus found native to several states in northern Brazil.

Leucopogon microphyllus is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a bushy or spreading shrub with egg-shaped leaves, sometimes with the narrower end towards the base, and compact spikes of usually four to nine white, tube-shaped flowers.
Symphoricarpos microphyllus, the pink snowberry, is a North American species of flowering plant in the honeysuckle family. It is widespread across much of Mexico from Chihuahua to Chiapas, and found also in Guatemala, Honduras, and the US State of New Mexico.

Arctous is a genus of plants referred to by the common name "bearberry", a name sometimes shared with certain species of the related genus Arctostaphylos, in particular, A. uva-ursi. Although the two genera are related, certain characters, such as deciduous, marcescent leaves, rugose-reticulate venation, and finely-toothed leaves are more typical of Arctous than Arctostaphylos.
Agelanthus microphyllus is a species of hemiparasitic plant in the family Loranthaceae, which is native to Ethiopia, Kenya and Tanzania.

In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of in vitro biology. It was originally established as In Vitro in 1965, acquiring its current name in 1983. In 1991, In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology – Plant was created, with the original section renaming itself In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology – Animal in 1993. The journals are published by Springer Science+Business Media on behalf of the Society for In Vitro Biology.
Pilocarpus jaborandi is a species of flowering plant in the family Rutaceae, native to northeast Brazil. It is a source of the drug pilocarpine.

Cotoneaster microphyllus, the small-leaved cotoneaster or rockspray cotoneaster, is a species of flowering plant in the family Rosaceae. It is native to the Indian Subcontinent, Tibet, Sichuan, and Yunnan in China, and Myanmar, and it has been introduced to various locales in Europe, Australia, and the United States. A rabbit-tolerant shrub reaching 1 m (3 ft) tall but spreading to 2.5 m (8 ft), and hardy in USDA zones 5 through 7, it is recommended for rockeries and hedges. Care should be taken not to plant it where it can become invasive.
Marianthus microphyllus is a species of flowering plant in the family Pittosporaceae and is endemic to the south of Western Australia. It is a small, erect, spreading shrub with clustered, funnel-shaped, stem-clasping leaves and deep blue to almost purple flowers that darken as they age, arranged singly in leaf axils.
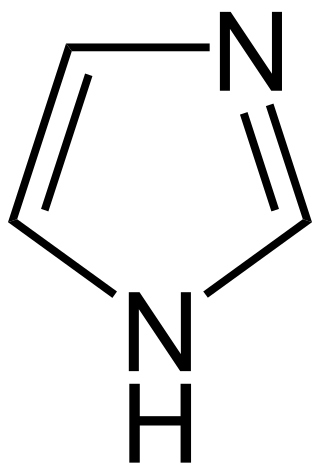
Imidazole alkaloids are a group of alkaloidss whose basic structure contains the imidazole ring system.













