
Charadriiformes is a diverse order of small to medium-large birds. It includes about 390 species and has members in all parts of the world. Most charadriiform birds live near water and eat invertebrates or other small animals; however, some are pelagic (seabirds), others frequent deserts, and a few are found in dense forest. Members of this group can also collectively be referred to as shorebirds.

The Ischnocera is a large superfamily of lice. They are mostly parasitic on birds, but including a large family parasitic on mammals. The genus Trichophilopterus is also found on mammals (lemurs), but probably belongs to the "avian Ischnocera" and represents a host switch from birds to mammals. It is a chewing louse, which feeds on the feathers and skin debris of birds. Many of the avian Ischnocera have evolved an elongated body shape. This allows them to conceal themselves between the feather shafts and avoid being dislodged during preening or flight.

Terns are seabirds in the family Laridae, subfamily Sterninae, that have a worldwide distribution and are normally found near the sea, rivers, or wetlands. Terns are treated in eleven genera in a subgroup of the family Laridae, which also includes several genera of gulls and the skimmers (Rynchops). They are slender, lightly built birds with long, forked tails, narrow wings, long bills, and relatively short legs. Most species are pale grey above and white below with a contrasting black cap to the head, but the marsh terns, the black-bellied tern, the Inca tern, and some noddies have dark body plumage for at least part of the year. The sexes are identical in appearance, but young birds are readily distinguishable from adults. Terns have a non-breeding plumage, which usually involves a white forehead and much-reduced black cap.
Coextinction and cothreatened refer to the phenomenon of the loss or decline of a host species resulting in the loss or endangerment of another species that depends on it, potentially leading to cascading effects across trophic levels. The term was originated by the authors Stork and Lyal (1993) and was originally used to explain the extinction of parasitic insects following the loss of their specific hosts. The term is now used to describe the loss of any interacting species, including competition with their counterpart, and specialist herbivores with their food source. Coextinction is especially common when a keystone species goes extinct.
A bird louse is any chewing louse of order Phthiraptera which parasitizes warm-blooded animals, especially birds. Bird lice may feed on feathers, skin, or blood. They have no wings, and their biting mouth parts distinguish them from true lice, which suck blood.

Troctomorpha is one of the three major suborders of Psocodea (barklice, booklice, and parasitic lice), alongside Psocomorpha and Trogiomorpha. There are more than 30 families and 5,800 described species in Troctomorpha. The order includes parasitic lice, which are most closely related to the booklice family Liposcelididae.

The Philopteridae are a family of Ischnocera, chewing lice. They are parasitic on birds.
Saemundssonia laticaudata is an insect species first described in 1869. It is part of the Saemundssonia genus and the Philopteridae family. It is a parasite of the Greater crested tern.

The Ricinidae are a family of a larger group Amblycera of the chewing lice. All species are relatively large bodied avian ectoparasites. They typically exhibit low prevalence and low intensity. They feed on host blood which is atypical in chewing lice. Two or three genera are recognized.
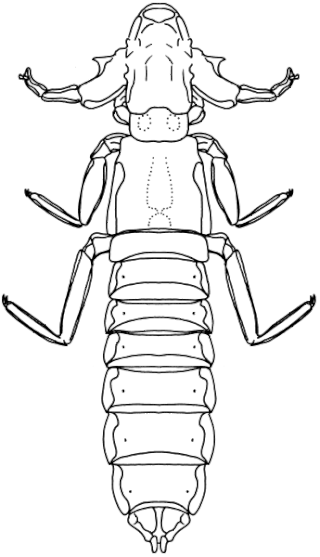
Harrisoniella hopkinsi is a species of phtilopterid louse that lives on and eats the feathers of albatrosses. The species was first described by W. Eichler in 1952.
Campanulotes is a genus of lice in the disputed, probably paraphyletic, family Philopteridae, the chewing lice, or in the family Goniodidae.

Campanulotes elegans is a species of lice in the disputed, probably paraphyletic, family Philopteridae, the chewing lice, or in the family Goniodidae.
Strigiphilus is a genus of chewing louse in the suborder Ischnocera. It was circumscribed in 1910 by Eric Mjöberg.

Rallicola is a genus of chewing louse. It is an ectoparasite of rails and other birds. It was named by Thomas Harvey Johnston and Launcelot Harrison in 1911. There are two subgenera aside from the nominotypical subgenus: Aptericola, whose species are found on kiwi birds, and Huiacola, a monospecific subgenus consisting of Rallicola extinctus, once found on the huia.

Quadraceps is a genus of louse. They are ectoparasites of birds in the order Charadriiformes, and the genus was circumscribed in 1939 by Theresa Clay and Richard Meinertzhagen. Infestation is believed to increase the rate of nest desertion, lowers the success rate of baby birds hatching, reduces the number of birds in the clutch, and cause birds to attract fewer mates. All in all, the survival of the nestlings is lowered drastically.

Harrison's rule is an observation in evolutionary biology by Launcelot Harrison which states that in comparisons across closely related species, host and parasite body sizes tend to covary positively.
Naubates is a genus of lice belonging to the family Philopteridae.
Columbicola is a genus of lice belonging to the family Philopteridae.

Nesiotinus is a genus of lice belonging to the family Philopteridae. The genus was first described in 1903 by Vernon Lyman Kellogg, and the type species is Nesiotinus demersus.

Acidoproctus is a genus of lice, in the family Philopteridae. They are known to be distributed across Asia and Australasia. There are two species in New Zealand.












