The Snowy Mountains, known informally as "The Snowies", is an IBRA subregion in southern New South Wales, Australia, and is the tallest mountain range in mainland Australia, being part of the continent's Great Dividing Range cordillera system. It makes up the northeastern half of the Australian Alps and contains Australia's five tallest peaks, all of which are above 2,100 m (6,890 ft), including the tallest Mount Kosciuszko, which reaches to a height of 2,228 m (7,310 ft) above sea level. The offshore Tasmanian highlands makes up the only other major alpine region present in the whole of Australia.

Dartmouth Dam is a large rock-fill embankment dam with an uncontrolled chute spillway across the Mitta Mitta, Gibbo and Dart rivers, the Morass Creek and a number of small tributaries. The dam is located near Mount Bogong in the north-east of the Australian state of Victoria. The dam's purpose includes irrigation, the generation of hydro-electric power, water supply and conservation. The impounded reservoir is called Dartmouth Reservoir, sometimes called Lake Dartmouth. The Dartmouth Power Station, a hydro-electric power station that generates power to the national grid, is located near the dam wall.
The Kosciuszko National Park is a 6,900-square-kilometre (2,700 sq mi) national park and contains mainland Australia's highest peak, Mount Kosciuszko, for which it is named, and Cabramurra, the highest town in Australia. Its borders contain a mix of rugged mountains and wilderness, characterised by an alpine climate, which makes it popular with recreational skiers and bushwalkers.

The Australian Alps are a mountain range in southeast Australia. The range comprises an interim Australian bioregion, and is the highest mountain range in Australia. The range straddles the borders of eastern Victoria, southeastern New South Wales, and the Australian Capital Territory. It contains Australia's only peaks exceeding 2,000 m (6,600 ft) in elevation, and is the only bioregion on the Australian mainland in which deep snow falls annually. The range comprises an area of 1,232,981 ha.

Kiewa River, a perennial river that is part of the Murray catchment within the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the Alpine bioregion, in the Australian state of Victoria.

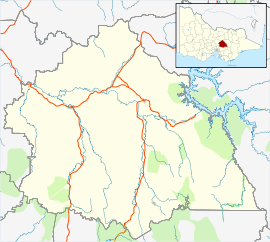
The Strzelecki Ranges is a set of low mountain ridges located in the West Gippsland and South Gippsland regions of the Australian state of Victoria.

Alexandra is a town in north-east Victoria, Australia, 130 kilometres north-east of the State Capital, Melbourne. It is located at the junction of the Goulburn Valley Highway (B340) and Maroondah Highway (B360), in the Shire of Murrindindi local government area. At the 2021 census, the town had a population of 2,801 and the broader area a population of 6,828.

Barmah is a town in the state of Victoria, Australia.

Orbost is a historic early settlers town in the Shire of East Gippsland, Victoria, 375 kilometres (233 mi) east of Melbourne and 235 kilometres (146 mi) south of Canberra where the Princes Highway crosses the Snowy River. It is about 16 kilometres (10 mi) from the surf and fishing seaside town of Marlo on the coast of Bass Strait and 217 km (135 mi) drive to Hotham Alpine Resort. Orbost is the service centre for the primary industries of beef, dairy cattle and sawmilling. More recently, tourism has become an important and thriving industry, being the major town close to several national parks that are between the east access to either the surf or the snow, including the famous Snowy River National Park, Alpine National Park, Errinundra National Park, Croajingolong National Park and Cape Conran Coastal Park.

The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme is the largest hydro-electric scheme in the Australian state of Victoria and the second-largest in mainland Australia after the Snowy Mountains Scheme. The scheme is situated in the Australian Alps in north-eastern Victoria about 350 kilometres from Melbourne and is wholly owned by AGL Energy. In 2024, AGL studied the options of expanding the scheme with pumped-storage hydroelectricity.
The Rubicon River, an inland perennial river of the Goulburn Broken catchment, part of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the lower South Eastern Highlands bioregion and Northern Country/North Central regions of the Australian state of Victoria. The headwaters of the Rubicon River rise on the western slopes of the Victorian Alps and descend to flow into the Goulburn River.

The Rubicon Hydroelectric Scheme is a small run-of-the-river hydroelectric scheme located on the Rubicon and Royston Rivers, north east of Melbourne, 40 km (25 mi) south-west of Alexandra, Victoria, Australia. The scheme commenced in 1922, and was the first state-owned hydroelectric scheme to generate electricity in mainland Australia, and among the first in the world to be remotely controlled. For the first ten years of its operation it supplied on average 16.9% of electricity generated by the State Electricity Commission of Victoria. It is now owned and operated by AGL Energy and contributes approximately 0.02% of Victoria's energy supply.
Toolangi is a locality in Victoria, Australia. At the 2021 census, Toolangi had a population of 366. It is situated on the edge of the Toolangi State Forest.

Barham is a town in the western Riverina district of New South Wales, Australia. The town is located 823 kilometres south west of the state capital, Sydney and 303 kilometres north west of Melbourne. Situated on the banks of the Murray River across from Koondrook in the neighbouring state of Victoria, Barham had a population of 1,159 at the 2016 census. The town is in the Murray River Council local government area.

Tolmie is a town in central Victoria, Australia. It is located 22 kilometres (14 mi) north-east of Mansfield in the Victorian high country. At the 2011 census, Tolmie had a population of 547.

Energy in Victoria, Australia is generated using a number of fuels or technologies, including coal, natural gas and renewable energy sources. Brown coal, historically, was the main primary energy source for the generation of electricity in the state, accounting for about 85% of electricity generation in 2008. The amount of coal-fired power has decreased significantly with the closure in 2017 of the Hazelwood power station which supplied around 20% of Victoria's electricity, and to a lesser extent with the exit of Anglesea power station in 2015. Brown coal is one of the largest contributors to Australia's total domestic greenhouse gas emissions and a source of controversy for the country. Australia is one of the highest polluters of greenhouse gas per capita in the world.

Coochin Creek is a coastal locality in the south of the Sunshine Coast Region, Queensland, Australia. The locality is named for the creek which flows through it.
The Royston River, an inland perennial river of the Goulburn Broken catchment, part of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the lower South Eastern Highlands bioregion and Northern Country/North Central regions of the Australian state of Victoria. The headwaters of the Royston River rise on the western slopes of the Victorian Alps and descend to flow into the Rubicon River.
Norman Houghton is a historian and archivist in Geelong, Victoria, who has published more than 40 books, many focusing on timber tramways and sawmills of the Otway and Wombat Forests of Western Victoria, Australia. Most of his works have been self-published, while he has provided numerous articles to the newsletter and journal of the Light Railway Research Society of Australia.
Deptford is a locality in the Shire of East Gippsland, Victoria, Australia. In the 2016 census, Deptford had a population of zero.