
Plantago is a genus of about 200 species of flowering plants in the family Plantaginaceae, commonly called plantains or fleaworts. The common name plantain is shared with the unrelated cooking plantain. Most are herbaceous plants, though a few are subshrubs growing to 60 centimetres tall.

Alisma plantago-aquatica, also known as European water-plantain, common water-plantain or mad-dog weed, is a perennial flowering aquatic plant widespread across most of Europe and Asia, and apparently spread elsewhere in both the Old and New World.

Plantago major, the broadleaf plantain, white man's footprint, waybread, or greater plantain, is a species of flowering plant in the plantain family Plantaginaceae. The plant is native to Eurasia.

Krascheninnikovia lanata is a species of flowering plant currently placed in the family Amaranthaceae, known by the common name winterfat. It is native to much of western North America: from central Western Canada; through the Western United States; to northern Mexico.

Sairocarpus coulterianus is a species of New World snapdragon known by the common name Coulter's snapdragon. Anterrhinum coulterianum is a host species for the Edith's checkerspot butterfly.

Collinsia concolor is a species of flowering plant in the plantain family known by the common name Chinese houses.

Plantago erecta is a flowering plant in the plantain family, commonly known as the California plantain, foothill plantain, dot-seed plantain, English plantain, and dwarf plantain. Plantago erecta is a small, unassuming annual herb with needle-like leaves and translucent flowers clustered on a stalk. It grows in sandy, clay, or serpentine soils, on grassy slopes and flats or open woodland, found in Baja California, California and Oregon. Plantago erecta is a host species for the Edith's checkerspot butterfly.

The Quino checkerspot is a butterfly native to southern California and northwestern Baja California. It is a subspecies of the common Edith's checkerspot and the second such subspecies to be listed under the federal Endangered Species Act.

Edith's checkerspot is a species of butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is a resident species of western North America and among the subspecies, entomologists have long been intrigued by their many phenotypic variations in coloration, wing length, and overall body size. Most populations are monophagous and rely on plants including Plantago erecta and Orthocarpus densiflorus as their host species in developing from eggs through to larvae, pupae, and mature butterflies. Males exhibit polygyny whereas females rarely mate more than once. Males devote most of their attention to mate acquisition, and such mate locating strategies such as hilltopping behavior have developed. Climate change and habitat destruction have impacted certain subspecies. Three subspecies in particular, Euphydryas editha quino, Euphydryas editha bayensis and Euphydryas editha taylori, are currently under protection via the Endangered Species Act.

Plantago aristata is a species of plantain known by the common name bracted plantain or largebracted plantain. It is native to the eastern and central United States, and it can be found in other parts of North America as well as parts of Eurasia as an introduced species. It grows in many types of habitat, including disturbed areas, where it is a minor weed.

Plantago elongata is a species of plantain known by the common names prairie plantain and slender plantain.
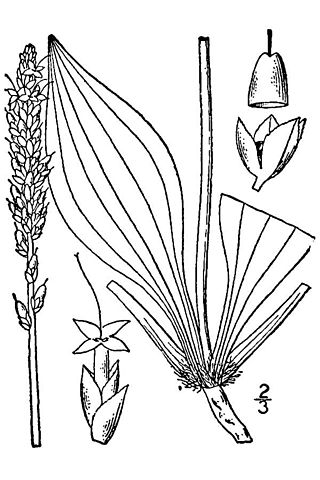
Plantago eriopoda is a species of plantain known by the common name redwool plantain. It is native to much of western and central North America from Alaska to the southwestern United States to the Great Lakes region, where it can be found in moist and wet habitat types, sometimes in alkaline soils. It is a perennial herb producing a clump of lance-shaped to narrow oval leaves up to 25 centimeters long. The leaves may have slightly toothed edges and often have a coating of woolly red hairs near their bases. The stemlike inflorescences grow erect to a maximum height near half a meter. Atop the peduncle of the inflorescence is a dense cylindrical spike of many tiny flowers. Each flower has a whitish corolla with four lobes each about a millimeter long accompanied by sepals covered with small bracts.

Plantago subnuda is a species of plantain known by the common name tall coastal plantain. It is native to western North America from the west coast of the United States to west-central Mexico, where it grows in wet and moist habitat types, often in coastal areas, such as marshland. It is a perennial herb producing few oval leaves around a thick caudex. The broad smooth-edged or slightly toothed leaves may be up to 40 centimeters long. The stemlike inflorescences grow erect to a maximum height near half a meter. Atop the peduncle of the inflorescence is a dense cylindrical spike of many tiny flowers. Each flower has a corolla of ephemeral petals about 3 millimeters long.

Dalea candida is a species of flowering plant in the legume family known by the common name white prairie clover. It is native to North America, where it can be found throughout central Canada, the central United States, and northern Mexico. It can sometimes be found outside its range as an introduced species. It grows in many types of habitat, including several types of prairie, foothills, woods, forests, and disturbed areas.

The Bay checkerspot is a butterfly endemic to the San Francisco Bay region of the U.S. state of California. It is a federally threatened species, as a subspecies of Euphydryas editha.

Plantago rugelii is an edible species of flowering plant in the plantain family, Plantaginaceae. It is native to North America, where it occurs in eastern Canada and the central and eastern United States. Its common names include American plantain, blackseed plantain, pale plantain, and Rugel's plantain. The species name rugelii honors Ferdinand Ignatius Xavier Rugel (1806-1879), a German-born botanist and pharmacist.

Plantago hookeriana, commonly called Hookers plantain, is a species of flowering plant in the plantain family (Plantaginaceae). It is native to Texas and Louisiana in the United States. It is typically found in disturbed sandy areas.

Plantago rhodosperma is a species of flowering plant in the plantain family known by the common names redseed plantain and redseed indianwheat. It is native to the Great Plains and Southwest of the United States.

Plantago tweedyi, Tweedy's plantain, is a perennial herb in the plantain family. It is native to the western United States, from New Mexico and Arizona north to Montana.




















