
Stomiiformes is an order of deep-sea ray-finned fishes of very diverse morphology. It includes, for example, dragonfishes, lightfishes, loosejaws, marine hatchetfishes and viperfishes. The order contains 4 families with more than 50 genera and at least 410 species. As usual for deep-sea fishes, there are few common names for species of the order, but the Stomiiformes as a whole are often called dragonfishes and allies or simply stomiiforms.

Marine hatchetfishes or deep-sea hatchetfishes are small deep-sea mesopelagic ray-finned fish of the stomiiform subfamily Sternoptychinae. They should not be confused with the freshwater hatchetfishes, which are not particularly closely related Teleostei in the characiform family Gasteropelecidae.
The name hatchetfish may refer to three groups of fishes:

The marine hatchetfishes or deep-sea hatchetfishes as well as the related bottlelights, pearlsides and constellationfishes are small deep-sea ray-finned fish of the stomiiform family Sternoptychidae. They are not closely related to and should not be confused with the freshwater hatchetfishes, which are teleosts in the characiform family Gasteropelecidae. The Sternoptychidae have 10 genera and about 70 species altogether.

Argyropelecus is an oceanic ray-finned fish genus in the deep sea hatchetfish family Sternoptychidae. A collective name is "silver hatchetfishes", but this can also refer to a species of the freshwater hatchetfishes which are not particularly closely related to. The large pupils of these marine hatchetfishes enable them to see dim objects in the deep sea, where light barely penetrates.

Polyipnus is a genus of oceanic ray-finned fish in the family Sternoptychidae. This is the largest genus of the marine hatchetfishes subfamily Sternoptychinae and indeed of the entire Sternoptychidae. It is not quite as apomorphic as their relatives; it may be that the genus is actually a paraphyletic assemblage of less advanced Sternoptychinae and would need to be split.
Danaphos is an oceanic ray-finned fish genus which belongs in the family Sternoptychidae. A common name is bottlelights.

Argyripnus is an oceanic ray-finned fish genus in the marine hatchetfish family Sternoptychidae. They are commonly known as bristle-mouth fishes, but that may also refer to the related bristlemouth family (Gonostomatidae). A. iridescens is called "pearlside", which usually refers to the closely related genus Maurolicus.
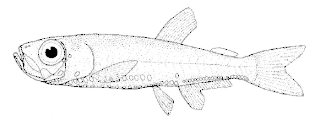
Maurolicus is an oceanic ray-finned fish genus which belongs in the marine hatchetfish family Sternoptychidae. They are commonly known as pearlsides, but the brilliant pearlside is the related Argyripnus iridescens. Occasionally, "bristle-mouth fishes" is used as a common name, but that usually refers to the genus Argyripnus or the family Gonostomatidae.

Barreleyes, also known as spook fish, are small deep-sea argentiniform fish comprising the family Opisthoproctidae found in tropical-to-temperate waters of the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans.

Argyropelecus hemigymnus, the half-naked hatchetfish, short silver hatchetfish or spurred hatchetfish, is a deep-sea hatchetfish of the genus Argyropelecus found mesopelagically in the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans as well as in the Mediterranean Sea. It is a small species rarely exceeding 38 millimetres (1.5 in) standard length. It feeds on zooplankton, particularly ostracods and copepods. Sexual maturation occurs at length of about 22 mm, and adult males have more developed olfactory organs than females, i.e. the species is sexually dimorphic.
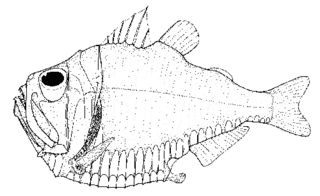
The giant hatchetfish or greater silver hatchetfish, is a marine fish of the genus Argyropelecus. It is found in every ocean except the north Pacific in the mesopelagic zone of tropical and subtropical waters. "Giant" in relative terms only, this is the largest species of marine hatchetfishes, often exceeding 110 millimetres (4.3 in) standard length.

The lovely hatchetfish or Atlantic silver hatchetfish is a species of fish in the family Sternoptychidae. It may exceed 70 millimetres (2.8 in) standard length (SL). It lives in the mesopelagic zone of all oceans and performs diel vertical migration. A. aculeatus feeds on a large range of prey items; in the Gulf of Mexico ostracods and copepods dominated the diet of small individuals and euphausiids, molluscs, and fish the diet of larger ones. The silvery coloration and bioluminescence of the lovely hatchetfish allows it to hide from predators and prey in the down-welling light of the twilight zone.

Argyropelecus affinis is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Sternoptychidae, found in the tropical and subtropical Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans. Common names for this fish include Pacific hatchetfish, deepsea hatchetfish and slender hatchetfish. It inhabits the mesopelagic zone and is either non-migratory or performs short daily vertical migrations.

Argyropelecus sladeni is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Sternoptychidae, found in the tropical and subtropical Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans. This small fish lives in the mesopelagic zone by day and makes a daily vertical migration to the epipelagic zone at night.

Sternoptyx diaphana, the diaphanous hatchetfish, is a species of deep sea ray-finned fish in the family Sternoptychidae. It is the type species of the genus Sternoptyx, and was first described by the French naturalist Johann Hermann in Der Naturforscher 1781.
Polyipnus clarus, commonly known as the stareye hatchetfish or slope hatchetfish, is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Sternoptychidae. It occurs in deep water in the western Atlantic Ocean from the Gulf of Maine southward to the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. It most commonly occurs between 300 and 400 metres but can range from 40 and 830 metres.

Polyipnus spinosus, commonly known as the spiny hatchetfish, is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Sternoptychidae. It occurs in deep water in the western central Pacific Ocean, at depths down to about 500 metres (1,600 ft).

Polyipnus triphanos, commonly known as the threelight hatchetfish, is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Sternoptychidae. It occurs in deep water in the Indo-Pacific Ocean, at depths between about 322 and 966 metres.
Polyipnus latirastrus, commonly known as the combside hatchetfish, is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Sternoptychidae. It occurs in deep water in the western Pacific Ocean, at depths between about 696 and 888 metres.













