
Sorrel, also called common sorrel or garden sorrel, is a perennial herbaceous plant in the family Polygonaceae. Other names for sorrel include spinach dock and narrow-leaved dock.

Bistorta officinalis, known as bistort, common bistort, European bistort, or meadow bistort, is a species of flowering plant in the dock family Polygonaceae native to Europe and northern and western Asia. Other common names include snakeroot, snake-root, snakeweed, and Easter-ledges.
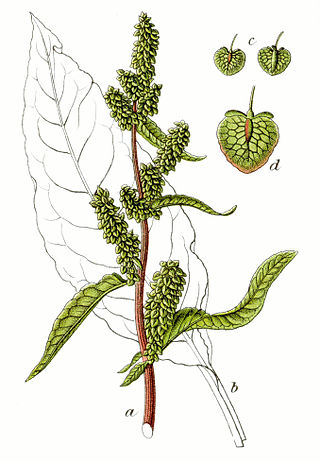
The docks and sorrels, genus Rumex, are a genus of about 200 species of annual, biennial, and perennial herbs in the buckwheat family, Polygonaceae. Members of this genus are very common perennial herbs with a native almost worldwide distribution, and introduced species growing in the few places where the genus is not native.

Rumex crispus, the curly dock, curled dock or yellow dock, is a perennial flowering plant in the family Polygonaceae, native to Europe and Western Asia.

Rumex obtusifolius, commonly known as bitter dock, broad-leaved dock, bluntleaf dock, dock leaf, dockens or butter dock, is a perennial plant in the family Polygonaceae. It is native to Europe, but is found on all temperate continents. It is a highly invasive species in some zones, resulting from its abundant seed dispersal, adaptability to reproduce, aggressive roots, ability to tolerate extreme climates, and hardiness.

Rumex acetosella, commonly known as red sorrel, sheep's sorrel, field sorrel and sour weed, is a species of flowering plant in the buckwheat family Polygonaceae. Native to Eurasia and the British Isles, the plant and its subspecies are common perennial weeds. It has green arrowhead-shaped leaves and red-tinted deeply ridged stems, and it sprouts from an aggressive and spreading rhizome. The flowers emerge from a tall, upright stem. Female flowers are maroon in color.

Eriogonum fasciculatum is a species of wild buckwheat known by the common names California buckwheat and flat-topped buckwheat. Characterized by small, white and pink flower clusters that give off a cottony effect, this species grows variably from a patchy mat to a wide shrub, with the flowers turning a rusty color after blooming. This plant is of great benefit across its various habitats, providing an important food resource for a diversity of insect and mammal species. It also provides numerous ecosystem services for humans, including erosion control, post-fire mitigation, increases in crop yields when planted in hedgerows, and high habitat restoration value.

Rumex maritimus, commonly called golden dock, bristle dock, or seashore dock, is an annual plant species of the genus Rumex. Rumex D maritimus grows in Argentina, Burma, Canada, China, and the United States. It is native to Canada and most of the 48 states. The life span of Rumex maritimus is rarely biennial in moist environments. This herb belongs to the family Polygonaceae.

Claytonia lanceolata is a species of wildflower in the family Montiaceae, known by the common names lanceleaf springbeauty and western springbeauty.

Antennaria rosea is a North American species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae known by the common name rosy pussytoes. Other common names include cat's foot and mountain everlasting. The second part of its scientific name, rosea, is Latin for pink.

Arnica sororia is a North American species of flowering plant known by the common name twin arnica. It is native to Western Canada and the Western United States. It grows in grasslands and in conifer forests, as well as the sagebrush steppe.

Artemisia bigelovii is a North American species of sagebrush known by the common name Bigelow sagebrush or flat sagebrush. It grows in the deserts of the southwestern United States.

Crepis acuminata is a North American species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae known by the common name tapertip hawksbeard. It is native to the western United States where it grows in many types of open habitat.

Hymenoxys hoopesii is a species of flowering plant in the daisy family known by the common names owl's claws, orange sneezeweed, and yerba del lobo. It is native to the western United States, where it grows in habitats of moderate elevation, such as mountain meadows in the Rocky Mountains, Sierra Nevada, southern Cascades, and other ranges. It has been found from Arizona, New Mexico, and central California north as far as Montana and Oregon.

Ribes cereum is a species of currant known by the common names wax currant and squaw currant; the pedicellare variety is known as whisky currant. The species is native to western North America.

Stephanomeria tenuifolia, the narrow-leaved wire-lettuce or narrow leaved stephanomeria, is a perennial plant in the family Asteraceae that grows in the Great Basin of the western United States. It has five ray flowers that give it the appearance of being petals of a single flower of a plant in another plant family.

Rumex sanguineus, commonly known as wood dock, bloody dock or red-veined dock, is a perennial flowering plant species in the family Polygonaceae. Rumex sanguineus is a dicot and can be observed in Europe with at least two varieties.

Rumex fueginus, known as American dock, golden dock, and Tierra del Fuego dock, is a flowering plant in the family Polygonaceae. Rumex fueginus was first formally named by Rodolfo Armando Phillipi. Rumex fueginus is native from Canada in northern North America to Tierra del Fuego at the southern tip of South America. It has previously been considered a subspecies or variety of Rumex maritimus, a Eurasian species.

Rumex occidentalis is a flowering plant species belonging to the family Polygonaceae. Commonly known as western dock, Rumex occidentalis can be found in parts of Western North America.
Rumex spiralis is a flowering plant commonly known as winged dock in the family Polygonaceae. This is a perennial herbaceous plant that is predominantly native to southern Texas. This plant grows between 0–200 m in altitude.


















