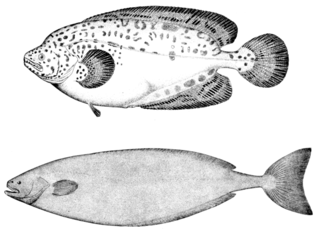
The ragfish is a ray-finned fish of the northern Pacific Ocean; although classified as a bony fish, its skeleton is mostly cartilage, and the larvae have pelvic fins that disappear as they mature. It is the sole member of the family Icosteidae within the order Scombriformes.
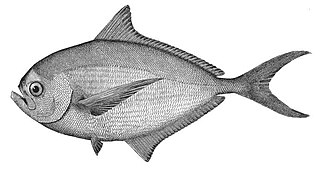
Pomfrets are scombriform fish belonging to the family Bramidae. The family currently includes 20 species across seven genera. Several species are important food sources for humans, especially Brama brama in South Asia. The earlier form of the pomfret's name was "pamflet", a word which probably ultimately comes from Portuguese pampo, referring to various fish such as the blue butterfish. The fish meat is white in color.

The family Stromateidae or butterfish contains 15 species of ray-finned fish in three genera. Butterfishes live in coastal waters off the Americas, western Africa and in the Indo-Pacific.

Lobotes is a genus of ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Lobotidae known as the tripletails. These fishes are found in subtropical and tropical waters in all oceans.

The cleftbelly trevally, also known as the cleftbelly kingfish, Kuweh trevally or thin crevalle, is a species of tropical marine fish of the jack family, Carangidae. The species inhabits coastal waters throughout the Indo-West Pacific region from South Africa in the west to Japan in the east, often found near the water's surface. The cleftbelly trevally is the only member of the genus Atropus and is distinguished by a number of anatomical characteristics, with a deep median groove in the belly giving the species its common name. It is not a large fish, growing to a maximum recorded length of 26.5 cm. Cleftbelly trevally are predatory fish, taking a variety of small crustaceans and fish. The species is of minor importance to fisheries throughout its range.

Scomber is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Scombridae living in the open ocean found in Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Ocean. The genus Scomber and the genus Rastrelliger comprise the tribe Scombrini, known as the "true mackerels". These fishes have an elongated body, highly streamlined, muscular and agile. The eyes are large, the head is elongated, with a big mouth provided with teeth. They have two triangular dorsal fins, with some stabilizing fins along the caudal peduncle. The basic color is blue-green with a silvery white belly and a darker back, usually black mottled.

The bullet tuna is a species of tuna, in the family Scombridae, found circumglobally in tropical oceans, including the Mediterranean Sea, in open surface waters to depths of 50 m (164 ft). The population of bullet tuna in the Eastern Pacific was classified as a subspecies of A. rochei, A. rochei eudorax, but some authorities regard this as a valid species Auxis eudorax. Its maximum length is 50 centimetres (20 in).

The spiny turbots are a family, Psettodidae, of relatively large, primitive flatfish found in the tropical waters of the east Atlantic and Indo-Pacific. The family contains just three species, all in the same genus, Psettodes. The common name comes from the presence of spines in the dorsal and anal fins, which may indicate an evolutionary relationship with the Perciformes. They are less asymmetrical than other flatfish, although the region around the eyes is twisted. They reach lengths of 55–80 cm (22–31 in).

Cynoglossus arel, commonly known as the largescale tonguesole, is a species of tonguefish. The eyed side of the fish is uniform brown, with a dark patch on the gill cover, and its blind side is white. They are harmless to humans and predominantly feed on bottom-living invertebrates.

Euthynnus lineatus, the black skipjack tuna or black skipjack, is a species of ray-finned bony fish in the family Scombridae. It belongs to the tribe Thunnini, better known as the tunas.
Barnardichthys fulvomarginata, the lemon sole, is a species of sole endemic to the coasts of South Africa. This species is the only known member of its genus.

Synapturichthys kleinii, Klein's sole or lace sole, is a species of economically important sole. It is the only known member of its genus.

Brama is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes from the family Bramidae, the pomfrets. Currently, there are 8 species within the genus.

Pteraclis is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Bramidae, the pomfrets. They are known commonly as fanfishes. The three species are distributed throughout the oceans of the world.
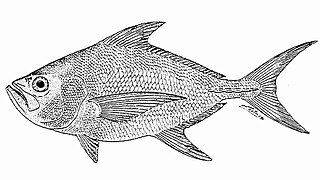
Taractes is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes from the family Bramidae, the pomfrets. Taractes can be distinguished from other bramid genera but having a flat, or slightly curved profile, between the eyes and by having scales on both the dorsal and anal fins.

Lepidotrigla guentheri is a species of marine, demersal ray-finned fish from the family Triglidae, the gurnards and sea robins. It is found in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.
Cynoglossus sinusarabici, the Red Sea tonguesole, is a species of tonguefish which occurs in the Red Sea and is now common in the eastern Mediterranean Sea following its migration through the Suez Canal. It was first recorded in the Mediterranean Sea off Israel in 1953 and successively observed in Turkey and Egypt. It has an elongated body with a rounded snout which has a rostral hook large, narrowly separated eyes. It has 99–101 dorsal fin rays, 78–79 rays in its anal fin and 8 rays in the caudal fin. The lateral line has 54–60 scales with 11 scales between the lateral line and the base of the dorsal fin. The lateral line is only present on the eyed side. It is uniform brown on the eyed side and whitish on the blind side. It grows to about 15 cm standard length.

Brama japonica, the Pacific pomfret, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a pomfret of the family Bramidae. B. japonica is closely related, and quite similar, to Brama brama, but can be distinguished by possessing a greater number of anal fin rays and a higher number of gill rakers.

Pterycombus brama is a species of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Bramidae (pomfrets).
Dagetichthys marginatus, commonly known as the white-margined sole, is a species of flatfish native to the eastern Atlantic Ocean. Little is known of the abundance or behaviour of this fish, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as being "data deficient".
















