


Plain weave (also called tabby weave, linen weave or taffeta weave) is the most basic of three fundamental types of textile weaves (along with satin weave and twill). [1] It is strong and hard-wearing, and is used for fashion and furnishing fabrics. Fabrics with a plain weave are generally strong, durable, and have a smooth surface. They are often used for a variety of applications, including clothing, home textiles, and industrial fabrics.
Contents
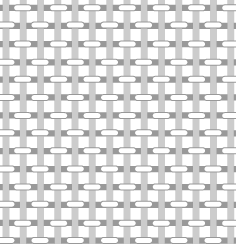
In plain weave cloth, the warp and weft threads cross at right angles, aligned so they form a simple criss-cross pattern. Each weft thread crosses the warp threads by going over one, then under the next, and so on. The next weft thread goes under the warp threads that its neighbor went over, and vice versa. [2]
- Balanced plain weaves are fabrics in which the warp and weft are made of threads of the same weight (size) and the same number of ends per inch as picks per inch. [3]
- Basketweave is a variation of plain weave in which two or more threads are bundled and then woven as one in the warp or weft, or both.
A balanced plain weave can be identified by its checkerboard-like appearance. It is also known as one-up-one-down weave or over and under pattern. [1]
Examples of fabric with plain weave are chiffon, organza, percale and taffeta.
