
Oxaloacetic acid (also known as oxalacetic acid or OAA) is a crystalline organic compound with the chemical formula HO2CC(O)CH2CO2H. Oxaloacetic acid, in the form of its conjugate base oxaloacetate, is a metabolic intermediate in many processes that occur in animals. It takes part in gluconeogenesis, the urea cycle, the glyoxylate cycle, amino acid synthesis, fatty acid synthesis and the citric acid cycle.
Shikimic acid, more commonly known as its anionic form shikimate, is a cyclohexene, a cyclitol and a cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. It is an important biochemical metabolite in plants and microorganisms. Its name comes from the Japanese flower shikimi, from which it was first isolated in 1885 by Johan Fredrik Eykman. The elucidation of its structure was made nearly 50 years later.

Phosphoenolpyruvate is the ester derived from the enol of pyruvate and phosphate. It exists as an anion. PEP is an important intermediate in biochemistry. It has the highest-energy phosphate bond found in organisms, and is involved in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. In plants, it is also involved in the biosynthesis of various aromatic compounds, and in carbon fixation; in bacteria, it is also used as the source of energy for the phosphotransferase system.
Carboxy-lyases, also known as decarboxylases, are carbon–carbon lyases that add or remove a carboxyl group from organic compounds. These enzymes catalyze the decarboxylation of amino acids, beta-keto acids and alpha-keto acids.

Guanosine monophosphate synthetase, also known as GMPS is an enzyme that converts xanthosine monophosphate to guanosine monophosphate.

The enzyme 3-dehydroquinate synthase catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 3-deoxy-8-phosphooctulonate synthase (EC 2.5.1.55) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N2-(2-carboxyethyl)arginine synthase (EC 2.5.1.66) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
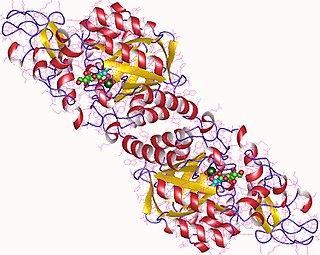
In enzymology, a N-acetylneuraminate synthase (EC 2.5.1.56) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acylneuraminate-9-phosphate synthase (EC 2.5.1.57) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Shikimate kinase (EC 2.7.1.71) is an enzyme that catalyzes the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of shikimate to form shikimate 3-phosphate. This reaction is the fifth step of the shikimate pathway, which is used by plants and bacteria to synthesize the common precursor of aromatic amino acids and secondary metabolites. The systematic name of this enzyme class is ATP:shikimate 3-phosphotransferase. Other names in common use include shikimate kinase (phosphorylating), and shikimate kinase II.
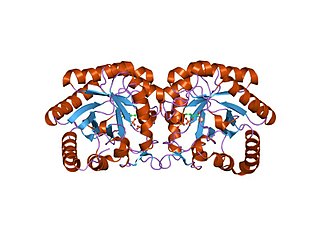
3-Deoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonate 7-phosphate (DAHP) synthase is the first enzyme in a series of metabolic reactions known as the shikimate pathway, which is responsible for the biosynthesis of the amino acids phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan. Since it is the first enzyme in the shikimate pathway, it controls the amount of carbon entering the pathway. Enzyme inhibition is the primary method of regulating the amount of carbon entering the pathway. Forms of this enzyme differ between organisms, but can be considered DAHP synthase based upon the reaction that is catalyzed by this enzyme.
5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase is an enzyme produced by plants and microorganisms. EPSPS catalyzes the chemical reaction:
UDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-N-acetyl-beta-L-altrosamine N-acetyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name acetyl-CoA:UDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-N-acetyl-beta-L-altrosamine N-acetyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
N,N'-diacetyllegionaminate synthase (EC 2.5.1.101, neuB (gene), legI (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name phosphoenolpyruvate:2,4-diacetamido-2,4,6-trideoxy-alpha-D-mannopyranose 1-(2-carboxy-2-oxoethyl)transferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-N-acetyl-beta-L-altrosamine transaminase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-N-acetyl-beta-L-altrosamine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Pseudaminic acid cytidylyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name CTP:5,7-diacetamido-3,5,7,9-tetradeoxy-L-glycero-alpha-L-manno-nonulosonic acid cytidylyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-N,N'-diacetylbacillosamine 2-epimerase (hydrolysing) (EC 3.2.1.184, UDP-Bac2Ac4Ac 2-epimerase, NeuC) is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N,N'-diacetylbacillosamine hydrolase (2-epimerising). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
UDP-2,4-diacetamido-2,4,6-trideoxy-beta-L-altropyranose hydrolase (EC 3.6.1.57, PseG, UDP-6-deoxy-AltdiNAc hydrolase, Cj1312) is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-2,4-bis(acetamido)-2,4,6-trideoxy-beta-L-altropyranose hydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction








