
Jellyfish, also known as sea jellies, are the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, which is a major part of the phylum Cnidaria.

Box jellyfish are cnidarian invertebrates distinguished by their box-like body. Some species of box jellyfish produce potent venom delivered by contact with their tentacles. Stings from some species, including Chironex fleckeri, Carukia barnesi, Malo kingi, and a few others, are extremely painful and often fatal to humans.

Aurelia aurita is a species of the family Ulmaridae. All species in the genus are very similar, and it is difficult to identify Aurelia medusae without genetic sampling; most of what follows applies equally to all species of the genus.

The lion's mane jellyfish is one of the largest known species of jellyfish. Its range is confined to cold, boreal waters of the Arctic, northern Atlantic, and northern Pacific Oceans. It is common in the English Channel, Irish Sea, North Sea, and in western Scandinavian waters south to Kattegat and Øresund. It may also drift into the southwestern part of the Baltic Sea. Similar jellyfish – which may be the same species – are known to inhabit seas near Australia and New Zealand. The largest recorded specimen was measured off the coast of Massachusetts in 1865 and had a bell with a diameter of 210 centimetres and tentacles around 36.6 m (120 ft) long. Lion's mane jellyfish have been observed below 42°N latitude for some time in the larger bays of the East Coast of the United States.

A maculopapular rash is a type of rash characterized by a flat, red area on the skin that is covered with small confluent bumps. It may only appear red in lighter-skinned people. The term "maculopapular" is a compound: macules are small, flat discolored spots on the surface of the skin; and papules are small, raised bumps. It is also described as erythematous, or red.

Cassiopea is a genus of true jellyfish and members of the family Cassiopeidae. They are found in warmer coastal regions around the world, including shallow mangrove swamps, mudflats, canals, and turtle grass flats in Florida, the Caribbean and Micronesia. The medusa usually lives upside-down on the sea floor in shallow areas, which has earned them their common name. These jellyfish partake in a symbiotic relationship with photosynthetic dinoflagellates and therefore, must lie upside-down in areas with sufficient light penetration to fuel their energy source. Where found, there may be numerous individuals with varying shades of white, blue, green and brown.

Chironex fleckeri, commonly known as the Australian box jelly, and nicknamed the sea wasp, is a species of extremely venomous box jellyfish found in coastal waters from northern Australia and New Guinea to Indonesia, Cambodia, Malaysia and Singapore, the Philippines and Vietnam. It has been described as "the most lethal jellyfish in the world", with at least 64 known deaths in Australia from 1884 to 2021.

Seabather's eruption is an itching dermatitis caused by a hypersensitivity reaction to the immature nematocysts of larval-stage thimble jellyfish, sea anemones and other larval cnidarians. The eruption is sometimes attributed to "sea lice" or "sea ants", but sea lice (Caligidae) are crustacean parasites of fish only.

Pelagia noctiluca is a jellyfish in the family Pelagiidae and the only currently recognized species in the genus Pelagia. It is typically known in English as the mauve stinger, but other common names are purple-striped jelly, purple stinger, purple people eater, purple jellyfish, luminous jellyfish and night-light jellyfish. In Greek, pelagia means "(she) of the sea", from pelagos "sea, open sea"; in Latin noctiluca is the combining form of nox, "night"", and lux, "light"; thus, Pelagia noctiluca can be described as a marine organism with the ability to glow in the dark (bioluminescence). It is found worldwide in tropical and warm temperate seas, although it is suspected that records outside the North Atlantic region, which includes the Mediterranean and Gulf of Mexico, represent closely related but currently unrecognized species.

Phacellophora, commonly known as the fried egg jellyfish or egg-yolk jellyfish, is a very large jellyfish in the monotypic family Phacellophoridae containing a single species Phacellophora camtschatica. This genus can be easily identified by the yellow coloration in the center of its body which closely resembles an egg yolk, hence its common name. Some individuals can have a bell close to 60 cm (2 ft) in diameter, and most individuals have 16 clusters of up to a few dozen tentacles, each up to 6 m (20 ft) long. A smaller jellyfish, Cotylorhiza tuberculata, typically found in warmer water, particularly in the Mediterranean Sea, is also popularly called a fried egg jellyfish. Also, P. camtschatica is sometimes confused with the Lion's mane jellyfish.

Carybdea is a genus of venomous box jellyfish within the family Carybdeidae that currently consists of a total of 8 species. This genus of jellyfish are often found in warm waters around the world in waters such as the Mediterranean Sea, the Pacific Ocean, and off the coast of Africa. Their sting can cause a range of effects depending on the species. These invertebrates will go through both sexual and asexual reproduction as they transform from a polyp to medusa. Carybdea have a box-shaped bell with four tentacles and eye-like sensory structures. There are distinct physical markings that differentiate many species within the genus. While Carybdea use their venom to act as predators, they are also preyed on by turtles and various fish. They feed on plankton, invertebrates, fish, and some crustaceans.

Chrysaora hysoscella, the compass jellyfish, is a common species of jellyfish that inhabits coastal waters in temperate regions of the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, including the North Sea and Mediterranean Sea. In the past it was also recorded in the southeastern Atlantic, including South Africa, but this was caused by confusion with close relatives; C. africana, C. fulgida and an undescribed species tentatively referred to as "C. agulhensis".

Carukia barnesi is an extremely venomous jellyfish found near Australia. Stings can result in Irukandji syndrome, and this species is commonly known as Irukandji jellyfish, although this name does not distinguish it from other Irukandji jellyfish such as Malo kingi.

Chiropsalmus quadrumanus, commonly known as the four-handed box jellyfish, is a species of box jellyfish found in the western Atlantic Ocean, the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean. The sting is venomous and dangerous to humans, especially children.

Carybdea marsupialis is a venomous species of box jellyfish, in the small family Carybdeidae within the class Cubozoa.

Cassiopea xamachana, commonly known as the upside-down jellyfish, is a species of jellyfish in the family Cassiopeidae. It is found in warm parts of the western Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea, and the Gulf of Mexico. It was first described by the American marine biologist Henry Bryant Bigelow in 1892.

Aglantha digitale is a species of hydrozoan in the family Rhopalonematidae. It is found in the Arctic and sub-Arctic where it is one of the most common jellyfish. It is unusual in having both a slow swimming action, through pulsating its bell, and a rapid escape response.
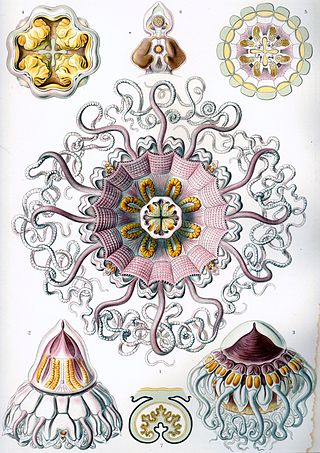
Coronamedusae is a subclass of jellyfish in the class Scyphozoa. It is the sister taxon of Discomedusae and contains about 50 named species, all included in the order Coronatae. Jellyfish in this subclass are either small medusae living in shallow marine environments, or large medusae living in the deep sea.

Linuche aquila is a species of cnidarian found in the tropical and subtropical areas of the Pacific Ocean. It is very small and is commonly known as a thimble jellyfish because of its size and shape. The larvae can cause bathers to develop an itchy red rash commonly known as seabather's eruption.

Bougainvillia superciliaris is a marine invertebrate, a species of athecate hydroid. It belongs to the Bougainvillidae family. It can be confused with Rathkea octopunctata, but differs from it in four bundles of tentacles of the outer circle.


















