
Zambia, officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central, Southern and East Africa. It is typically referred to being in South-Central Africa or Southern Africa. It is bordered to the north by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania to the north-east, Malawi to the east, Mozambique to the southeast, Zimbabwe and Botswana to the south, Namibia to the southwest, and Angola to the west. The capital city of Zambia is Lusaka, located in the south-central part of Zambia. The population is concentrated mainly around Lusaka in the south and the Copperbelt Province to the north, the core economic hubs of the country.

Zambia is a landlocked country located in Southern Africa, to the east of Angola. It has a total area of 752,618 square kilometres, of which 9 220 km2 is water.

Malawi is a landlocked country in southeast Africa. It is wholly within the tropics; from about 9°30S at its northernmost point to about 17°S at the southernmost tip. The country occupies a thin strip of land between Zambia and Mozambique, extending southwards into Mozambique along the valley of the Shire River. In the north and north east it also shares a border with Tanzania. Malawi is connected by rail to the Mozambican ports of Nacala and Beira. It lies between latitudes 9° and 18°S, and longitudes 32° and 36°E.

The Zambezi is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers 1,390,000 km2 (540,000 sq mi), slightly less than half of the Nile's. The 2,574 km (1,599 mi) river rises in Zambia and flows through eastern Angola, along the north-eastern border of Namibia and the northern border of Botswana, then along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe to Mozambique, where it crosses the country to empty into the Indian Ocean.

Brachystegia spiciformis, commonly known as zebrawood, or msasa, is a medium-sized African tree having compound leaves and racemes of small fragrant green flowers. The tree is broad and has a distinctive amber and wine red colour when the young leaves sprout during spring (August–September). It grows in savanna, both open woodland and closed woodland of Southern and Eastern Africa, mostly Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Malawi and Mozambique. The word msasa is commonly used as a proper name in African place names. The word also means 'rough plant' in Swahili. Other common names: mundu, myombo, mtondo (Tanzania), muputu (Zambia). The plant is known in the Venda language as mutsiwa, which means 'the one that is left behind'. An outlying population of Brachystegia has recently been discovered in the Soutpansberg mountains of northern South Africa. This tree is a protected species in South Africa.

Miombo woodland is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome located in central and southern tropical Africa. It includes three woodland savanna ecoregions characterized by the dominant presence of Brachystegia and Julbernardia species of trees, and has a range of climates ranging from humid to semi-arid, and tropical to subtropical or even temperate. The trees characteristically shed their leaves for a short period in the dry season to reduce water loss and produce a flush of new leaves just before the onset of the wet season with rich gold and red colours masking the underlying chlorophyll, reminiscent of autumn colours in the temperate zone.

Brachystegia is a genus of tree of the subfamily Detarioideae that is native to tropical Africa.
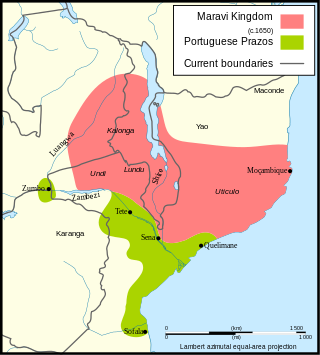
Maravi was a kingdom which straddled the current borders of Malawi, Mozambique, and Zambia, in the 16th century. The present-day name "Maláŵi" is said to derive from the Chewa word malaŵí, which means "flames". "Maravi" is a general name of the peoples of Malawi, eastern Zambia, and northeastern Mozambique. The Chewa language, which is also referred to as Nyanja, Chinyanja or Chichewa, and is spoken in southern and central Malawi, in Zambia and to some extent in Mozambique, is the main language that emerged from this empire.

Tecomaria capensis, the Cape honeysuckle, is a species of flowering plant in the family Bignoniaceae, native to southern Africa. Despite its common name, it is not closely related to the true honeysuckle.

Tecomaria is a genus of flowering plants in the family Bignoniaceae. It includes two species of shrubs or trees native to sub-Saharan Africa, ranging from the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Tanzania to South Africa.

The rattling cisticola is a species of bird in the family Cisticolidae which is native to Africa south of the equator, and parts of East Africa. It is a common to abundant species in open savanna and scrubland habitats, whether in arid, moist or upland regions. Especially during summer, it is highly conspicuous due to its strident and repetitive call-notes from prominent perches.

Souza's shrike is a species of passerine bird in the family Laniidae, the shrikes. It is thought to be a mainly sedentary species that is found in miombo woodland in southern central Africa. It was named after Portuguese zoologist José Augusto de Sousa.
The biomes and ecoregions in the ecology of Zambia are described, listed and mapped here, following the World Wildlife Fund's classification scheme for terrestrial ecoregions, and the WWF freshwater ecoregion classification for rivers, lakes and wetlands. Zambia is in the Zambezian region of the Afrotropical biogeographic realm. Three terrestrial biomes are well represented in the country . The distribution of the biomes and ecoregions is governed mainly by the physical environment, especially climate.

Hyparrhenia is a genus of grasses. Many species are known commonly as thatching grass.

Vwaza Marsh Wildlife Reserve is a national game reserve in Malawi.

The Central Zambezian miombo woodlands ecoregion spans southern central Africa. Miombo woodland is the predominant plant community. It is one of the largest ecoregions on the continent, and home to a great variety of wildlife, including many large mammals.

Aeollanthus (rocksage) is a genus in the mint family, Lamiaceae. All the species are native to Africa.
Aspidoglossum is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1838. It is native to Africa.

The black file snake, also known commonly as the dwarf file snake or the Nyassa file snake, is a species of snake in the subfamily Lamprophiinae of the family Lamprophiidae. The species is endemic to Africa.
The Zambezian region is a large biogeographical region in Africa. The Zambezian region includes woodlands, savannas, grasslands, and thickets, extending from east to west in a broad belt across the continent. The Zambezian region lies south of the rainforests of the Guineo-Congolian region. The Zambezian region is bounded by deserts and xeric shrublands on the southwest, the Highveld grasslands of South Africa to the south, and the subtropical Maputaland forests on the southeast.

















