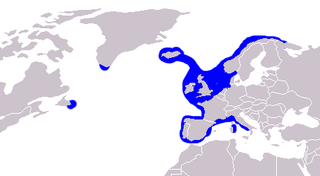
The common ling, also known as the white ling or simply the ling, is a large member of the family Lotidae, a group of cod-like fishes. It resembles the related rocklings, but it is much larger and has a single barbel. This species is unrelated to the pink ling, Genypterus blacodes, from the Southern Hemisphere. The common ling is found in the northern Atlantic, mainly off Europe, and into the Mediterranean Basin. It is an important quarry species for fisheries, especially in the northeastern Atlantic, although some doubts exist as to the sustainability of the fisheries. As an edible species, it is eaten fresh, frozen, or dried, but also preserved in lye, while the roe is a delicacy in Spain.

The sailfin roughshark is a species of dogfish shark in the family Oxynotidae, found in the eastern North Atlantic from Scotland to Senegal between latitudes 61°N and 11°N, at depths of between 265 and 720 m. Its length is up to 1.2 m (3.9 ft).

The white ghost catshark is a shark of the catshark family Scyliorhinidae found in deep water in the northeast Atlantic between latitudes 57°N and 58°N. A deep-water catshark known from the eastern North Atlantic from depths of 1,014 to 1,800 m, it is known from only a limited number of specimens. It reaches a maximum of 54 cm or 1.7 ft total length which is a medium size for the Apristurus genus.

Squatina squatina, the angelshark or monkfish, is a species of shark in the family Squatinidae, that were once widespread in the coastal waters of the northeastern Atlantic Ocean. Well-adapted for camouflaging itself on the sea floor, the angelshark has a flattened form with enlarged pectoral and pelvic fins, giving it a superficial resemblance to a ray. This species can be identified by its broad and stout body, conical barbels, thornless back, and grayish or brownish dorsal coloration with a pattern of numerous small light and dark markings. It measures up to 2.4 m (7.9 ft) long.

The witch, known in English by a variety of other common names including the witch flounder, pole flounder, craig fluke, Torbay sole, and grey sole, is a species of flatfish from the family Pleuronectidae. It occurs on both sides of the North Atlantic Ocean on muddy sea beds in quite deep water. In northern Europe it has some importance in fisheries as a food fish.

The European flounder is a flatfish of European coastal waters from the White Sea in the north to the Mediterranean and the Black Sea in the south. It has been introduced into the United States and Canada accidentally through transport in ballast water. It is caught and used for human consumption.

The solenette or yellow sole, Buglossidium luteum, is a species of flatfish in the family Soleidae, and the only member of its genus. It is characterized by its small size, low-slung semi-circular mouth, and regularly placed dark fin rays. A common and widespread species, it is native to sandy bottoms in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It is of little commercial value.
The spotted dragonet is a species of dragonet native to the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea where it occurs at depths of from 45 to 650 metres. This species is important to local peoples engaged in subsistence fishing.

The Mediterranean scaldfish, also known as the scaldfish, is a species of benthic left eyed flatfish belonging to the family Bothidae. It is found in the eastern Atlantic of Europe and Africa as well as the Mediterranean, and is of minor interest to fisheries.

Helicolenus dactylopterus, blackbelly rosefish, bluemouth rockfish, and bluemouth seaperch, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae which is classified within the family Scorpaenidae. This Atlantic species is a typical sit-and-wait predator with a highly cryptic coloration.

The wedge sole, is a flatfish of the family Soleidae. It is a bottom dwelling predatory fish inhabiting both sandy and muddy soils at depths between 10 and 450 m in the East Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea. It achieves a maximum size of 30 cm (12 in).

Zebrias is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Soleidae.
Synodus macrostigmus, commonly known as the largespot lizardfish, is a species of fish in the lizardfish family, Synodontidae, a basal ray-finned fish in the class Actinopterygii. It is native to the warm temperate western Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico.

The Egyptian sole is a species of flatfish in the true sole family, Soleidae. It lives on the sandy or muddy seabed of the Mediterranean Sea, and is now colonising the Red Sea. It often semi-immerses itself in the substrate. The upper side is greyish-brown while the underside is white. It grows to a maximum length of about 70 cm (28 in). This fish is used for human consumption and is prized as a food fish. It is caught mostly by trawling on the seabed.
Equulites klunzingeri, or Klunzinger's ponyfish, is a marine, demersal species of ponyfish from the family Leiognathidae which was originally found only in the Red Sea. It is colonizing the Mediterranean as part of the Lessepsian migration through the Suez Canal.

Solea senegalensis, the Senegalese sole, is a species of flatfish from the family of the true soles, the Soleidae, from the eastern Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea.

Trachyrincus scabrus, the roughsnout grenadier or Mediterranean longsnout grenadier, is a species of bathydemersal marine fish from the subfamily Trachyrincinae, part of the family Macrouridae. It is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean.
Dagetichthys lusitanicus, commonly known as the Portuguese sole, is a species of flatfish native to the eastern Atlantic Ocean. Little is known of the abundance or behaviour of this fish, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as being "data deficient".
Microchirus azevia, commonly known as the bastard sole, is a species of flatfish in the family Soleidae. It is found on the continental slope of the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea at depths down to about 250 m (800 ft).

Peristedion cataphractum, the African armoured gurnard, the mailed gurnard or armed gurnard, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Peristediidae, the armoured gurnards or armored sea robins. It is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.

















