
Flour is a powder made by grinding raw grains, roots, beans, nuts, or seeds. Flours are used to make many different foods. Cereal flour, particularly wheat flour, is the main ingredient of bread, which is a staple food for many cultures. Corn flour has been important in Mesoamerican cuisine since ancient times and remains a staple in the Americas. Rye flour is a constituent of bread in both Central Europe and Northern Europe.

Tapioca is a starch extracted from the tubers of the cassava plant, a species native to the North and Northeast regions of Brazil, but which has now spread throughout South America. It is a perennial shrub adapted to the hot conditions of tropical lowlands. Cassava copes better with poor soils than many other food plants.

Curd is obtained by coagulating milk in a sequential process called curdling. It can be a final dairy product or the first stage in cheesemaking. The coagulation can be caused by adding rennet, a culture, or any edible acidic substance such as lemon juice or vinegar, and then allowing it to coagulate. The increased acidity causes the milk proteins (casein) to tangle into solid masses, or curds. Milk that has been left to sour will also naturally produce curds, and sour milk cheeses are produced this way.
Ultrafiltration (UF) is a variety of membrane filtration in which forces such as pressure or concentration gradients lead to a separation through a semipermeable membrane. Suspended solids and solutes of high molecular weight are retained in the so-called retentate, while water and low molecular weight solutes pass through the membrane in the permeate (filtrate). This separation process is used in industry and research for purifying and concentrating macromolecular (103–106 Da) solutions, especially protein solutions.

Hydrocyclones are a type of cyclonic separators that separate product phases mainly on basis of differences in gravity with aqueous solutions as the primary feed fluid.

Industrial wastewater treatment describes the processes used for treating wastewater that is produced by industries as an undesirable by-product. After treatment, the treated industrial wastewater may be reused or released to a sanitary sewer or to a surface water in the environment. Some industrial facilities generate wastewater that can be treated in sewage treatment plants. Most industrial processes, such as petroleum refineries, chemical and petrochemical plants have their own specialized facilities to treat their wastewaters so that the pollutant concentrations in the treated wastewater comply with the regulations regarding disposal of wastewaters into sewers or into rivers, lakes or oceans. This applies to industries that generate wastewater with high concentrations of organic matter, toxic pollutants or nutrients such as ammonia. Some industries install a pre-treatment system to remove some pollutants, and then discharge the partially treated wastewater to the municipal sewer system.

Instant mashed potatoes are potatoes that have been through an industrial process of cooking, mashing and dehydrating to yield a packaged convenience food that can be reconstituted by adding hot water or milk or both, producing an approximation of mashed potatoes. They are available in many different flavors.

Sewage sludge treatment describes the processes used to manage and dispose of sewage sludge produced during sewage treatment. Sludge treatment is focused on reducing sludge weight and volume to reduce transportation and disposal costs, and on reducing potential health risks of disposal options. Water removal is the primary means of weight and volume reduction, while pathogen destruction is frequently accomplished through heating during thermophilic digestion, composting, or incineration. The choice of a sludge treatment method depends on the volume of sludge generated, and comparison of treatment costs required for available disposal options. Air-drying and composting may be attractive to rural communities, while limited land availability may make aerobic digestion and mechanical dewatering preferable for cities, and economies of scale may encourage energy recovery alternatives in metropolitan areas.

Sake kasu (酒粕) or sake lees are the pressed lees left from the production of sake. It is a white paste used in cooking. Its taste is fruity and similar to sake. A by-product of Japanese sake production, it typically contains 8% alcohol, has high nutritional value, and might have health benefits.

Tofu is a food prepared by coagulating soy milk and then pressing the resulting curds into solid white blocks of varying softness: silken, soft, firm, and extra firm. Tofu is translated as bean curd in English. Tofu originated in China and has been consumed in the country for over 2,000 years. Tofu is a traditional component of many East Asian and Southeast Asian cuisines; in modern Western cooking, it is often used as a meat substitute.

A great variety of cassava-based dishes are consumed in the regions where cassava is cultivated. Manihot esculenta is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America, from Brazil, Paraguay and parts of the Andes.
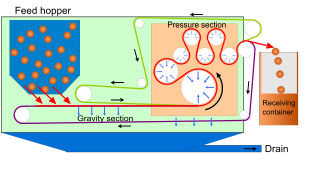
The belt filter is an industrial machine, used for solid/liquid separation processes, particularly the dewatering of sludges in the chemical industry, mining and water treatment. Belt filter presses are also used in the production of apple juice, cider and winemaking. The process of filtration is primarily obtained by passing a pair of filtering cloths and belts through a system of rollers. The system takes a sludge or slurry as a feed, and separates it into a filtrate and a solid cake.

Paper chemicals designate a group of chemicals that are used for paper manufacturing, or modify the properties of paper. These chemicals can be used to alter the paper in many ways, including changing its color and brightness, or by increasing its strength and resistance to water. The chemicals can be defined on basis of their usage in the process.

Pea protein is a food product and protein supplement derived and extracted from yellow and green split peas, Pisum sativum. It can be used as a dietary supplement to increase an individual's protein or other nutrient intake, or as a substitute for other food products. As a powder, it is used as an ingredient in food manufacturing, such as a thickener, foaming agent, or an emulsifier.

Cassava production is vital to the economy of Nigeria as the country is the world's largest producer of the commodity. The crop is produced in 24 of the country's 36 states. In 1999, Nigeria produced 33 million tonnes, while a decade later, it produced approximately 45 million tonnes, which is almost 19% of production in the world. The average yield per hectare is 10.6 tonnes.

A solid bowl centrifuge is a type of centrifuge that uses the principle of sedimentation. A centrifuge is used to separate a mixture that consists of two substances with different densities by using the centrifugal force resulting from continuous rotation. It is normally used to separate solid-liquid, liquid-liquid, and solid-solid mixtures. Solid bowl centrifuges are widely used in various industrial applications, such as wastewater treatment, coal manufacturing, and polymer manufacturing. One advantage of solid bowl centrifuges for industrial uses is the simplicity of installation compared to other types of centrifuge. There are three design types of solid bowl centrifuge, which are conical, cylindrical, and conical-cylindrical.

Sludge is a semi-solid slurry that can be produced from a range of industrial processes, from water treatment, wastewater treatment or on-site sanitation systems. It can be produced as a settled suspension obtained from conventional drinking water treatment, as sewage sludge from wastewater treatment processes or as fecal sludge from pit latrines and septic tanks. The term is also sometimes used as a generic term for solids separated from suspension in a liquid; this soupy material usually contains significant quantities of interstitial water. Sludge can consist of a variety of particles, such as animal manure.

Corn wet-milling is a process of breaking corn kernels into their component parts: corn oil, protein, corn starch, and fiber. It uses water and a series of steps to separate the parts to be used for various products.
Bellmer GmbH is a company founded in 1842 in Niefern-Öschelbronn, Germany by Carl Bellmer. It is still family-owned with over 600 employees globally. Bellmer operates 16 sites around the world but the products are manufactured in Germany and Finland.
Mieczysław Pałasiński, 2005. Technology of Carbohydrate Processing (in Polish). Polish Society of Food Technologists, Małopolska Branch, Kraków, p. 63 - 76.
















