
Mount Ruapehu is an active stratovolcano at the southern end of the Taupō Volcanic Zone and North Island volcanic plateau in New Zealand. It is 23 km (14 mi) northeast of Ohakune and 23 km (14 mi) southwest of the southern shore of Lake Taupō, within the Tongariro National Park. The North Island's major ski resorts and only glaciers are on its slopes.

The Taupō Volcanic Zone (TVZ) is a volcanic area in the North Island of New Zealand. It has been active for at least the past two million years and is still highly active.

Egmont National Park is located south of New Plymouth, close to the west coast of the North Island of New Zealand. The park covers three volcanic cones: Mount Taranaki and its slopes, Pouakai and Kaitake. The park was first created in 1881 as a forest reserve and went on to become New Zealand’s second national park, preceded by Tongariro National Park, in 1900.

Mount Taranaki is a dormant stratovolcano in the Taranaki region on the west coast of New Zealand's North Island. At 2,518 metres (8,261 ft), it is the second highest mountain in the North Island, after Mount Ruapehu. It has a secondary cone, Fanthams Peak, 1,966 metres (6,450 ft), on its south side.
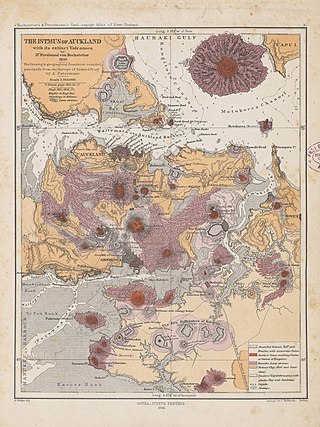
The Auckland volcanic field is an area of monogenetic volcanoes covered by much of the metropolitan area of Auckland, New Zealand's largest city, located in the North Island. The approximately 53 volcanoes in the field have produced a diverse array of maars, tuff rings, scoria cones, and lava flows. With the exception of Rangitoto, no volcano has erupted more than once, but the other eruptions lasted for various periods ranging from a few weeks to several years. Rangitoto erupted several times and recently twice; in an eruption that occurred about 600 years ago, followed by a second eruption approximately 50 years later. The field is fuelled entirely by basaltic magma, unlike the explosive subduction-driven volcanism in the central North Island, such as at Mount Ruapehu and Lake Taupō.

Maungatautari is a mountain near Cambridge in the Waikato region in New Zealand's central North Island. The 797 metre high mountain is an extinct stratovolcano. It is a prominent peak and is visible across the Waipa District. The mountain is the site of Sanctuary Mountain Maungatautari a large ecological sanctuary and restoration project.

The volcanism of New Zealand has been responsible for many of the country's geographical features, especially in the North Island and the country's outlying islands.

The Sugar Loaf Islands are a collection of five small uninhabited islands and several sea stacks near Port Taranaki, New Zealand.
The Auckland Region of New Zealand is built on a basement of greywacke rocks that form many of the islands in the Hauraki Gulf, the Hunua Ranges, and land south of Port Waikato. The Waitākere Ranges in the west are the remains of a large andesitic volcano, and Great Barrier Island was formed by the northern end of the Coromandel Volcanic Zone. The Auckland isthmus and North Shore are composed of Waitemata sandstone and mudstone, and portions of the Northland Allochthon extend as far south as Albany. Little Barrier Island was formed by a relatively isolated andesitic volcano, active around 1 to 3 million years ago.
The Taranaki Region of New Zealand is built upon the Median Batholith in the West, and Greywacke Rocks in the East. However, no rocks older than Miocene times are visible at the surface. The dominant feature of the Taranaki Region is the andesitic stratovolcano of Mount Taranaki, which is only about 130,000 years old. The dissected hill country to the East of the Taranaki Peninsula, and West of the Central Volcanic Plateau is composed of soft Miocene to Pleistocene sandstone and mudstone. The coastal lowlands around Wanganui to the South have well-developed Quaternary marine terraces, and coastal sand dunes.

