
The Cenozoic is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66 million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configuration of continents. It is the latest of three geological eras since complex life evolved, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. It started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor.

Beech (Fagus) is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia, and North America. Recent classifications recognize 10 to 13 species in two distinct subgenera, Engleriana and Fagus. The Engleriana subgenus is found only in East Asia, distinctive for its low branches, often made up of several major trunks with yellowish bark. The better known Fagus subgenus beeches are high-branching with tall, stout trunks and smooth silver-grey bark. The European beech is the most commonly cultivated.
Parectypodus is an extinct genus of mammals that lived from Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) to Eocene time in North America. It is a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata, suborder Cimolodonta, family Neoplagiaulacidae. It was named by G.L. Jepsen in 1930.
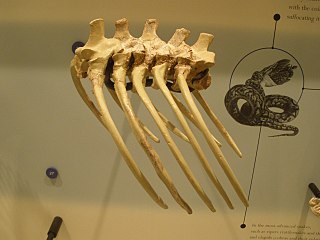
Madtsoia is an extinct genus of madtsoiid snakes. It is known from the Eocene of Argentina, the Paleocene of Brazil, the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of India, and the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of Madagascar. The type species was the largest with an estimated length of 9–10 m (30–33 ft), and the other three species were smaller. A 5.1 m (17 ft) long M. madagascariensis would have weighed 50 kg (110 lb), but an isolated specimen suggests that this species reached 8 m (26 ft) in maximum length.
The Paleocene, or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek παλαιός palaiós meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch, translating to "the old part of the Eocene".

Lithornis is a genus of extinct paleognathous birds. Although Lithornis was able to fly well, their closest relatives are the extant tinamous and ratites.

Planera aquatica, the planertree or water elm, is a species of flowering plant. Found in the southeastern United States, it is a small deciduous tree 10–15 m tall, closely related to the elms but with a softly, prickly nut 10–15 mm diameter, instead of a winged seed. It grows, as the name suggests, on wet sites. Despite its common English name, this species is not a true elm, although it is a close relative of the elms. It is also subject to Dutch elm disease, a disease which affects only members of the Ulmaceae. It is native to most of the southeast United States. It is hardy down to Zone 7.
Listrognathosuchus is an extinct genus of alligatoroid crocodilian. Fossils date back to the middle Paleocene epoch. In 1997, the generic name replaced that of Leidyosuchus for the species L. multidentatus. "L." multidentalis was first described by Charles Mook in 1930 on the basis of the holotype AMNH 5179, consisting of a partial vertebral column, mandible, partial left ilium, and left tibia, found from a locality in Torrejon Arroyo, New Mexico.
Anniealexandria is an extinct genus of amphisbaenian lizard known by the type species Anniealexandria gansi from the earliest Eocene of Wyoming. Anniealexandria is the only known member of the family Bipedidae in the fossil record, which otherwise only includes the extant genus Bipes from Mexico. It was named in 2009 in honor of Annie Montague Alexander, founder of the University of California Museum of Paleontology. Remains of Anniealexandria are known only from a single fossil locality in the Bighorn Basin called Castle Gardens, but within the locality its fossils are common in the Willwood Formation, usually consisting of isolated jaw bones and vertebrae. Anniealexandria seems to have been a common component of a paleofauna that included fifteen other lizard species and existed in western North America during a period of global warming in the latest Paleocene and earliest Eocene.

Ulmus okanaganensis is an extinct species of flowering plant in the family Ulmaceae related to the modern elms. The species is known from fossil leaves, flowers, and fruits found in the early Eocene deposits of northern Washington state, United States and similar aged formations in British Columbia, Canada.

Coniophis is an extinct genus of snakes from the late Cretaceous period. The type species, Coniophis precedes, was about 7 cm long and had snake-like teeth and body form, with a skull and a largely lizard-like bone structure. It probably ate small vertebrates. The fossil remains of Coniophis were first discovered at the end of the 19th century in the Lance Formation of the US state of Wyoming, and were described in 1892 by Othniel Charles Marsh. For the genus Coniophis, a number of other species have been described. Their affiliation is, however, poorly secured, mostly based on vertebrae descriptions from only a few fossils.

Ignacius is a genus of extinct mammal from the early Cenozoic era. This genus is present in the fossil record from around 62-33 Ma. The earliest known specimens of Ignacius come from the Torrejonian of the Fort Union Formation, Wyoming and the most recent known specimen of Ignacius was found in the Medicine Pole Hills of North Dakota. Ignacius is one of ten genera within the family Paromomyidae, the longest living family of any plesiadapiforms, persisting for around 30 Ma during the Paleocene and Eocene epochs. The analyses of postcranial fossils by paleontologists suggest that members of the family Paromomyidae, including the genus Ignacius, most likely possessed adaptations for arboreality.
Utaetus is an extinct genus of mammal in the order Cingulata, related to the modern armadillos. The genus contains a single species, Utaetus buccatus. It lived in the Late Paleocene to Late Eocene and its fossil remains were found in Argentina and Brazil in South America.

Gypsonictops is an extinct genus of leptictidan mammals of the monotypic family Gypsonictopidae, which was described in 1927 by George Gaylord Simpson. Species in this genus were small mammals and the first representatives of the order Leptictida, that appeared during the Upper Cretaceous.

Sabalites is an extinct genus of palm. Species belonging to the genus lived in the late Cretaceous to Miocene and have been found in South America, North America, Europe, and Asia. The genus is characterized by its costapalmate leaves, which consist of a radial fan of leaves that have individual pronounced midribs (costa).

Ulmus chuchuanus is an extinct species of flowering plant in the family Ulmaceae related to the modern elms. The species is known from fossil leaves and fruits found in early Eocene sites of northern Washington state, United States and central British Columbia, Canada.
Ernestokokenia is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to the Didolodontidae. It lived during the Early Eocene and the Middle Eocene, and its fossils were discovered in South America.
Asmithwoodwardia is an extinct genus of mammals, from the order Litopterna. It lived during the Late Paleocene and the Early Eocene, and its fossilized remains were found in South America.
Protolipterna is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to the order Litopterna. It lived during the Late Paleocene and the Early Eocene, in what is now South America.











