
The Dioscoreales are an order of monocotyledonous flowering plants, organized under modern classification systems, such as the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group or the Angiosperm Phylogeny Web. Among monocot plants, Dioscoreales are grouped with the lilioid monocots, wherein they are a sister group to the Pandanales. In total, the order Dioscoreales comprises three families, 22 genera and about 850 species.

Liliales is an order of monocotyledonous flowering plants in the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group and Angiosperm Phylogeny Web system, within the lilioid monocots. This order of necessity includes the family Liliaceae. The APG III system (2009) places this order in the monocot clade. In APG III, the family Luzuriagaceae is combined with the family Alstroemeriaceae and the family Petermanniaceae is recognized. Both the order Lililiales and the family Liliaceae have had a widely disputed history, with the circumscription varying greatly from one taxonomist to another. Previous members of this order, which at one stage included most monocots with conspicuous tepals and lacking starch in the endosperm are now distributed over three orders, Liliales, Dioscoreales and Asparagales, using predominantly molecular phylogenetics. The newly delimited Liliales is monophyletic, with ten families. Well known plants from the order include Lilium (lily), tulip, the North American wildflower Trillium, and greenbrier.

The Malpighiales comprise one of the largest orders of flowering plants, containing about 36 families and more than 16,000 species, about 7.8% of the eudicots. The order is very diverse, containing plants as different as the willow, violet, poinsettia, manchineel, rafflesia and coca plant, and are hard to recognize except with molecular phylogenetic evidence. It is not part of any of the classification systems based only on plant morphology. Molecular clock calculations estimate the origin of stem group Malpighiales at around 100 million years ago (Mya) and the origin of crown group Malpighiales at about 90 Mya.

Viola is a genus of flowering plants in the violet family Violaceae. It is the largest genus in the family, containing over 680 species. Most species are found in the temperate Northern Hemisphere; however, some are also found in widely divergent areas such as Hawaii, Australasia, and the Andes.

The Salicaceae are the willow family of flowering plants. The traditional family included the willows, poplars. Genetic studies summarized by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG) have greatly expanded the circumscription of the family to contain 56 genera and about 1220 species, including the tropical Scyphostegiaceae and many of the former Flacourtiaceae.

Violaceae is a family of flowering plants established in 1802, consisting of about 1000 species in about 25 genera. It takes its name from the genus Viola, the violets and pansies.

Violales is a botanical name of an order of flowering plants and takes its name from the included family Violaceae; it was proposed by Lindley (1853). The name has been used in several systems, although some systems used the name Parietales for similar groupings. In the 1981 version of the influential Cronquist system, order Violales was placed in subclass Dilleniidae with a circumscription consisting of the families listed below. Some classifications such as that of Dahlgren placed the Violales in the superorder Violiflorae.

Burmanniaceae is a family of flowering plants, consisting of 99 species of herbaceous plants in eight genera.

Maesobotrya is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Phyllanthaceae. It was first described as a genus in 1879 and is native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is dioecious, with male and female flowers on separate plants.

Rinorea is a genus of flowering plants in family Violaceae. It includes 212 species native to the subtropics and tropics.

Hybanthus (green-violet) is a genus of flowering plants in the family Violaceae. This genus name is Greek for "humpback flower", referring to the drooping pedicels of plants that are part of this genus. The genus is grossly polyphyletic and may contain up to nine different genera, of which Pombalia Vand., Cubelium Raf. and Pigea DC. have been previously recognised.

The Amaryllidaceae are a family of herbaceous, mainly perennial and bulbous flowering plants in the monocot order Asparagales. The family takes its name from the genus Amaryllis and is commonly known as the amaryllis family. The leaves are usually linear, and the flowers are usually bisexual and symmetrical, arranged in umbels on the stem. The petals and sepals are undifferentiated as tepals, which may be fused at the base into a floral tube. Some also display a corona. Allyl sulfide compounds produce the characteristic odour of the onion subfamily (Allioideae).

Amaryllidoideae is a subfamily of monocot flowering plants in the family Amaryllidaceae, order Asparagales. The most recent APG classification, APG III, takes a broad view of the Amaryllidaceae, which then has three subfamilies, one of which is Amaryllidoideae, and the others are Allioideae and Agapanthoideae. The subfamily consists of about seventy genera, with over eight hundred species, and a worldwide distribution.
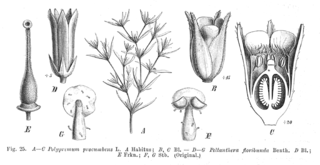
Peltanthera is a genus of flowering plants containing a single species, Peltanthera floribunda. The genus was originally placed in family Loganiaceae and has since been variously placed in Buddlejaceae, Scrophulariaceae, Gesneriaceae, or in its own family Peltantheraceae. In 2016, it was considered by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group to be unplaced in any family, but within the order Lamiales, while Christenhusz et al. in 2017 placed it in family Gesneriaceae as subfamily Peltantheroideae. The placement in Gesneriaceae was accepted by Plants of the World Online as of March 2024.

Noisettia is a genus of flowering plants in the violet family Violaceae, with a single known species.

Calyptrion is a genus of flowering plants in the violet family Violaceae, with four known species.

Agatea is a genus of flowering plants in the violet family Violaceae, with seven accepted species, found in New Guinea and New Caledonia.

Anchietea is a genus of flowering plants in the violet family Violaceae, with six accepted species, found in tropical South America.
Hybanthopsis is a genus of flowering plants in the violet family Violaceae, with a single accepted species, found in north-east Brazil.

