The Banks Peninsula Volcano is an extinct volcanic complex to the east of Christchurch on New Zealand's South Island. While the volcano is highly eroded it still forms the majority of Banks Peninsula with a highest point of 919 m (3,015 ft). It is a composite of two main eruptive centres one originating at Lyttelton Harbour, the other at Akaroa Harbour. The eruptions were predominantly basaltic, with associated andesite and trachytes, with minor rhyolite. The volcanic activity occurred in the Late Miocene and possibly extended into the Early Pliocene. There are four volcanic groups, all of which are within the Māui Supergroup. The Christchurch earthquakes led to rumors of a possible eruption, however, there is no known magma chamber beneath the volcano and there has not been any sign of volcanic activity in the last 5 million years.
The Kaitake Range, like the neighbouring Pouakai Range, is an eroded and heavily vegetated stratovolcano that formed during the Pleistocene epoch in the Taranaki region of New Zealand. Kaitake is the northwesternmost of the stratovolcanoes in the region. It is about 500,000 years old and last erupted around 350,000 years ago. Its final collapse about 250,000 years ago appears to have been potentially associated with a collapse event of the Pouakai volcano.
The Waitākere volcano, also known as the Manukau volcano, was a Miocene era volcano that formed off the west coast of the modern Auckland Region of New Zealand's North Island. Erupting intermittently between 23 million and 15 million years ago, the volcano was at one point one of the tallest mountains in New Zealand. The volcano alternated between periods as a seamount and as a volcanic island, before tectonic forces raised the volcano up from the seafloor 17 million years ago. Volcanism at the site ceased 15 million years ago and the cone has mostly eroded, however the modern Waitākere Ranges are formed from the remnants of the volcano's eastern slopes. A number of visible volcanic sites associated with the Waitākere volcano remain around Auckland, including Pukematekeo, Karekare and Lion Rock.

The South Auckland volcanic field, also known as the Franklin Volcanic Field, is an area of extinct monogenetic volcanoes around Pukekohe, the Franklin area and north-western Waikato, south of the Auckland volcanic field. The field contains at least 82 volcanoes, which erupted between 550,000 and 1,600,000 years ago.
The Auckland regional geologic faults have low seismic activity, compared to much of New Zealand, but do result in an earthquake risk to the Auckland metropolitan area, New Zealand's largest city. There is also evidence of past tectonic, volcanic associations in a city located within what is, at best, a very recently dormant Auckland volcanic field.
The Alexandra Volcanic Group is a chain of extinct calc-alkalic basaltic stratovolcanoes that were most active between 2.74 and 1.60 million years ago but is now known to have had more recent activity between 1.6 and 0.9 million years ago. They extend inland from Mount Karioi near Raglan with Mount Pirongia being the largest, with Pukehoua on the eastern slopes of Pirongia, Kakepuku, Te Kawa, and Tokanui completing the definitive lineament. The associated, but usually separated geologically basaltic monogenetic Okete volcanic field, lies mainly between Karioi and Pirongia but extends to the east and is quite scattered.
The Tauranga Volcanic Centre is a geologic region in New Zealand's Bay of Plenty. It extends from the southern end of Waihi Beach and from the old volcanoes of the Coromandel Peninsula that make up the northern part of the Kaimai Range, towards the Taupō Volcanic Zone.

The Coromandel Volcanic Zone (CVZ) is an extinct intraplate volcanic arc stretching from Great Barrier Island in the north, through the Coromandel Peninsula, to the Kaimai Range in the south. The area of transition between it and the newer and still active Taupō Volcanic Zone is now usually separated and is called the Tauranga Volcanic Centre. Its volcanic activity was associated with the formation and most active period of the Hauraki Rift.
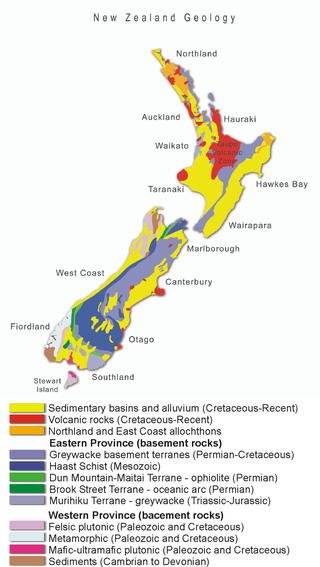
Much of the volcanic activity in the northern portions of the North Island of New Zealand is recent in geological terms and has taken place over the last 30 million years. This is primarily due to the North Island's position on the boundary between the Indo-Australian and Pacific Plates, a part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, and particularly the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Indo-Australian Plate. The activity has included some of the world's largest eruptions in geologically recent times and has resulted in much of the surface formations of the North Island being volcanic as shown in the map.
The volcanic activity in the South Island of New Zealand terminated 5 million years ago as the more northern parts of the North Island became extremely volcanically active. The South Islands surface geology reflects the uplift of the Pacific Plate as it collides with the Indo-Australian Plate along the Alpine Fault over the last 12 million years and the termination of subduction, about 100 to 105 million years ago. There is a very small chance of reactivation of volcanism in the Dunedin Volcano. This chance is made slightly higher by the observation that Southland's Solander Islands / Hautere just off the coast of the South Island were active as recently as 50,000 years old, and on a larger scale 150,000 years old.












