Muppandal is a small village on the southern tip of India in Kanyakumari District, in the state of Tamil Nadu. It is located in a hilly region where wind from the Arabian Sea gusts through mountain passes.

The Montezuma Hills comprise a small range of low-elevation hills at the northern banks of the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta and southwestern Sacramento Valley in California in the United States.

The Tehachapi Pass wind farm is one of the first large-scale wind farms installed in the U.S., with around 700 MW capacity.

The San Gorgonio Pass wind farm is a wind farm located on the eastern slope of the San Gorgonio Pass in Riverside County, just east of White Water, California, United States. Developed beginning in the 1980s, it is one of three major wind farms in California, along with those at Altamont and the Tehachapi Passes. The gateway into the Coachella Valley, the San Gorgonio Pass is one of the windiest places in Southern California.

Wind power in the United States is a branch of the energy industry that has expanded quickly over the latest several years. For the twelve months through November 2017, 254.2 terawatt-hours were generated by wind power, or 6.33% of all generated electrical energy.

Blood Hill is a wind farm near Hemsby in Norfolk, England. It is the smallest windfarm owned by E.ON; taking up 3 hectares. It has a nameplate capacity of 2.25MW which is enough to power 1000 homes at peak. There are 10 Vestas V27-225 kW turbines which are 30 metres tall and stand on top of Blood Hill. They are visible from the villages of Hemsby and Winterton-on-Sea. Blood Hill began operating in December 1992 and was one of the first windfarms in the United Kingdom.
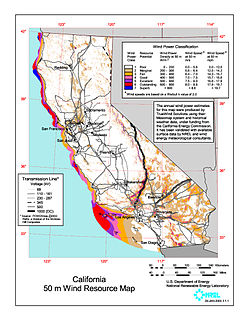
Wind power has a long history in the state of California, with the initiative and early development occurring during Governor Jerry Brown's first two terms in the late 1970s and early 1980s. California's wind power capacity has grown by nearly 350% since 2001, when it was less than 1,700 MW. In 2016, wind energy now supplies about 6.9% of California's total electricity needs, or enough to power more than 1.3 million households. Most of California's wind generation is found in the Tehachapi area of Kern County, California, with some big projects in Solano, Contra Costa and Riverside counties as well. California is among the states with the largest amount of installed wind power capacity. In recent years, California has lagged behind other states when it comes to the installation of wind power. It was ranked 4th overall for wind power electrical generation at the end of 2016 behind Texas, Iowa, and Oklahoma. As of December 31, 2016, California had 5,662 megawatts (MW) of wind powered electricity generating capacity.

Gwynt y Môr is a 576-megawatt (MW) offshore wind farm located off the coast of North Wales and is the fourth largest operating offshore windfarm in the world. The farm has 160 wind turbines of 150 metres (490 ft) tip height above mean sea level.

In 2017 France reached a total of 13,759 MW installed wind power capacity placing France at that time as the world's eighth largest wind power nation by installed capacity, behind the United Kingdom and Canada and ahead of Italy and Brazil. According to the IEA the yearly wind production was 20.2 TWh in 2015, representing almost 23% of the 88.4 TWh from renewable sources in France during that year. Furthermore wind provided for 4.3% of the country’s electricity demand out of the 18.7% provided by renewables in 2015.

The Shiloh wind power plant is a wind farm located in the Montezuma Hills of Solano County, California, USA, close to Bird's Landing and Collinsville, 40 miles (64 km) northeast of San Francisco. It has a nameplate capacity of 505 megawatts (MW) of power and was built in four stages between 2005 and 2012.

The environmental impact of wind power when compared to the environmental impacts of fossil fuels, is relatively minor. Compared with other low carbon power sources, wind turbines have some of the lowest global warming potential per unit of electrical energy generated. According to the IPCC, in assessments of the life-cycle global warming potential of energy sources, wind turbines have a median value of between 15 and 11 (gCO2eq/kWh) depending on whether off- or onshore turbines are being assessed.
John Ellis Eckland is a former CIA Alternative Energy Analyst, and pioneer of early renewable energy efforts in the 1970s and 1980s. He was the founder and president of the now defunct Fayette Manufacturing Corporation, a Fortune 500 company. His is the 1979 recipient of the Arthur S. Flemming Award for Excellence in Government Service and the first member of the CIA to receive this recognition.

Wind power in Belgium depends partially on regional governments and partially on the Belgian federal government. Wind energy producers in both the Flemish and Walloon regions get green certificates but not with the same conditions.
Wind power in the Netherlands reached an installed capacity of 4,341 MW by year end 2017, 1,118 MW of which were based offshore. The 2,294 turbines sited in the Netherlands by the end of 2017 provided the country with 9% of its electricity demand during the year, a figure that is growing but somewhat below the average of 11.6% that wind power provides across the whole of the EU’s electricity consumption. 2015 was a record year for new installations in the Netherlands with 586 MW added of which 180 MW were offshore.

Raptor conservation concerns are threats affecting the population viability of birds of prey. Because of their hunting lifestyle, raptors face distinct conservation challenges. As top predators, they are important for healthy ecosystem functioning, and by protecting them many other species are safeguarded. Their extensive habitat requirements make regional conservation strategies necessary for protecting birds of prey.
The Criterion Wind Project is a wind farm located on Backbone Mountain east of Oakland, Maryland, United States. The project has a rated capacity of 70 MW and uses 28 Liberty Wind Turbines manufactured by Clipper Windpower. Each of the wind turbines is about 415 feet tall. The Criterion Wind Project is owned by Criterion Power Partners, LLC, which is a subisiary of Exelon, and interconnected with the transmission system of the Potomac Edison Company. Electricity and renewable energy credits from the project are sold to the Old Dominion Electric Cooperative under a 20-year supply contract.

Wind power in New Jersey is in the early stages of development. There are various projects underway to create windfarms along coastal areas in the state on land, on piers, and on the continental shelf of the Atlantic Ocean off the southern Jersey Shore. Legislation has been enacted to support the industry through economic incentives and to permit wind turbines on existing piers. Several proposals have been made to expand the use of wind-generated power which may lead to the nation's first offshore wind power pilot project. In October 2010, North American Offshore Wind Conference was held in Atlantic City, site of the US's first on-shore coastal facility. New Jersey is part of the Atlantic Offshore Wind Energy Consortium. As of 2013, 9MW were produced by wind power.

The Soma Wind Farm is an onshore wind power plant located in Soma district of Manisa Province in northwestern Aegean Region of Turkey. Built in two phases and consisting of 119 wind turbines with an installed output power of 140.4 MW in total, it is one of Turkey's largest wind farms.

The Bahçe Wind Farm, aka Gökçedağ Wind Farm, is an onshore wind power plant located in Bahçe district of Osmaniye Province in eastern Mediterranean Region of Turkey. Consisting of 54 wind turbines with an installed output power of 135 MW in total, the wind farm was the country's largest one as it was commissioned in 2009.
Pattern Energy Group Inc is a Wind and Solar Power Generator headquartered in San Francisco, California with projects in Canada, Chile, Japan and United States. Mike M. Garland is the President, and CEO. It is the largest wind power generator in Canada and is building the largest wind farm in North America.


























