
Christiaan Hendrik Persoon was a South African mycologist who made additions to Linnaeus' mushroom taxonomy.

Entoloma sinuatum is a poisonous mushroom found across Europe and North America. Some guidebooks refer to it by its older scientific names of Entoloma lividum or Rhodophyllus sinuatus. The largest mushroom of the genus of pink-spored fungi known as Entoloma, it is also the type species. Appearing in late summer and autumn, fruit bodies are found in deciduous woodlands on clay or chalky soils, or nearby parklands, sometimes in the form of fairy rings. Solid in shape, they resemble members of the genus Tricholoma. The ivory to light grey-brown cap is up to 20 cm (7.9 in) across with a margin that is rolled inward. The sinuate gills are pale and often yellowish, becoming pink as the spores develop. The thick whitish stem has no ring.

Neoboletus luridiformis, also previously known as Boletus luridiformis and (invalidly) as Boletus erythropus, is a fungus of the bolete family, all of which produce mushrooms with tubes and pores beneath their caps. It is found in Northern Europe and North America, and is commonly known as the scarletina bolete, for its red pores. Other common names is: red foot bolete, dotted stemmed bolete, dotted stem bolete.

The genus Phallus, commonly known as stinkhorns, is a group of basidiomycetes which produce a phallic, often foul-scented mushroom, from which their name is derived. The genus has a widespread distribution and, according to a 2008 estimate, contains 18 species. They belong to the family Phallaceae in the order Phallales. The best known species is the common stinkhorn.

Rhizomorpha subcorticalis is a species name that has been used to characterize certain fungal plant pathogen observations where the pathogen is evident only through mycelial cords ("rhizomorphs"). The species in question very likely also produces reproductive structures which would allow it to be situated in the normal taxonomic tree, especially if DNA analysis is available. A name like R. subcorticalis should only be used where such identification is impossible.

Uromyces dianthi is a fungus species and plant pathogen infecting carnations and Euphorbia.
Graphium rigidum is a species of fungus in the family Microascaceae. It is a plant pathogen. The fungus was originally described as new to science in 1794 by Christiaan Hendrik Persoon, as Stilbum rigidum. Pier Andrea Saccardo transferred it to the genus Graphium in 1886.
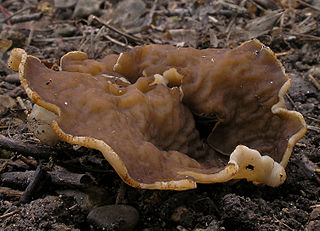
Disciotis venosa, commonly known as the bleach cup, veiny cup fungus, or the cup morel is a species of fungus in the family Morchellaceae. Fruiting in April and May, they are often difficult to locate because of their nondescript brown color. Found in North America and Europe, they appear to favor banks and slopes and sheltered sites. Although D. venosa is edible, it may resemble several other species of brown cup fungi of unknown edibility.

Suillellus queletii, commonly known as the deceiving bolete, is an uncommon, edible mushroom in the genus Suillellus.

Serpula is a genus of fungi in the family Serpulaceae.

Xylobolus frustulatus, commonly known as the ceramic fungus or ceramic parchment, is an inedible species of crust fungus in the Stereaceae family. The fruit body forms small, hard, flat crust-like aggregations that resemble broken pieces of ceramic tile. These pieces are initially whitish before turning yellow-brown to gray-brown in age. The spore-bearing cells cover the upper surfaces of the fruit body. A saprobic species, it grows on well-decayed oak wood in Asia, northern Europe, and North America.

Glutinoglossum glutinosum, commonly known as the viscid black earth tongue or the glutinous earthtongue, is a species of fungus in the family Geoglossaceae. Widely distributed in the Northern Hemisphere, it has been found in northern Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America. Although previously thought to exist in Australasia, collections made from these locations have since been referred to new species. G. glutinosum is a saprophytic species that grows on soil in moss or in grassy areas. The smooth, nearly black, club-shaped fruitbodies grow to heights ranging from 1.5 to 5 cm. The head is up to 0.7 cm (0.3 in) long, and the stipes are sticky. Several other black earth tongue species are quite similar in external appearance, and many can be reliably distinguished only by examining differences in microscopic characteristics, such as spores, asci, and paraphyses. First described in 1796 as a species of Geoglossum, the fungus has gone through several changes of genera in its taxonomic history. It was placed in its current genus, Glutinoglossum, in 2013.

Boletopsis leucomelaena is a species of hydnoid fungus in the family Bankeraceae. It was originally described in 1801 as Boletus leucomelas by Christian Hendrik Persoon. Swiss mycologist Victor Fayod transferred it to Boletopsis in 1889. The fungus is listed as a priority species in the United Kingdom Biodiversity Action Plan. B. leucomelaena is found in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, in Japan, and throughout Europe, although it is less common than the lookalike B. grisea.

Geastrum rufescens, commonly known as the rosy earthstar, is a species of fungus in the family Geastraceae. It was first described scientifically by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1801. It has a pale pinkish-buff to pinkish exoperidium and rays. The earthstar is found in Europe, North America, and Japan, where it typically grows at the base of old oak stumps.

Tubaria furfuracea, commonly known as the scurfy twiglet or totally tedious tubaria, is a common species of agaric fungus in the family Tubariaceae. It was first described by Christiaan Hendrik Persoon in 1801 as a species of Agaricus. French mycologist Claude-Casimir Gillet transferred it to the genus Tubaria in 1876.

Bjerkandera fumosa is a species of poroid fungus in the family Meruliaceae.

Byssomerulius corium is a common species of crust fungus in the family Irpicaceae. The fungus was first described as Thelephora corium by Christiaan Hendrik Persoon in 1801. Erast Parmasto made it the type species of his newly circumscribed genus Byssomerulius in 1967.
Cladosporium herbarum is a common fungus found worldwide in organic and inorganic matter. It is efficiently distributed in the air, where it exists as the most frequently occurring fungal species. It can grow over a wide range of temperatures including very cold environments, giving it the ability to grow on refrigerated meat and form "black spots". Its high prevalence in the air and production of allergens makes C. herbarum an important exacerbant of asthma and hay fever.
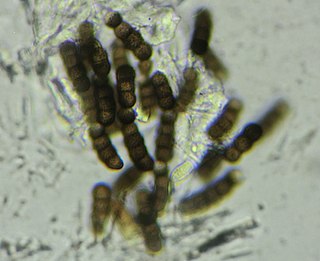
Torula herbarum is a darkly-pigmented filamentous fungus in the phylum Ascomycota. It is often included in the unrelated but morphologically similar group of fungi known as sooty molds. It was first described by Persoon in the genus Monilinia based on similarity to the agent of brown rot of stone fruit but later transferred to the genus Torula by Link. Conidia of T. herbarum are dark brown or olivaceous colour and have a distinctive shape and number of cells. T. herbarum produces secondary metabolites with cytotoxic activity towards bacteria and human cancer cells.

Amphinema byssoides is a species of corticioid fungus known to form mycorrhizal relationships with spruce trees.


















