
The Araceae are a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants in which flowers are borne on a type of inflorescence called a spadix. The spadix is usually accompanied by, and sometimes partially enclosed in, a spathe. Also known as the arum family, members are often colloquially known as aroids. This family of 140 genera and about 4,075 known species is most diverse in the New World tropics, although also distributed in the Old World tropics and northern temperate regions.

Brodiaea, also known by the common name cluster-lilies, is a monocot genus of flowering plants.

Acorus is a genus of monocot flowering plants. This genus was once placed within the family Araceae (aroids), but more recent classifications place it in its own family Acoraceae and order Acorales, of which it is the sole genus of the oldest surviving line of monocots. Some older studies indicated that it was placed in a lineage, that also includes aroids (Araceae), Tofieldiaceae, and several families of aquatic monocots. However, modern phylogenetic studies demonstrate that Acorus is sister to all other monocots. Common names include calamus and sweet flag.

Calypso is a genus of orchids containing one species, Calypso bulbosa, known as the calypso orchid, fairy slipper or Venus's slipper. It is a perennial member of the orchid family found in undisturbed northern and montane forests. It has a small pink, purple, pinkish-purple, or red flower accented with a white lip, darker purple spottings, and yellow beard. The genus Calypso takes its name from the Greek signifying concealment, as they tend to favor sheltered areas on conifer forest floors. The specific epithet, bulbosa, refers to the bulb-like corms.

Anthurium is a genus of about 1,000 species of flowering plants, the largest genus of the arum family, Araceae. General common names include anthurium, tailflower, flamingo flower, and laceleaf.

Apocynum, commonly known as dogbane or Indian hemp, is a small genus of the flowering plant family Apocynaceae. Its name comes from Ancient Greek ἀπόκυνονapókunon, from ἀπο-apo- "away" and κύωνkúōn "dog", referring to dogbane, which was used to poison dogs. The genus is native to North America, temperate Asia, and southeastern Europe.

Symplocarpus foetidus, commonly known as skunk cabbage or eastern skunk cabbage, is a low-growing plant that grows in wetlands and moist hill slopes of eastern North America. Bruised leaves present an odor reminiscent of skunk.

Calla is a genus of flowering plant in the family Araceae, containing the single species Calla palustris.

Cardiocrinum is a genus of bulbous plants of the lily family first described in 1846. They are native to the Himalaya, China, the Russian Far East, and Japan. The bulbs are usually formed at the soil surface. The preferred habitat is woodland. The plants tend to be monocarpic, dying after flowering.

Corallorhiza trifida, commonly known as early coralroot, northern coralroot, or yellow coralroot, is a coralroot orchid native to North America and Eurasia, with a circumboreal distribution. The species has been reported from the United States, Canada, Russia, China, Japan, Korea, India, Nepal, Kashmir, Pakistan, and almost every country in Europe.

Pinellia is a genus of plants in the family Araceae native to East Asia. Its species are commonly called green dragons due to the color and shape of the inflorescence, which possesses a green, hooded spathe from which protrudes a long, tongue-like extension of the spadix. The leaves vary greatly in shape among different species, from simple and cordate to compound with three to many leaflets. Pinellia reproduces rapidly from seed and many species also produce bulbils on the leaves. Both characteristics have allowed some species to become weedy in temperate areas outside their native range, notably Pinellia ternata in eastern North America.

Disporum is a genus of about 20 species of perennial flowering plants, found in Asia from northern India to Japan, south to Indonesia and north into the Russian Far East.
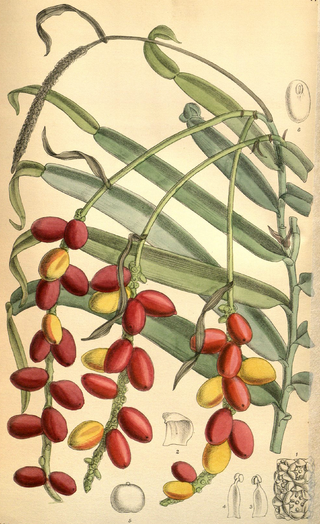
Pothos is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to China, the Indian Subcontinent, Australia, New Guinea, Southeast Asia, and various islands of the Pacific and Indian Oceans.

Neottia is a genus of orchids. The genus now includes the former genus Listera, commonly known as twayblades referring to the single pair of opposite leaves at the base of the flowering stem. The genus is native to temperate, subarctic and arctic regions across most of Europe, northern Asia, and North America, with a few species extending into subtropical regions in the Mediterranean, Indochina, the southeastern United States, etc.

Brodiaea coronaria is the type species of Brodiaea and also known by the common names harvest brodiaea and crown brodiaea. It is native to western North America from British Columbia to northern California, where it grows in mountains and grasslands.

Asterostigma is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to Brazil and Argentina. The leaves are pinnate and the plant is tuberous.
- Asterostigma cryptostylumBogner - Brasília, Goiás, Minas Gerais
- Asterostigma cubense(A.Rich.) K.Krause ex Bogner - São Paulo
- Asterostigma lividum(G.Lodd.) Engl. - southern Brazil; Misiones Province of Argentina
- Asterostigma lombardiiE.G.Gonç. - Minas Gerais, Espírito Santo
- Asterostigma luschnathianumSchott - southern Brazil
- Asterostigma reticulatumE.G.Gonç - southern Brazil
- Asterostigma riedelianum(Schott) Kuntze - eastern Brazil
- Asterostigma tweedieanumSchott - Santa Catarina in southern Brazil

Urospatha is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae that consists of approximately 10 known species. They are found growing in South America and Central America in swamps, wet savannahs, and brackish water. The leaves of the species in this genus are upward pointing and sagittate (arrow-shaped). The inflorescences are quite unique; the spathe is mottled and elongated with a spiral twist at the end. The seeds are distributed by water and have a texture similar to cork that allows them to float. They also quickly germinate in water.

Rhaphidophora decursiva is a species of flowering plant in the family Araceae. It is native to China, the Indian Subcontinent, and Indochina.

Daphniphyllum macropodum is a shrub or small tree found in China, Japan and Korea. Like all species in the genus Daphniphyllum, D. macropodum is dioecious, that is male and female flowers are borne on different plants. The timber is used in China in construction and furniture making. It is grown as an ornamental plant, chiefly for its foliage.

Bambusa multiplex is a species of bamboo native to China, Nepal, Bhutan, Assam, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, and northern Indochina. It is also naturalized in Japan, Iraq, Madagascar, Mauritius, Seychelles, the Indian subcontinent, parts of South America, the West Indies, and the southeastern United States.




















