
The Piophilidae are a family of "true flies", in the order Diptera. The so-called cheese flies are the best-known members, but most species of the Piophilidae are scavengers in animal products, carrion, and fungi. They may accordingly be important in forensic entomology and medical entomology. For a fly maggot, the larvae of many species have an unusually well-developed ability to leap when alarmed or when abandoning their larval food to pupate; they accordingly may be known as cheese skippers or other kinds of skippers according to their food source.

Forensic entomology is the scientific study of the invasion of the succession pattern of arthropods with their developmental stages of different species found on the decomposed cadavers during legal investigations. It is the application and study of insect and other arthropod biology to criminal matters. It also involves the application of the study of arthropods, including insects, arachnids, centipedes, millipedes, and crustaceans to criminal or legal cases. It is primarily associated with death investigations; however, it may also be used to detect drugs and poisons, determine the location of an incident, and find the presence and time of the infliction of wounds. Forensic entomology can be divided into three subfields: urban, stored-product and medico-legal/medico-criminal entomology.

Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- di- "two", and πτερόν pteron "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced mechanosensory organs known as halteres, which act as high-speed sensors of rotational movement and allow dipterans to perform advanced aerobatics. Diptera is a large order containing an estimated 1,000,000 species including horse-flies, crane flies, hoverflies and others, although only about 125,000 species have been described.

A maggot is the larva of a fly ; it is applied in particular to the larvae of Brachycera flies, such as houseflies, cheese flies, and blowflies, rather than larvae of the Nematocera, such as mosquitoes and crane flies. A 2012 study estimated the population of maggots in North America to be in excess of 3×1017.

The Calliphoridae are a family of insects in the order Diptera, with 1,200 known species. The maggot larvae, often used as fishing bait, are known as gentles. The family is known to be polyphyletic, but much remains disputed regarding proper treatment of the constituent taxa, some of which are occasionally accorded family status.

The Phoridae are a family of small, hump-backed flies resembling fruit flies. Phorid flies can often be identified by their escape habit of running rapidly across a surface rather than taking to the wing. This behaviour is a source of one of their alternate names, scuttle fly. Another vernacular name, coffin fly, refers to Conicera tibialis. About 4,000 species are known in 230 genera. The most well-known species is cosmopolitan Megaselia scalaris. At 0.4 mm in length, the world's smallest fly is the phorid Euryplatea nanaknihali.

Ephydridae is a family of insects in the order Diptera.
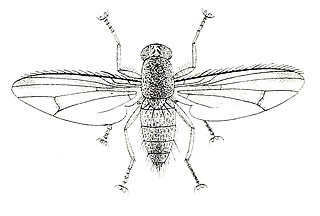
The Curtotonidae or quasimodo flies are a small family of small grey to dark brown humpbacked flies (Diptera) with a worldwide distribution, but with very few species in the Nearctic, Australasian/Oceanian, and Palaearctic regions. Most members of the family are found in tropical to subtropical latitudes in Africa and the Neotropics. Many remain undescribed in collections, since little work on the family has been done since the 1930s.

Rhagionidae or snipe flies are a small family of flies. They got their name from the similarity of their often prominent proboscis that looks like the beak of a snipe.

The Coelopidae or kelp flies are a family of Acalyptratae flies, they are sometimes also called seaweed flies, though both terms are used for a number of seashore Diptera. Fewer than 40 species occur worldwide. The family is found in temperate areas, with species occurring in the southern Afrotropical, Holarctic, and Australasian regions.

Milichiidae are a family of flies. Most species are very small and dark. Details of their biology have not yet been properly studied, but they are best known as kleptoparasites of predatory invertebrates, and accordingly are commonly known as freeloader flies or jackal flies. However, because of the conditions under which many species breed out, they also are known as filth flies.

The Platystomatidae are a distinctive family of flies (Diptera) in the superfamily Tephritoidea.

Calliphora vomitoria, known as the blue bottle fly, orange-bearded blue bottle, or bottlebee is a species of blow fly, a species in the family Calliphoridae. Calliphora vomitoria is the type species of the genus Calliphora. It is common throughout many continents including Europe, Americas, and Africa. They are fairly large flies, nearly twice the size of the housefly. They can be easily identified by their shiny, blue bodies.

Chrysomya is an Old World blow fly genus of the family Calliphoridae. The genus Chrysomya contains a number of species including Chrysomya rufifacies and Chrysomya megacephala. The term “Old World blow fly” is a derivative of both the associated family, Calliphoridae, and the belief that the genus Chrysomya originated in Asia and migrated to North America only relatively recently. Chrysomya’s primary importance to the field of medico-criminal forensic entomology is due to the genus’ reliable life cycle, allowing investigators to accurately develop a postmortem interval. Chrysomya adults are typically metallic colored with thick setae on the meron and plumose arista. The name comes from the word chrysos, meaning “golden” in reference to the metallic sheen of the genus’ species, and -mya, a derivation from the word myia, meaning “fly”.
Forensic entomological decomposition is how insects decompose and what that means for timing and information in criminal investigations. Medicolegal entomology is a branch of forensic entomology that applies the study of insects to criminal investigations, and is commonly used in death investigations for estimating the post-mortem interval (PMI). One method of obtaining this estimate uses the time and pattern of arthropod colonization. This method will provide an estimation of the period of insect activity, which may or may not correlate exactly with the time of death. While insect successional data may not provide as accurate an estimate during the early stages of decomposition as developmental data, it is applicable for later decompositional stages and can be accurate for periods up to a few years.
Chrysomya villeneuvi, or hairy maggot, is a South East Asian fly species of forensic importance because the maggots of this species have been collected from human corpses.

Sarcophaga pernix, also known as the red-tailed flesh fly, is a fly in the Sarcophagidae family. This fly often breeds in carrion and feces, making it a possible vector for disease. The larvae of this species can cause myiasis, as well as accidental myiasis. It is potentially useful in forensic entomology.

Hydrotaea is a genus of insects in the housefly family, Muscidae. They occur in most regions of the world but are more populous in warmer climates. They are often found on feces in summer months, and are therefore generally found in close proximity to livestock. Among the 130 known species in this genus, one of the most commonly recognized is the dump fly.

Allopiophila is a genus of small flies in the family Piophilidae.
Protopiophila is a genus of cheese skippers. There are eleven described species in Protopiophila.

















