
Paranthropus is a genus of extinct hominin which contains two widely accepted species: P. robustus and P. boisei. However, the validity of Paranthropus is contested, and it is sometimes considered to be synonymous with Australopithecus. They are also referred to as the robust australopithecines. They lived between approximately 2.9 and 1.2 million years ago (mya) from the end of the Pliocene to the Middle Pleistocene.

Paranthropus robustus is a species of robust australopithecine from the Early and possibly Middle Pleistocene of the Cradle of Humankind, South Africa, about 2.27 to 0.87 million years ago. It has been identified in Kromdraai, Swartkrans, Sterkfontein, Gondolin, Cooper's, and Drimolen Caves. Discovered in 1938, it was among the first early hominins described, and became the type species for the genus Paranthropus. However, it has been argued by some that Paranthropus is an invalid grouping and synonymous with Australopithecus, so the species is also often classified as Australopithecus robustus.

Janenschia is a large herbivorous sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Tendaguru Formation of Lindi Region, Tanzania around 155 million years ago.
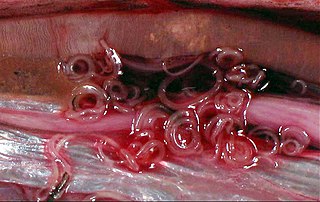
The Chromadorea are a class of the roundworm phylum, Nematoda. They contain a single subclass (Chromadoria) and several orders. With such a redundant arrangement, the Chromadoria are liable to be divided if the orders are found to form several clades, or abandoned if they are found to constitute a single radiation.
Pratylenchus vulnus is a species of plant pathogenic nematode best known for infecting Persian walnut. It is also known to infest potatoes, apricots, peaches and nectarines, holiday cacti, grape and citruses.
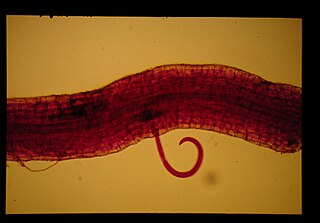
Helicotylenchus dihystera is a plant pathogenic nematode. It is known to inhabit sugarcane, rice, potatoes, corn, peanut, millet, sorghum, banana and forest trees.
Xiphinema diversicaudatum is an amphimictic ectoparasitic nematode species. This species has a characteristically long stylet capable of penetrating into a host's vascular tissue. They have a wide host range with some of the extensively studied ones being strawberry, hops and raspberry, due to their economic importance. The direct root damage caused through penetration near the root tip and formation of galls is a secondary concern when compared with the damage caused by vectoring the Arabis mosaic virus. The virus attaches to the interior cuticle lining and can be transferred from infected to uninfected root tissue as the nematode feeds and sheds. Management of this particular nematode relies on nematicides such as 1,3-Dichloropropene (Telone) at 40 gpa.or methyl bromide at 1000 lb/ac to control to 28 in deep.
Rotylenchus brachyurus is a plant pathogenic nematode infecting African violets.

The robust yellow bat is a species of vesper bat. It is found only in Madagascar.

The robust golden mole is a species of mammal in the golden mole family, Chrysochloridae. It is endemic to parts of Mpumalanga province in South Africa. Its natural habitats are temperate forests, subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest, temperate and subtropical or tropical dry shrubland, dry lowland grassland, arable land, pastureland, plantations, rural gardens, and urban areas.
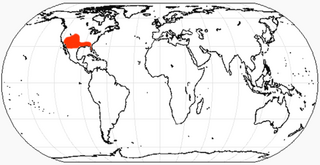
Carpocyon is an extinct genus of the Borophaginae subfamily of canids native to North America. It lived from the Middle to the Late Miocene, 13.6 to 5.3 Ma Mya, existing for approximately 16.5 million years. The four species in the genus varied in size, with the largest being about the size of a wolf; all had relatively small teeth, suggesting a diet that was more omnivorous than that of other contemporary borophagines.

The nematodes, roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but there are many that are parasitic. The parasitic worms (helminths) are the cause of soil-transmitted helminthiases.

Voay is an extinct genus of crocodile from Madagascar that lived during the Late Pleistocene to Holocene, containing only one species, V. robustus. Numerous subfossils have been found, including complete skulls, noted for their distinctive pair of horns on the posterior, as well as vertebrae and osteoderms from such places as Ambolisatra and Antsirabe. The genus is thought to have become extinct relatively recently. It has been suggested to have disappeared in the extinction event that wiped out much of the endemic megafauna on Madagascar, such as the elephant bird and Malagasy hippo, following the arrival of humans to Madagascar around 2000 years ago. Its name comes from the Malagasy word for crocodile.

Hoplolaimidae is a family of plant pathogenic nematodes. It has two subfamilies, Hoplolaiminae and Rotylenchulinae. Typically hoplolaimids are ecto- or semi endoparasites of higher plants.

Antarctica is one of the most physically and chemically extreme terrestrial environments to be inhabited by lifeforms. The largest plants are mosses, and the largest animals that do not leave the continent are a few species of insects.
R. robustus may refer to:

Bolboschoenus robustus is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family. It is known by many common names: saltmarsh bulrush, alkali bulrush, sturdy bulrush, seacoast bulrush, stout bulrush, three-cornered sedge or leafy three-cornered sedge, and seaside club-rush.
Nematoctonus was a genus of fungi in the Pleurotaceae family, which is now considered a synonym of Hohenbuehelia. Originally the generic name —an anamorphic form of Hohenbuehelia—has a widespread distribution and contains 16 species. Under the one fungus - one name convention, the correct name for the group is Hohenbuehelia and species where the fruitbodies have not been discovered or that are older names for those described as fruitbodies have all been transferred to Hohenbuehelia.
Pterygodermatites peromysci is an intestinal parasitic nematode in the genus Pterygodermatites of the family Rictulariidae.
Prodontorhabditis is a genus of nematodes belonging to the family Rhabditidae.












