
Raleigh is the capital city of the U.S. state of North Carolina and the county seat of Wake County. It is the second-most populous city in North Carolina, after Charlotte. Raleigh is the tenth-most populous city in the Southeast, the 41st-most populous city in the U.S., and the largest city of the Research Triangle metro area. Raleigh is known as the "City of Oaks" for its many oak trees, which line the streets in the heart of the city. The city covers a land area of 148.54 square miles (384.7 km2). The U.S. Census Bureau counted the city's population as 467,665 at the 2020 census. It is one of the fastest-growing cities in the United States. It is ranked as a sufficiency-level world city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network. The city of Raleigh is named after Sir Walter Raleigh, who established the now-lost Roanoke Colony in present-day Dare County.

Gaston County is a county in the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2020 census, the population was 227,943. The county seat is Gastonia. Dallas served as the original county seat from 1846 until 1911.

Burlington is a city in Alamance and Guilford counties in the U.S. state of North Carolina. It is the principal city of the Burlington, NC Metropolitan Statistical Area, which encompasses all of Alamance County, in which most of the city is located, and is a part of the Greensboro–Winston-Salem–High Point, NC Combined Statistical Area. The population was 57,303 at the 2020 census, which makes Burlington the 18th-most populous city in North Carolina.

Garner is a town in Wake County, North Carolina, United States. The population is 31,159 as of the 2020 census. A suburb of Raleigh, the city limits are entirely within Wake County, though portions of unincorporated Wake County, as well as the Cleveland community in northern Johnston County, have Garner mailing addresses. It is part of the Research Triangle region of North Carolina and serves as a bedroom community for the region.

Wake Forest is a town in Wake and Franklin counties in the U.S. state of North Carolina. Located almost entirely in Wake County, it lies just north of the state capital, Raleigh. At the 2020 census, the population was 47,601, up from 30,117 in 2010. It is part of the Raleigh metropolitan area. Wake Forest was the original home of Wake Forest University for 122 years before it moved to Winston-Salem in 1956.

The Research Triangle, or simply The Triangle, are both common nicknames for a metropolitan area in the Piedmont region of the U.S. state of North Carolina. Anchored by the cities of Raleigh and Durham and the town of Chapel Hill, the region is home to three major research universities: North Carolina State University, Duke University, and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, respectively. The "Triangle" name originated in the 1950s with the creation of Research Triangle Park located between the three anchor cities, which is the largest research park in the United States and home to numerous high tech companies.

William B. Umstead State Park is a North Carolina state park in Wake County, North Carolina in the United States. It covers 5,599 acres (22.66 km2) nestled between the expanding cities of Raleigh, Cary, and Durham, North Carolina. It offers hiking, bridle, and bike trails, boat rentals, camping, picnic areas, and educational programs.
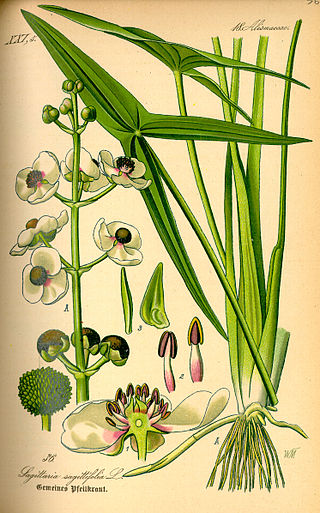
Sagittaria is a genus of about 30 species of aquatic plants whose members go by a variety of common names, including arrowhead, duck potato, swamp potato, tule potato, and wapato. Most are native to South, Central, and North America, but there are also some from Europe, Africa, and Asia.

Sagittaria latifolia is a plant found in shallow wetlands and is sometimes known as broadleaf arrowhead, duck-potato, Indian potato, or wapato. This plant produces edible tubers that have traditionally been extensively used by Native Americans.

Interstate 40 (I-40) is a part of the Interstate Highway System that travels 2,556.61 miles (4,114.46 km) from Barstow, California, to Wilmington, North Carolina. In North Carolina, I-40 travels 420.21 miles (676.26 km) across the entirety of the state from the Tennessee state line along the Pigeon River Gorge to U.S. Highway 117 (US 117) and North Carolina Highway 132 (NC 132) in Wilmington. I-40 is the longest Interstate Highway in North Carolina and is the only Interstate to completely span the state from west to east.

The State Library of North Carolina is an institution which serves North Carolina libraries, state government employees, genealogists, and the citizens of North Carolina. The library is the main depository for North Carolina state publications and serves the needs of North Carolina government agencies and state government employees by providing access to information resources that are vital to public decision-making and economic development.

U.S. Route 70 (US 70) is a part of the United States Numbered Highway System that runs from Globe, Arizona, to the Crystal Coast of the US state of North Carolina. In North Carolina, it is a major 488-mile-long (785 km) east–west highway that runs from the Tennessee border to the Atlantic Ocean. From the Tennessee state line near Paint Rock to Asheville it follows the historic Dixie Highway, running concurrently with US 25. The highway connects several major cities including Asheville, High Point, Greensboro, Durham, Raleigh, Goldsboro, and New Bern. From Beaufort on east, US 70 shares part of the Outer Banks Scenic Byway, a National Scenic Byway, before ending in the community of Atlantic, located along Core Sound.

Quercus ilicifolia, commonly known as bear oak or scrub oak, is a small shrubby oak native to the Eastern United States and, less commonly, in southeastern Canada. Its range in the United States extends from Maine to North Carolina, with reports of a few populations north of the international frontier in Ontario. The name ilicifolia means "holly-leaved."
In 2019, North Carolina's total gross state product was around $591 billion.

Sagittaria cuneata is a North American species of flowering plant in the water plantain family known by the common name arumleaf arrowhead or duck potato. Like some other Sagittaria species, it may be called wapato.

North Carolina Highway 79 (NC 79) is an 8.7-mile-long (14.0 km) primary state highway in the U.S. state of North Carolina. NC 79 runs from the South Carolina border as a continuation of South Carolina Highway 79 at Gibson to U.S. Route 15 (US 15), US 401, US 501, and US 74 Business in Laurinburg. While signed north–south, NC 79 physically travels in an east–west direction between its termini. NC 79 is primarily a two-lane road running through rural Scotland County and residential areas west of Laurinburg. Combined with SC 79, the highways form a coherent route between SC 9 northwest of Bennettsville, South Carolina and Laurinburg.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Raleigh, North Carolina, USA.

Sagittaria teres, the quill-leaved arrowhead or slender arrowhead, is an aquatic plant species in the genus Sagittaria. It is a perennial herb up to 80 centimetres tall. The leaves can grow both under and above the water. The flowers are white, up to 1.5 cm in diameter, borne in one or more whorls on a stalk rising above the leaves.

Sagittaria subulata, the awl-leaf arrowhead, narrow-leaved arrowhead or dwarf sagittaria, is an aquatic plant species.
Gaylussacia orocola, is a plant species native only to the southern Appalachians of western North Carolina. This plant grows only in Mountain Bogs, severely limiting available habitat. This plant has many common names which may be shared with other species. It is known to The North Carolina Natural Heritage Program as the Appalachian dwarf huckleberry and The North Carolina Botanical Garden knows it as the Blue Ridge bog huckleberry. It may also be referred to as the Gopherberry, Blue Ridge huckleberry, or Dwarf Huckleberry.


















