
The Galápagos Islands are an archipelago of volcanic islands in the Eastern Pacific, located around the Equator 900 km (560 mi) west of the mainland of South America. They form the Galápagos Province of the Republic of Ecuador, with a population of slightly over 33,000 (2020). The province is divided into the cantons of San Cristóbal, Santa Cruz, and Isabela, the three most populated islands in the chain. The Galápagos are famous for their large number of endemic species, which were studied by Charles Darwin in the 1830s and inspired his theory of evolution by means of natural selection. All of these islands are protected as part of Ecuador's Galápagos National Park and Marine Reserve.

The Galapagos crake, also called the Galapagos rail and Darwin's rail, is a vulnerable species of rail in subfamily Rallinae of family Rallidae, the rails, gallinules, and coots. It is endemic to the Galápagos Islands. It resembles its sister species, the black rail of the Americas, from which it diverged 1.2 million years ago.

The Galápagos Islands xeric scrub, also known as the Galápagos Islands scrubland mosaic, is a terrestrial deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion that covers the Galápagos Islands. The Galápagos Islands are volcanic in origin, and remote from continents and other islands. The ecoregion is well known for its unique endemic species, including giant tortoises, birds, and marine iguanas, which evolved in isolation to adapt to islands' environments.

The marine iguana, also known as the sea iguana, saltwater iguana, or Galápagos marine iguana, is a species of iguana found only on the Galápagos Islands (Ecuador). Unique among modern lizards, it is a marine reptile that has the ability to forage in the sea for algae, which makes up almost all of its diet. Marine iguanas are the only extant lizard that spends time in a marine environment. Large males are able to dive to find this food source, while females and smaller males feed during low tide in the intertidal zone. They mainly live in colonies on rocky shores where they bask after visiting the relatively cold water or intertidal zone, but can also be seen in marshes, mangrove swamps and beaches. Large males defend territories for a short period, but smaller males have other breeding strategies. After mating, the female digs a nest hole in the soil where she lays her eggs, leaving them to hatch on their own a few months later.

Jasminocereus is a genus of cacti with only one species, Jasminocereus thouarsii, endemic to the Galápagos Islands, territorially a part of Ecuador. In English it is often called the candelabra cactus. At maturity it has a branched, treelike habit, and may be up to 7 m (23 ft) tall. The stems are made up of individual sections with constrictions between them. Its creamy white to greenish flowers open at night and are followed by greenish to reddish fruits.

Scalesia is a genus in the family Asteraceae endemic to the Galapagos Islands. It contains fifteen species that grow as shrubs or trees. This is unusual, because tree species are uncommon in Asteraceae. The genus Scalesia resulted from a blunder by Arnott who named it in honour of "W. Scales Esq., Cawdor Castle, Elginshire" but discovered after publication that the name should have read 'Stables', after Scottish botanist, William Alexander Stables (1810–1890).
Scalesia microcephala is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is endemic to the Galápagos Islands.

The medium tree finch is a critically endangered species of bird in the Darwin's finch group of the tanager family Thraupidae. It is endemic to the Galápagos Islands where it is only found on Floreana Island. Its name is derived from the fact that the bird's beak is intermediate in size between that of the small tree finch and the large tree finch. Because it has a very small range on a single island, and because of the introduction of a parasitic fly which kills the nestlings, the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated the medium tree finch as "critically endangered".

The common cactus finch or small cactus finch is a species of bird in the Darwin's finch group of the tanager family Thraupidae. It is endemic to the Galapagos Islands, where it is found on most islands, with the notable exception of Fernandina, Española, Genovesa, Darwin and Wolf. Most of these islands are inhabited by its close relative, the Española cactus finch.

The Galápagos mockingbird is a species of bird in the family Mimidae. It is endemic to the Galápagos Islands, Ecuador.

Sesuvium edmonstonei, commonly known as Galapagos carpet weed, is a species of plant in the family Aizoaceae. It is endemic to the Galápagos Islands (Ecuador).
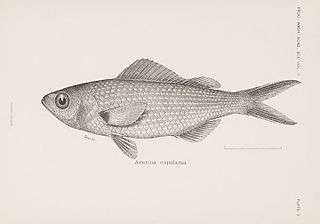
The Galápagos damsel, also known as the blackspot chromis, is a possibly extinct fish species from the family Pomacentridae. It is endemic to the waters near the Galápagos Islands and Cocos Island.

Utetheisa connerorum is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is endemic to the Galapagos archipelago, where it is the most widespread of all Utetheisa species. It has been found on Baltra, Fernandina, Floreana, Genovesa, Isabela, Marchena, Pinta, San Cristóbal, Santa Cruz, Santa Fé, and Santiago.

Hellinsia nephogenes is a moth of the family Pterophoridae. It is found on the Galapagos Islands.

Darwin's flycatcher or little vermilion flycatcher is a species of flycatcher, closely related to the vermilion flycatcher. It is endemic to the Galápagos Islands. The same threats that led to the San Cristóbal flycatcher's extinction, including invasive species such as rats, threaten the Darwin's flycatcher today. Populations exist on the islands of Santa Cruz, Fernandina, Rabida and Isabela. It lives in humid forests and shrubland and has an average lifespan of five years.

Scalesia pedunculata is a flowering plant species in the family Asteraceae, growing to a slender tree, and found in dense stands on the humid windward coasts of the islands of Santa Cruz, San Cristobal, Santiago and Floreana in the Galapagos Islands. The Galapagos archipelago lies in the southeast trade wind zone, so that climate and weather are dominated by the moisture-bearing trade winds and the topography of the islands. In general, the windward sides of the islands have a much higher precipitation than the leeward sides. Scalesia pedunculata is regarded as vulnerable because of human encroachment, invasive introduced plant species such as Cedrela odorata and Psidium guajava, and grazing by introduced goats. Fires and cutting for fuel are also contributory problems, though the tree's wood is soft, with a large, pithy centre.

Chelonoidis niger donfaustoi, known as the eastern Santa Cruz tortoise, is a subspecies of Galápagos tortoise living on Santa Cruz Island, within the Galápagos. Until 2015, C. n. donfaustoi was considered conspecific with the western Santa Cruz tortoise, C. n. porteri.
Cerro Pajas is an inactive volcano located in the south of Floreana Island in the Galápagos Islands, Ecuador. It is the highest peak on Floreana, with a maximum elevation of 640 meters above sea level.

The western Santa Cruz tortoise is a subspecies of Galápagos tortoise endemic to Santa Cruz Island in the Galápagos. They are found only on the southwestern slopes of the island, with an estimated range of 141 sq. kilometers. There are approximately 3400 individuals in the wild, and have seen rising numbers in population, despite being critically endangered. MtDNA evidence shows that there are actually three genetically distinct populations on Santa Cruz Island. They are characterised by a black, oval carapace that is domed, higher in the centre than in the front, and broad anteriorly. Their life expectancy is 175 years.

















