
Terra Cimmeria is a large Martian region, centered at 34.7°S 145°E and covering 5,400 km (3,400 mi) at its broadest extent. It covers latitudes 15 N to 75 S and longitudes 170 to 260 W. It lies in the Eridania quadrangle. Terra Cimmeria is one part of the heavily cratered, southern highland region of the planet. The Spirit rover landed near the area.
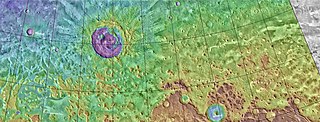
Deuteronilus Mensae is a region on Mars 937 km across and centered at 43.9°N 337.4°W. It covers 344°–325° West and 40°–48° North. Deuteronilus region lies just to the north of Arabia Terra and is included in the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle. It is along the dichotomy boundary, that is between the old, heavily cratered southern highlands and the low plains of the northern hemisphere. The region contains flat-topped knobby terrain that may have been formed by glaciers at some time in the past. Deuteronilus Mensae is to the immediate west of Protonilus Mensae and Ismeniae Fossae. Glaciers persist in the region in modern times, with at least one glacier estimated to have formed as recently as 100,000 to 10,000 years ago. Recent evidence from the radar on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter has shown that parts of Deuteronilus Mensae do indeed contain ice.

The Casius quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the north-central portion of Mars' eastern hemisphere and covers 60° to 120° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Casius quadrangle is also referred to as MC-6. Casius quadrangle contains part of Utopia Planitia and a small part of Terra Sabaea. The southern and northern borders of the Casius quadrangle are approximately 3,065 km and 1,500 km wide, respectively. The north to south distance is about 2,050 km. The quadrangle covers an approximate area of 4.9 million square km, or a little over 3% of Mars' surface area.

The Cebrenia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northeastern portion of Mars' eastern hemisphere and covers 120° to 180° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Cebrenia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-7. It includes part of Utopia Planitia and Arcadia Planitia. The southern and northern borders of the Cebrenia quadrangle are approximately 3,065 km (1,905 mi) and 1,500 km (930 mi) wide, respectively. The north to south distance is about 2,050 km (1,270 mi). The quadrangle covers an approximate area of 4.9 million square km, or a little over 3% of Mars' surface area.

The Arcadia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the north-central portion of Mars’ western hemisphere and covers 240° to 300° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Arcadia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-3. The name comes from a mountainous region in southern Greece. It was adopted by IAU, in 1958.

The Hellas quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Hellas quadrangle is also referred to as MC-28 . The Hellas quadrangle covers the area from 240° to 300° west longitude and 30° to 65° south latitude on the planet Mars. Within the Hellas quadrangle lies the classic features Hellas Planitia and Promethei Terra. Many interesting and mysterious features have been discovered in the Hellas quadrangle, including the giant river valleys Dao Vallis, Niger Vallis, Harmakhis, and Reull Vallis—all of which may have contributed water to a lake in the Hellas basin in the distant past. Many places in the Hellas quadrangle show signs of ice in the ground, especially places with glacier-like flow features.
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Phaethontis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24.

The Mare Australe quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Mare Australe quadrangle is also referred to as MC-30. The quadrangle covers all the area of Mars south of 65°, including the South polar ice cap, and its surrounding area. The quadrangle's name derives from an older name for a feature that is now called Planum Australe, a large plain surrounding the polar cap. The Mars polar lander crash landed in this region.

Lobate debris aprons (LDAs) are geological features on Mars, first seen by the Viking Orbiters, consisting of piles of rock debris below cliffs. These features have a convex topography and a gentle slope from cliffs or escarpments, which suggest flow away from the steep source cliff. In addition, lobate debris aprons can show surface lineations as do rock glaciers on the Earth.
Fretted terrain is a type of surface feature common to certain areas of Mars and was discovered in Mariner 9 images. It lies between two different types of terrain. The surface of Mars can be divided into two parts: low, young, uncratered plains that cover most of the northern hemisphere, and high-standing, old, heavily cratered areas that cover the southern and a small part of the northern hemisphere. Between these two zones is a region called the Martian dichotomy and parts of it contain fretted terrain. This terrain contains a complicated mix of cliffs, mesas, buttes, and straight-walled and sinuous canyons. It contains smooth, flat lowlands along with steep cliffs. The scarps or cliffs are usually 1 to 2 km high. Channels in the area have wide, flat floors and steep walls. Fretted terrain shows up in northern Arabia, between latitudes 30°N and 50°N and longitudes 270°W and 360°W, and in Aeolis Mensae, between 10 N and 10 S latitude and 240 W and 210 W longitude. Two good examples of fretted terrain are Deuteronilus Mensae and Protonilus Mensae.
A concentric crater fill (CCF) is a landform where the floor of a crater is mostly covered with many parallel ridges. It is common in the mid-latitudes of Mars, and is widely believed to be caused by glacial movement. Areas on Mars called Deuteronilus Mensae and Protonilus Mensae contain many examples of concentric crater fill.

