Various aspects of specialized lexicography
The study of specialized lexicography deals with several important aspects within the general field of lexicography. The problems involved in designing and making bilingual dictionaries within a culture-dependent subject field involves aspects such as the user's linguistic competence in both languages as well as the user's extra-linguistic (factual) competence in both cultures.
Lexicography is divided into two separate but equally important groups:
As described in Nielsen 1994, the coverage of dictionaries may be divided into three lexicographically relevant types. First, the multi-field dictionary, which covers several subject-fields; secondly, the single-field dictionary, which covers one subject-field; and thirdly, the sub-field dictionary, which covers one sub-field within a general subject-field. This distinction is lexicographically important, because the best treatment of a subject-field is given in single-field and sub-field dictionaries, as these are the best reference tools for containing and presenting the relevant data.
A multi-field dictionary is a specialized dictionary that has been designed and compiled to cover the terms within two or more subject fields. Multi-field dictionaries should be contrasted with single-field dictionaries and sub-field dictionaries.
A single-field dictionary is a specialized dictionary that has been designed and compiled to cover the terms of one particular subject field. Single-field dictionaries should be contrasted with multi-field dictionaries and sub-field dictionaries.
A sub-field dictionary is a specialized dictionary that has been designed and compiled to cover the terms of one sub-fields of a particular subject field. It is therefore a sub-division of the class of dictionary called a single-field dictionary. Sub-field dictionaries should be contrasted with multi-field dictionaries and single-field dictionaries.
The function for which the dictionary has been designed is also relevant. The dictionary may have been designed to help the user with two general types of function: communication-oriented and knowledge-oriented. The former deals with the translation of texts, understanding of texts, production of texts and editing/revision of texts, and the latter deals with the acquisition of knowledge (data and information) in situations that are independent of communication.
Specialized lexicography is therefore the discipline where scholars attempt to develop principles and techniques that can help both the compilers of dictionaries and the users. Nielsen 2008 argues that, in particular, the presentation of data in the dictionary should be structured in such a way that the lexicographic information costs are kept at a minimum.
Lexicographic information cost is a concept within the field of lexicography. The term refers to the difficulties and inconveniences that the user of a dictionary believes or feels are associated with consulting a particular dictionary or dictionary article. For example, the extensive use of abbreviations in articles in order to save space may annoy the user, because it is often difficult to read such condensed texts and understand the abbreviations, thereby increasing the lexicographic information costs.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
A Monolingual learner's dictionary is a type of dictionary designed to meet the reference needs of people learning a foreign language. MLDs are based on the premise that language-learners should progress from a bilingual dictionary to a monolingual one as they become more proficient in their target language, but that general-purpose dictionaries are inappropriate for their needs. Dictionaries for learners include information on grammar, usage, common errors, collocation, and pragmatics, which is largely missing from standard dictionaries, because native speakers tend to know these aspects of language intuitively. And while the definitions in standard dictionaries are often written in difficult language, those in a monolingual learner’s dictionary aim to be simple and accessible.
Terminology is the study of terms and their use. Terms are words and compound words or multi-word expressions that in specific contexts are given specific meanings—these may deviate from the meanings the same words have in other contexts and in everyday language. Terminology is a discipline that studies, among other things, the development of such terms and their interrelationships within a specialized domain. Terminology differs from lexicography, as it involves the study of concepts, conceptual systems and their labels (terms), whereas lexicography studies words and their meanings.
Sandro Nielsen is a Danish metalexicographer, Associate Professor at Centre for Lexicography at the Aarhus School of Business, Denmark, from where he received his PhD in 1992. Nielsen has contributed to lexicography as a theoretical and practical lexicographer with particular reference to bilingual specialised dictionaries. He is the author and co-author of more than one hundred publications on lexicography, theoretical papers, printed and electronic (online) dictionaries.
Legal lexicography is the complex of activities concerned with the development of theories and principles for the design, compilation, use, and evaluation of dictionaries within the field of law, see e.g. Nielsen 1994.
A language-for-specific-purposes dictionary is a reference work which defines the specialised vocabulary used by experts within a particular field, for example, architecture. The discipline that deals with these dictionaries is specialised lexicography. Medical dictionaries are well-known examples of the type.

A law dictionary is a dictionary that is designed and compiled to give information about terms used in the field of law.
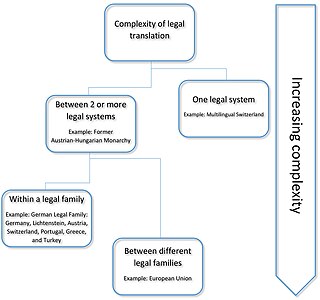
Legal translation is the translation of texts within the field of law. As law is a culture-dependent subject field, legal translation is not necessarily linguistically transparent. Intransparency in translation can be avoided somewhat by use of Latin legal terminology, where possible.
The term cross-reference can refer to either:
Centre for Lexicography is a research centre affiliated with the Aarhus School of Business, University of Aarhus Denmark, and was established in 1996. The Centre's aim is to carry out lexicographic research into needs-adapted information and data access, i.e. research work into dictionary theory in general and it has built a solid, international reputation in that field.

A bilingual dictionary or translation dictionary is a specialized dictionary used to translate words or phrases from one language to another. Bilingual dictionaries can be unidirectional, meaning that they list the meanings of words of one language in another, or can be bidirectional, allowing translation to and from both languages. Bidirectional bilingual dictionaries usually consist of two sections, each listing words and phrases of one language alphabetically along with their translation. In addition to the translation, a bilingual dictionary usually indicates the part of speech, gender, verb type, declension model and other grammatical clues to help a non-native speaker use the word. Other features sometimes present in bilingual dictionaries are lists of phrases, usage and style guides, verb tables, maps and grammar references. In contrast to the bilingual dictionary, a monolingual dictionary defines words and phrases instead of translating them.
Beryl T. (Sue) Atkins is a lexicographer, specialising in computational lexicography, who pioneered the creation of bilingual dictionaries from corpus data.
Contrastive linguistics is a practice-oriented linguistic approach that seeks to describe the differences and similarities between a pair of languages.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to second-language acquisition:



