
The Juan Fernández Islands are a sparsely inhabited series of islands in the South Pacific Ocean reliant on tourism and fishing. Situated 670 km off the coast of Chile, they are composed of three main volcanic islands: Robinson Crusoe, Alejandro Selkirk and Santa Clara. The group is part of Insular Chile.

Robinson Crusoe is an English adventure novel by Daniel Defoe, first published on 25 April 1719. Written with a combination of epistolary, confessional, and didactic forms, the book follows the title character after he is cast away and spends 28 years on a remote tropical desert island near the coasts of Venezuela and Trinidad, encountering cannibals, captives, and mutineers before being rescued. The story has been thought to be based on the life of Alexander Selkirk, a Scottish castaway who lived for four years on a Pacific island called "Más a Tierra" which was renamed Robinson Crusoe Island in 1966. Pedro Serrano is another real-life castaway whose story might have inspired the novel.
This article contains information about the literary events and publications of 1719.

The Swiss Family Robinson is a novel by the Swiss author Johann David Wyss, first published in 1812, about a Swiss family of immigrants whose ship en route to Port Jackson, Australia goes off course and is shipwrecked in the East Indies. The ship's crew is lost, but the family and several domestic animals survive. They make their way to shore, where they build a settlement, undergoing several adventures before being rescued; some refuse rescue and remain on the island.

Friday is one of the main characters of Daniel Defoe's 1719 novel Robinson Crusoe and its sequel The Farther Adventures of Robinson Crusoe. Robinson Crusoe names the man Friday, with whom he cannot at first communicate, because they first meet on that day. The character is the source of the expression "Man Friday", used to describe a male personal assistant or servant, especially one who is particularly competent or loyal.
Charles Gildon, was an English hack writer and translator. He produced biographies, essays, plays, poetry, fictional letters, fables, short stories, and criticism. He is remembered best as a target of Alexander Pope in Pope's Dunciad and his Epistle to Dr. Arbuthnot and as an enemy of Jonathan Swift. Due to Pope's caricature of Gildon as well as the volume and rapidity of his writings, Gildon has become the epitome of the hired pen and literary opportunist.
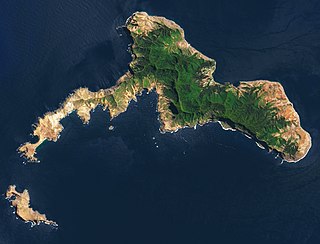
Robinson Crusoe Island is the second largest of the Juan Fernández Islands, situated 670 km west of San Antonio, Chile, in the South Pacific Ocean. It is the more populous of the inhabited islands in the archipelago, with most of that in the town of San Juan Bautista at Cumberland Bay on the island's north coast. The island was formerly known as Más a Tierra.

Robinsonade is a literary genre of fiction wherein the protagonist is suddenly separated from civilization, usually by being shipwrecked or marooned on a secluded and uninhabited island, and must improvise the means of their survival from the limited resources at hand. The genre takes its name from the 1719 novel Robinson Crusoe by Daniel Defoe. The success of this novel spawned so many imitations that its name was used to define a genre, which is sometimes described simply as a "desert island story" or a "castaway narrative".

An uninhabited island, desert island, or deserted island, is an island, islet or atoll which lacks permanent human population. Uninhabited islands are often depicted in films or stories about shipwrecked people, and are also used as stereotypes for the idea of "paradise". Some uninhabited islands are protected as nature reserves, and some are privately owned. Devon Island in Canada's far north is the largest uninhabited island in the world.

Schefflera is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araliaceae with 13 species native to New Zealand and some Pacific islands.

Archipiélago de Juan Fernández National Park is a national park located in the Pacific Ocean 665 kilometres west of Chile's mainland port of San Antonio, in the Juan Fernández Archipelago. The park covers 96 square kilometres and comprises the Santa Clara, Alejandro Selkirk and the most part of the Robinson Crusoe Island islands.
Sonchus neriifolius, synonym Dendroseris neriifolia is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is a tree with droopy, elongated leaves and small yellow-white flowers. The plant was originally native to Continental Chile but is now endemic to Robinson Crusoe Island. The plant is endangered and very rare: only two specimens are known to exist in a ravine in the eastern part of the island, although there exist other human-cultivated specimens. It is classified as critically endangered by the World Conservation Monitoring Centre.

The Adventures of Robinson Crusoe is a 1922 American adventure film serial directed by Robert F. Hill and based upon the 1719 novel by Daniel Defoe. It is now considered to be a lost film.

Crusoe is an adventure-drama television series, based loosely on the 1719 novel Robinson Crusoe by Daniel Defoe. The series' 13 episodes aired on NBC from October 17, 2008, to January 31, 2009, during the first half of the 2008–09 television season. It follows the adventures of Robinson Crusoe: a man who has been shipwrecked on an island for six years and is desperate to return home to his wife and children. His lone companion is Friday, a native whom Crusoe rescued and taught English.
Friday, or, The Other Island is a 1967 novel by French writer Michel Tournier. It retells Daniel Defoe's Robinson Crusoe.
Robinson Crusoe is a 1927 British silent drama film produced and directed by M.A. Wetherell who also played the title role. A sound version was released in 1932. While the sound version had no audible dialog, it featured a synchronized musical score with sound effects. In addition to M.A. Wetherell, the film also starred Fay Compton and Herbert Waithe. It is an adaptation of the 1719 novel Robinson Crusoe by Daniel Defoe. The screenplay concerns a shipwrecked man stranded on a desert island. The film was made at Cricklewood Studios and Lime Grove Studios in London.

Robinson Crusoe is a 1902 French silent film directed by Georges Méliès, based on Daniel Defoe's 1719 book of the same name.

Robinson Crusoe is a 2016 3D animated adventure comedy film directed by Vincent Kesteloot and Ben Stassen and written by Lee Christopher, Domonic Paris and Graham Weldon. The film is loosely based on the 1719 novel Robinson Crusoe by Daniel Defoe, but from the point of view of the island's animals. The film was released in the United States on September 9, 2016. Despite receiving negative reviews from the critics and earning a 17% approval rating on Rotten Tomatoes, Robinson Crusoe was a moderate box office success, grossing $39.5 million worldwide against a budget of $13 million.

Selkirkia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Boraginaceae. Three species occur on the South American mainland and one, Selkirkia berteroi, the first of the genus to be reported, is an endemic on Robinson Crusoe Island off the coast of Chile. It was previously considered a monotypic genus.












