
Narcissus is a genus of predominantly spring flowering perennial plants of the amaryllis family, Amaryllidaceae. Various common names including daffodil, narcissus and jonquil, are used to describe all or some members of the genus. Narcissus has conspicuous flowers with six petal-like tepals surmounted by a cup- or trumpet-shaped corona. The flowers are generally white and yellow, with either uniform or contrasting coloured tepals and corona.

Texas root rot is a disease that is fairly common in Mexico and the southwestern United States resulting in sudden wilt and death of affected plants, usually during the warmer months. It is caused by a soil-borne fungus named Phymatotrichopsis omnivora that attacks the roots of susceptible plants. It was first discovered in 1888 by Pammel and later named by Duggar in 1916.
Root rot is a condition in which anoxic conditions in the soil or potting media around the roots of a plant cause them to rot. This occurs due to excessive standing water around the roots. It is found in both indoor and outdoor plants, although it is more common in indoor plants due to overwatering, heavy potting media, or containers with poor drainage. The leaves of plants experiencing root rot often yellow and die, and if allowed to continue, the condition can be fatal.

The fungus Cochliobolus sativus is the teleomorph of Bipolaris sorokiniana (anamorph) which is the causal agent of a wide variety of cereal diseases. The pathogen can infect and cause disease on roots, leaf and stem, and head tissue. C. sativus is extremely rare in nature and thus it is the asexual or anamorphic stage which causes infections. The two most common diseases caused by B. sorokiniana are spot blotch and common root rot, mainly on wheat and barley crops.

Partitiviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Plants, fungi, and protozoa serve as natural hosts. It has been suggested that they can also infect bacteria. The name comes from the Latin partitius, which means divided, and refers to the segmented genome of partitiviruses. There are five genera and 60 species in the family, 15 of which are unassigned to a genus.

A wood-decay or xylophagous fungus is any species of fungus that digests moist wood, causing it to rot. Some species of wood-decay fungi attack dead wood, such as brown rot, and some, such as Armillaria, are parasitic and colonize living trees. Excessive moisture above the fibre saturation point in wood is required for fungal colonization and proliferation. In nature, this process causes the breakdown of complex molecules and leads to the return of nutrients to the soil. Wood-decay fungi consume wood in various ways; for example, some attack the carbohydrates in wood, and some others decay lignin. The rate of decay of wooden materials in various climates can be estimated by empirical models.
Cylindrocarpon magnusianum is a fungal plant pathogen that causes root rot in alfalfa and red clover.

Phytophthora cryptogea is a species of water mould in the family Pythiaceae. It is a plant pathogen that infects several species of cultivated plants, including over 40 species of cultivated flowers. It was first described as the cause of tomato foot rot in tomatoes
Microdochium bolleyi is a fungal plant pathogen that causes root rot in flax and wheat.
Nectria radicicola is a plant pathogen that is the causal agent of root rot and rusty root. Substrates include ginseng and Narcissus. It is also implicated in the black foot disease of grapevine. It is of the genus Nectria and the family Nectriaceae. N. radicicola is recognizable due to its unique anatomy, morphology, and the formation of its anamorph Cylindrocarpon desructans.
Calonectria ilicicola is a fungal plant pathogen in the family Nectriaceae. It has been found to cause leaf spot in holly, root rot in blueberry, red crown rot in soybean, a root and crown rot of anthurium, and a soft rot of ginger.
Rosellinia bunodes is a plant pathogen infecting several hosts including avocados, bananas, cacao and tea.

Rosellinia subiculata is a fungal plant pathogen infecting citruses. It is a uniperitheciate pyrenomycete in division Ascomycota. It can be distinguished by its scattered growth on decaying wood, its singular ostiole, and yellow subiculum.

Rosellinia is a genus of fungi in the family Xylariaceae consisting of over 90 species. Several of the species in this genus are plant pathogens. Fossils of Rosellinia have been found in 12 million year old rocks from central England.
Forest pathology is the research of both biotic and abiotic maladies affecting the health of a forest ecosystem, primarily fungal pathogens and their insect vectors. It is a subfield of forestry and plant pathology.

Armillaria root rot is a fungal root rot caused by several different members of the genus Armillaria. The symptoms are variable depending on the host infected, ranging from stunted leaves to chlorotic needles and dieback of twigs and branches. However, all infected hosts display symptoms characteristic of being infected by a white rotting fungus. The most effective ways of management focus on limiting the spread of the fungus, planting resistant species, and removing infected material. This disease poses a threat to the lumber industry as well as affecting recreational areas.

Muscardine is a disease of insects. It is caused by many species of entomopathogenic fungus. Many muscardines are known for affecting silkworms. Muscardine may also be called calcino.
Phoma narcissi is a fungal plant pathogen of Narcissus, Hippeastrum and other Amaryllidaceae, where it causes a leaf scorch, neck rot and red leaf spot disease

Victorivirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Totiviridae. Filamentous fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 14 species in this genus.
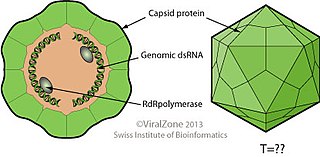
Megabirnaviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses with one genus Megabirnavirus which infects fungi. The group name derives from member's bipartite dsRNA genome and mega that is greater genome size than families Birnaviridae and Picobirnaviridae. There is only one species in this family: Rosellinia necatrix megabirnavirus 1. Diseases associated with this family include: reduced host virulence.