A Ring mold crater is a kind of crater on the planet Mars that looks like the ring molds used in baking. They are believed to be caused by an impact into ice. The ice is covered by a layer of debris. They are found in parts of Mars that have buried ice. Laboratory experiments confirm that impacts into ice result in a "ring mold shape." They are also bigger than other craters in which an asteroid impacted solid rock. Impacts into ice warm the ice and cause it to flow into the ring mold shape. These craters are common in lobate debris aprons and lineated valley fill. Many have been found in Mamers Valles, a channel found along the dichotomy boundary in Deuteronilus Mensae. They may be an easy way for future colonists of Mars to find water ice.

Lineated valley fill (LVF), also called lineated floor deposit, is a feature of the floors of some channels on Mars, exhibiting ridges and grooves that seem to flow around obstacles. Shadow measurements show that at least some of the ridges are several metres high. LVF is believed to be ice-rich. Hundreds of metres of ice probably lie protected in LVF under a thin layer of debris. The debris consists of wind-borne dust, material from alcove walls, and lag material remaining after ice sublimated from a rock-ice mixture. Some glaciers on Earth show similar ridges. High-resolution pictures taken with HiRISE reveal that some of the surfaces of lineated valley fill are covered with strange patterns called closed-cell and open-cell brain terrain. The terrain resembles a human brain. It is believed to be caused by cracks in the surface accumulating dust and other debris, together with ice sublimating from some of the surfaces. The cracks are the result stress from gravity and seasonal heating and cooling. This same type of surface is present on Lobate debris aprons and Concentric crater fill so all three are believed to be related. Indeed, lobate debris aprons (LDA's) and lineated valley fill (LVF) are basically the same--mostly ice with a covering of debris, their shapes are dependent on their locations. When confined within a valley, LVF is present; in contrast when not confined, this flowing debris covered ice forms LDA's.

Protonilus Mensae is an area of Mars in the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle. It is centered on the coordinates of 43.86° N and 49.4° E. Its western and eastern longitudes are 37° E and 59.7° E. North and south latitudes are 47.06° N and 39.87° N. Protonilus Mensae is between Deuteronilus Mensae and Nilosyrtis Mensae; all lie along the Martian dichotomy boundary. Its name was adapted by the IAU in 1973.
HiWish is a program created by NASA so that anyone can suggest a place for the HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to photograph. It was started in January 2010. In the first few months of the program 3000 people signed up to use HiRISE. The first images were released in April 2010. Over 12,000 suggestions were made by the public; suggestions were made for targets in each of the 30 quadrangles of Mars. Selected images released were used for three talks at the 16th Annual International Mars Society Convention. Below are some of the over 4,224 images that have been released from the HiWish program as of March 2016.

Glaciers, loosely defined as patches of currently or recently flowing ice, are thought to be present across large but restricted areas of the modern Martian surface, and are inferred to have been more widely distributed at times in the past. Lobate convex features on the surface known as viscous flow features and lobate debris aprons, which show the characteristics of non-Newtonian flow, are now almost unanimously regarded as true glaciers.

The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter's HiRISE instrument has taken many images that strongly suggest that Mars has had a rich history of water-related processes. Many features of Mars appear to be created by large amounts of water. That Mars once possessed large amounts of water was confirmed by isotope studies in a study published in March 2015, by a team of scientists showing that the ice caps were highly enriched with deuterium, heavy hydrogen, by seven times as much as the Earth. This means that Mars has lost a volume of water 6.5 times what is stored in today's polar caps. The water for a time would have formed an ocean in the low-lying Mare Boreum. The amount of water could have covered the planet about 140 meters, but was probably in an ocean that in places would be almost 1 mile deep.
The common surface features of Mars include dark slope streaks, dust devil tracks, sand dunes, Medusae Fossae Formation, fretted terrain, layers, gullies, glaciers, scalloped topography, chaos terrain, possible ancient rivers, pedestal craters, brain terrain, and ring mold craters.

Brain terrain, also called knobs-brain coral and brain coral terrain, is a feature of the Martian surface, consisting of complex ridges found on lobate debris aprons, lineated valley fill and concentric crater fill. It is so named because it suggests the ridges on the surface of the human brain. Wide ridges are called closed-cell brain terrain, and the less common narrow ridges are called open-cell brain terrain. It is thought that the wide closed-cell terrain contains a core of ice, and when the ice disappears the center of the wide ridge collapses to produce the narrow ridges of the open-cell brain terrain. Shadow measurements from HiRISE indicate the ridges are 4-5 meters high. Brain terrain has been observed to form from what has been called an "Upper Plains Unit." The process begins with the formation of stress cracks. The upper plains unit fell from the sky as snow and as ice coated dust.

Sinton is a crater in the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle on Mars. Sinton crater lies in the northern hemisphere, south of the very large crater Lyot and west of Ismeniae Fossae. It was named after Harvard astronomer William M. Sinton. The name was approved in 2007.





























































