
The Chiasmodontidae, snaketooth fishes or swallowers, are a family of deep-sea predatory ray-finned fishes, part of the order Scombriformes, that are found in all oceans.
The peppered flounder is a species of flatfish in the monotypic family Paralichthodidae and the only species in the monotypic genus Paralichthodes. It is a demersal fish that lives on sandy and muddy bottoms in subtropical waters, at depths of up to 100 metres (330 ft). Its native habitat is the south-eastern Atlantic and the western Indian Ocean, specifically the African coastline from Mossel Bay, South Africa, to Delagoa Bay, Mozambique. It grows up to 50 centimetres (20 in) in length.
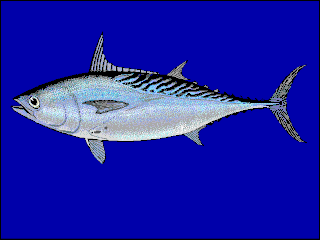
Euthynnus is a genus of ray-finned bony fish in the family Scombridae, or mackerel family, and in the tribe Thunnini, more commonly known as the tunas.

Peprilus is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Stromateidae found in Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.

The scaldfishes comprise a genus, Arnoglossus, of lefteye flounders. They are found in the Pacific, Indian and Atlantic Oceans, including the Mediterranean and Black Sea. They are entirely absent from most of the Americas; the only exceptions are A. coeruleosticta and A. multirastris found off Chile. The genus include both species found in shallow and deeper water. The largest species reaches 28 cm (11 in).

Engyprosopon is a genus of small lefteye flounders. They are found in the Indo-Pacific, ranging from shallow coastal waters to depths in excess of 400 m (1,300 ft).
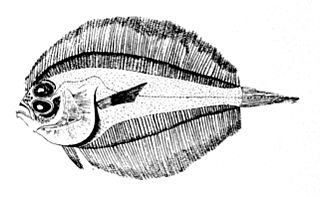
Laeops is a genus of small lefteye flounders from the Indo-Pacific. They are mainly found in deep water, although a few species have been recorded shallower than 100 m (330 ft).

Psettina is a genus of small lefteye flounders native to the Indo-Pacific.

Pseudorhombus is a genus of large-tooth flounders. With the exception of P. binii found off Peru, species in this genus are native to the Indo-Pacific. The largest species reaches 40 cm (16 in) in length.

Samariscus is a genus of crested flounders native to the Indo-Pacific.

Brachirus is a genus of small and medium-sized soles. Most are native to marine and brackish waters in the Indo-Pacific, but several species can also be seen freshwater in southern Asia, Eastern Africa, New Guinea and Australia.

Synaptura is a genus of soles. Most species are found in salt and brackish water in the Indo-Pacific and tropical East Atlantic, but S. salinarum is restricted to fresh water in Australia. The largest species in the genus reaches a length of 50 cm (20 in).

Pteraclis is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Bramidae, the pomfrets. They are known commonly as fanfishes. The three species are distributed throughout the oceans of the world.

Caristius is a genus of manefishes native to the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
Neocaristius heemstrai is a species of fish in the family Caristiidae, the manefishes. It is native to the oceans of the southern hemisphere where it is known to occur at depths of from 420 to 1,360 metres. This species grows to a length of 11.8 centimetres (4.6 in) SL.

Platyberyx is a genus of manefishes native to the eastern Atlantic Ocean.

Chiasmodon is a genus of snaketooth fishes.

Dysalotus is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Chiasmodontidae found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Ocean.

Kali is a genus of snaketooth fishes, deep ocean fish from the family Chiasmodontidae.

Lepidopus is a genus of cutlassfishes.
















