
The Ludington Pumped Storage Plant is a hydroelectric plant and reservoir in Ludington, Michigan. It was built between 1969 and 1973 at a cost of $315 million and is owned jointly by Consumers Energy and DTE Energy and operated by Consumers Energy. At the time of its construction, it was the largest pumped storage hydroelectric facility in the world.

Fawley is a village and civil parish in Hampshire, England. It is situated in the New Forest on the western shore of the Solent, approximately 7 miles south of Southampton. Fawley is also the site of Fawley Refinery, operated by ExxonMobil, which is the largest facility of its kind in the United Kingdom. The decommissioned Fawley Power Station is also located less than a mile to the south east of the village.

Daggett is an unincorporated community located in San Bernardino County, California in the United States. The town is located on Interstate 40 ten miles (16 km) east of Barstow. The town has a population of about 200. The ZIP code is 92327 and the community is inside area code 760.

ExxonMobil's Baton Rouge Refinery in Baton Rouge, Louisiana is the fourth-largest oil refinery in the United States and twelfth-largest in the world, with an input capacity of 502,500 barrels (79,890 m3) per day as of January 1, 2016. The refinery is the site of the first commercial fluid catalytic cracking plant that began processing at the refinery on May 25, 1942.

The SOLAR Project consists of the Solar One, Solar Two and Solar Tres solar thermal power plants based in the Mojave Desert, United States and Andalucía, Spain. The US Department of Energy (DOE) and a consortium of US utilities built this country's first two large-scale, demonstration solar power towers in the desert near Barstow, California.

The Altamont Pass wind farm is located in the Altamont Pass of the Diablo Range in Northern California. It is one of the earliest wind farms in the United States. The first wind turbines were placed on the Altamont in the early 1980s by Fayette Manufacturing Corporation on land owned by cattle rancher Joe Jess. The wind farm is composed of 4930 relatively small wind turbines of various types, making it at one time the largest wind farm in the world in terms of capacity. Altamont Pass is still one of the largest concentration of wind turbines in the world, with a capacity of 576 megawatts (MW), producing about 125 MW on average and 1.1 terawatt-hours (TWh) yearly. They were installed after the 1970s energy crisis in response to favorable tax policies for investors.

The Tehachapi Pass wind farm is one of the first large-scale wind farms installed in the U.S., with around 700 MW capacity.

Wind power in the United States is a branch of the energy industry that has expanded quickly over the latest several years. For the twelve months through November 2017, 254.2 terawatt-hours were generated by wind power, or 6.33% of all generated electrical energy.

Wind power in Texas consists of many wind farms with a total installed nameplate capacity of 22,637 MW from over 40 different projects. Texas produces the most wind power of any U.S. state. According to ERCOT, wind power accounted for at least 15.7% of the electricity generated in Texas during 2017, as wind was 17.4% of electricity generated in ERCOT, which manages 90% of Texas's power.
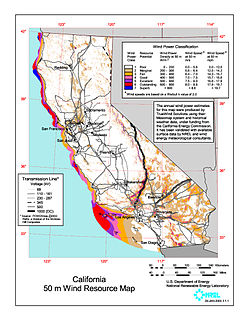
Wind power has a long history in the state of California, with the initiative and early development occurring during Governor Jerry Brown's first two terms in the late 1970s and early 1980s. California's wind power capacity has grown by nearly 350% since 2001, when it was less than 1,700 MW. In 2016, wind energy now supplies about 6.9% of California's total electricity needs, or enough to power more than 1.3 million households. Most of California's wind generation is found in the Tehachapi area of Kern County, California, with some big projects in Solano, Contra Costa and Riverside counties as well. California is among the states with the largest amount of installed wind power capacity. In recent years, California has lagged behind other states when it comes to the installation of wind power. It was ranked 4th overall for wind power electrical generation at the end of 2016 behind Texas, Iowa, and Oklahoma. As of December 31, 2016, California had 5,662 megawatts (MW) of wind powered electricity generating capacity.

"Fossil fuels lobby" is the umbrella term used to name the paid representatives of large fossil fuel and electric utilities corporations who attempt to influence governmental policy. So-called Big Oil companies such as ExxonMobil, Royal Dutch Shell, BP, Total S.A., Chevron Corporation, and ConocoPhillips are amongst the largest corporations associated with the fossil fuels lobby. General Electric, Southern Company, First Energy, and the Edison Electric Institute are also among the most influential electric utilities corporations. However, electric companies and big oil and gas companies are consistently not among the ten highest-spending lobbyists – the United States Chamber of Commerce is currently #1. By sector, "Energy/Nat Resource" comes fifth, behind "Misc Business", "Finance/Insur/RealEst", Health and "Communic/Electronics".

Fawley Refinery is an oil refinery located at Fawley, Hampshire, England. The refinery is owned by Esso, which acquired the site in 1925. Situated on Southampton Water, it was rebuilt and extended in 1951 and is now the largest oil refinery in the United Kingdom, and one of the most complex refineries in Europe. With a capacity of 270,000 barrels a day, Fawley provides 20 percent of UK refinery capacity. An estimated 2,300 people are employed at the site.

BrightSource Energy, Inc. is an Oakland, California based, corporation that designs, builds, finances, and operates utility-scale solar power plants.

The Shepherds Flat Wind Farm is an 845 megawatt (MW) wind farm in the U.S. state of Oregon. The facility is located in Eastern Oregon in both Morrow and Gilliam counties, near Arlington. Approved in 2008 by state regulators, groundbreaking came in 2009. The wind farm was built by Caithness Energy using General Electric (GE) 2.5 MW wind turbines, and it supplies electricity to Southern California Edison. The wind farm is estimated to have an economic impact of $16 million annually for Oregon. It is one of the largest land-based wind farms in the world. It officially opened in September 2012.
Exxon Mobil Corporation, doing business as ExxonMobil, is an American multinational oil and gas corporation headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is the largest direct descendant of John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil Company, and was formed on November 30, 1999 by the merger of Exxon and Mobil. ExxonMobil's primary brands are Exxon, Mobil, Esso, and ExxonMobil Chemical.

Alta Wind Energy Center (AWEC), also known as Mojave Wind Farm, is the third largest onshore wind energy project in the world. The Alta Wind Energy Center is a wind farm located in Tehachapi Pass of the Tehachapi Mountains, in Kern County, California. As of 2013, it is the largest wind farm in the United States, with a combined installed capacity of 1,547 MW (2,075,000 hp). The project, being developed near Tehachapi Pass Wind Farm— site of the first large-scale wind farms installed in the U.S. in the 1970s and 1980s—is "a powerful illustration of the growing size and scope of modern wind projects".
The Benicia Refinery is an oil refinery located near the San Francisco Bay Area city of Benicia, California. The refinery is owned by Valero Energy Corporation.
California is the most populous state in the nation, but its total energy demand is second to the state of Texas. The state has one of the lowest per capita energy consumption rates in the country due in part to the relatively mild weather comparative to the rest of the nation.





















