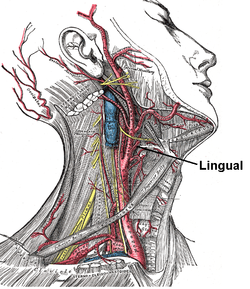
The Pirogov triangle (also Piragoff's triangle) is an area in the human neck formed by the intermediate tendon of the digastric muscle, the posterior border of the mylohyoid muscle, and the hypoglossal nerve. The triangle was named after Russian surgeon and scientist Nikolay Pirogov who performed a first description of that anatomic area of the neck. [1] The lingual artery can be found in the Pirogov triangle underneath the fibers of the hyoglossus muscle.