
Clavulina cristata, commonly known as the wrinkled coral fungus, white coral fungus or the crested coral fungus, is a white- or light-colored edible coral mushroom present in temperate areas of the Americas and Europe. It is the type species of the genus Clavulina.

Verpa conica, commonly known as the bell morel or the early morel, is a species of fungus in the family Morchellaceae. Sometimes mistaken for a true morel, this species is characterized by a cap resembling a thimble that is freely attached to the stipe.

Ramaria botrytis, commonly known as the clustered coral, the pink-tipped coral mushroom, or the cauliflower coral, is an edible species of coral fungus in the family Gomphaceae. Its robust fruit body can grow up to 15 cm (6 in) in diameter and 20 cm (8 in) tall, and resembles some marine coral. Its dense branches, which originate from a stout, massive base, are swollen at the tips and divided into several small branchlets. The branches are initially whitish but age to buff or tan, with tips that are pink to reddish. The flesh is thick and white. The spores, yellowish in deposit, are ellipsoid, feature longitudinal striations, and measure about 13.8 by 4.7 micrometers.

Armillaria nabsnona is a species of fungus in the family Physalacriaceae. The species is found in the west coast of North America, Hawaii, and Japan, where it grows on decaying hardwoods, particularly species of alder. Its fruit bodies have convex to flattened orange-brown caps up to 7 cm in diameter, brown stipes, and whitish to pinkish-tan gills.

Caloboletus rubripes, commonly known as the red-stipe bolete or the red-stemmed bitter bolete, is a mushroom in the family Boletaceae. It was known as Boletus rubripes until 2014. Fruit bodies (mushrooms) are robust, with caps up to 18 cm in diameter, atop thick stipes 5–12 cm long. Mushrooms are non-toxic, but is so bitter as to be inedible. The mushroom flesh has a very strong bluing reaction when cut or damaged. and forms mycorrhizal relationships, primarily with conifers. It can be differentiated from similar boletes by its cap color and non-reticulate stipe.

Amanita nothofagi is a species of fungus in the family Amanitaceae. Endemic to New Zealand, the species was first described by mycologist Greta Stevenson in 1962. The fruit bodies have dark brown caps that are up to 13 cm (5.1 in) in diameter and covered with patches of soft greyish-brown scales or warts. The gills underneath the cap are crowded together, free from attachment to the stem, and white, becoming tinged with yellow in age. The stem of the mushroom is 4–14 cm (1.6–5.5 in) long by 0.5–2.5 cm (0.2–1.0 in) thick, and has a ring. The spore print is white, and individual spores are spherical to ellipsoid, measuring 7.5–9 by 7.5–9 micrometres. The mushroom may be confused with another New Zealand species, A. australis, but can be distinguished by certain characteristics. Amanita nothofagi is a mycorrhizal species, and grows in association with native New Zealand trees such as Southern Beech.

Mycena aurantiomarginata, commonly known as the golden-edge bonnet, is a species of agaric fungus in the family Mycenaceae. First formally described in 1803, it was given its current name in 1872. Widely distributed, it is common in Europe and North America, and has also been collected in North Africa, Central America, and Japan. The fungus is saprobic, and produces fruit bodies (mushrooms) that grow on the floor of coniferous forests. The mushrooms have a bell-shaped to conical cap up to 2 cm in diameter, set atop a slender stipe up to 6 cm long with yellow to orange hairs at the base. The fungus is named after its characteristic bright orange gill edges. A microscopic characteristic is the club-shaped cystidia that are covered with numerous spiky projections, resembling a mace. The edibility of the mushroom has not been determined. M. aurantiomarginata can be distinguished from similar Mycena species by differences in size, color, and substrate. A 2010 publication reported the discovery and characterization of a novel pigment named mycenaaurin A, isolated from the mushroom. The pigment is responsible for its color, and it has antibiotic activity that may function to prevent certain bacteria from growing on the mushroom.

Hygrophorus goetzii is a species of fungus in the family Hygrophoraceae. It is a snowbank mushroom with a rosy-pink cap that fades to cream color in maturity.

Ramaria fennica, commonly known as the bitter coral, is a coral mushroom in the family Gomphaceae. It is found in Australia, Europe and North America.

Phaeoclavulina abietina, commonly known as the green-staining coral, is a coral mushroom in the family Gomphaceae. It is characterized by the green staining reaction it develops in response to bruising or injury.

Ramaria stricta, commonly known as the strict-branch coral or strict coral mushroom, is a coral fungus of the genus Ramaria. It has a cosmopolitan distribution, and grows on dead wood, stumps, trunks, and branches of both deciduous and coniferous trees. Its fruit body is up to 10 cm tall, made of multiple slender, compact, and vertical parallel branches. Its color is typically light tan to vinaceous-brown. All parts of the mushroom will bruise when handled. There are several lookalike corals that can usually be distinguished from R. stricta by differences in coloration, bruising reaction, or microscopic features. The fungus is inedible due to its unpleasant odor and bitter taste.

Tremellodendropsis tuberosa, commonly known as the ashen coral, is a species of coral fungus in the family Tremellodendropsidaceae found in Europe, North America, South America, and Asia.

Ramaria rasilispora, commonly known as the yellow coral, is a coral mushroom in the family Gomphaceae. Described as new to science in 1974, it is found in western North America south to Mexico, and in the eastern Himalaya.

Ramaria araiospora, commonly known as the red coral, is a coral mushroom in the family Gomphaceae. First described in 1974, it is found in North America, and the Himalaya. An edible species, it is sold in local markets in Mexico.

Ramaria rubrievanescens, commonly known as the fading pink coral, is a coral mushroom in the family Gomphaceae. It is found in North America.

Ramaria rubripermanens is a species of coral fungus in the family Gomphaceae. Described as new to science in 1973, it is found in the western United States and Mexico. Its fruit bodies, which resemble sea coral, grow up to 16 cm (6.3 in) tall and feature whitish to light yellow branches with pinkish to reddish tips. It is edible.

Clitocybe albirhiza, commonly known as the snowmelt clitocybe, is a species of agaric fungus in the family Tricholomataceae. It is found in high-elevation locations in the western United States.

Ramaria magnipes is a coral fungus in the family Gomphaceae. It is found in western North America, where it fruits on the ground in mixed forests.

Pholiota nubigena, commonly known as the gastroid pholiota or the bubble gum fungus, is a species of secotioid fungus in the family Strophariaceae. It is found in mountainous areas of the western United States, where it grows on rotting conifer wood, often fir logs. It fruits in spring, often under snow, and early summer toward the end of the snowmelt period in high mountain forests. Fruit bodies appear similar to unopened mushrooms, measuring 1–4 centimetres tall with 1–2.4 cm diameter caps that are whitish to brownish. They have a short but distinct whitish stipe that extend through the internal spore mass (gleba) of the fruit body into the cap. The gleba consists of irregular chambers made of contorted gills that are brownish in color. A whitish, cottony partial veil is present in young specimens, but it often disappears in age and does not leave a ring on the stipe.
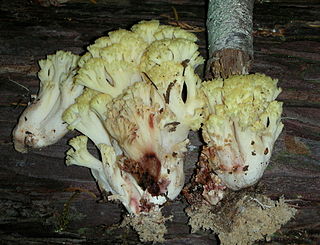
Ramaria rubiginosa is a coral mushroom in the family Gomphaceae. It is found in North America.




















