
Stomiiformes is an order of deep-sea ray-finned fishes of very diverse morphology. It includes, for example, dragonfishes, lightfishes, loosejaws, marine hatchetfishes and viperfishes. The order contains 4 families with more than 50 genera and at least 410 species. As usual for deep-sea fishes, there are few common names for species of the order, but the Stomiiformes as a whole are often called dragonfishes and allies or simply stomiiforms.
Batoteuthis skolops, the bush-club squid, is the single rare species in genus Batoteuthis, which is the only genus in family Batoteuthidae. The squid is found in Antarctic waters, and reaches a mantle length of at least 350 mm (14 in). Some features of this creature are a small head, a long tail and a very peculiar tentacle, with six series of suckers on the club.

Chtenopteryx is a genus of small, muscular, midwater squid in the monotypic family Chtenopterygidae. Four species are presently recognized in the genus, but more are believed to exist.

Histioteuthis is a genus of squid in the family Histioteuthidae. It goes by the common name cock-eyed squid, because in all species the right eye is normal-sized, round, blue and sunken; whereas the left eye is at least twice the diameter of the right eye, tubular, yellow-green, faces upward, and bulges out of the head.
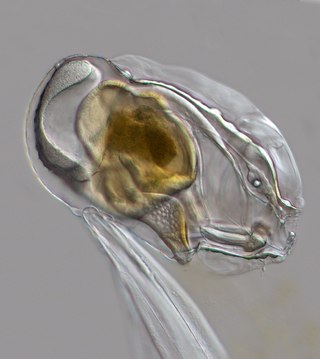
Oikopleura is a genus of tunicate in the class Appendicularia (larvaceans). It forms a mucus house every four hours at 20 degrees Celsius. This house has a coarse mesh to keep out big particles, and a fine mesh that collects the small particles, down to the nanoplankton that includes (pelagic) bacteria.
Egea inermis is a species of glass squid in the monotypic genus Egea.

Taonius is a small genus of glass squid. Although it comprises only three recognised species, it has been suggested there may be as many as five species. Taonius borealis is found in the North Pacific Ocean and Taonius pavo is found in the Atlantic and possibly the south-western Indian Ocean.
Mastigoteuthis is a genus of whip-lash squid containing at least seven valid species. Some teuthologists consider Idioteuthis synonymous with this taxon.
Echinoteuthis is a genus of whip-lash squid containing approximately three to five species. Some teuthologists consider Idioteuthis synonymous with this taxon.

Eledone is a genus of octopuses forming the only genus in the family Eledonidae. It is mainly distributed in the northern and southern Atlantic Ocean, with one species, E. palari, described from the southwestern Pacific Ocean and eastern Indian Ocean in waters around Indonesia and Australia and another, E. microsicya, from the western Indian Ocean. One species, E. thysanophora, is now regarded as a synonym of the brush-tipped octopus.
Teuthowenia pellucida, the googly-eyed glass squid, is a rare deep-sea glass squid whose habitat ranges throughout the oceans of the Southern Hemisphere.

The neon flying squid, sometimes called the red flying squid, akaika, and red squid is a species of large flying squid in the family Ommastrephidae. They are found in subtropical and temperate oceanic waters globally.

Teuthowenia megalops, sometimes known as the Atlantic cranch squid, is a species of glass squid from the subarctic and temperate waters of the northern Atlantic Ocean. They are moderately sized squid with a maximum mantle length of 40 cm (16 in). Their very large eyes are the source for the specific name megalops. Like other members of the genus Teuthowenia, they are easily recognizable by the presence of three bioluminescent organs (photophores) on their eyeballs.
Teuthowenia maculata is a species of glass squid in the genus Teuthowenia. It is similar to the two other members of its genus - T. megalops and T. pellucida, but it is only found in the tropical waters off the coast of Africa in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. The largest recorded specimen is an immature male with a mantle length of 143 millimetres (5.6 in).

Taonius pavo is a species of glass squid found in the Atlantic Ocean. Its exact geographic distribution is uncertain, but it may extend to the southwestern Indian Ocean through the Agulhas Current.
Richard E. Young is a teuthologist. He is an Emeritus Professor of Oceanography at the University of Hawaii's School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology.
Eucleoteuthis is a monotypic genus of squid from the family Ommastrephidae; the only species is Eucleoteuthis luminosa, the striped flying squid or luminous flying squid.
Ornithoteuthis is a small genus of squid, with two species, from the family Ommastrephidae, the "flying squids", the two species in this genus are known as "bird squids". They are relatively small squid, with mantle lengths of around 100–200 mm (3.9–7.9 in), highly agile and rather uncommon. Their characteristics that distinguish then from other members of the subfamily Ommastrephinae are that their mantle and fins are drawn out into a narrow tail and that they have a luminous stripe along their midline on the viscera.

Abylopsis is a siphonophore genus in the Abylidae. The genus contains bioluminescent species.

Bassia is a monotypic siphonophore genus in the family Abylidae. The genus contains the single species Bassia bassensis.










