
The cat, commonly referred to as the domestic cat or house cat is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae. Recent advances in archaeology and genetics have shown that the domestication of the cat occurred in the Near East around 7500 BC. It is commonly kept as a house pet and farm cat, but also ranges freely as a feral cat avoiding human contact. It is valued by humans for companionship and its ability to kill vermin. Because of its retractable claws it is adapted to killing small prey like mice and rats. It has a strong flexible body, quick reflexes, sharp teeth, and its night vision and sense of smell are well developed. It is a social species, but a solitary hunter and a crepuscular predator. Cat communication includes vocalizations like meowing, purring, trilling, hissing, growling, and grunting as well as cat body language. It can hear sounds too faint or too high in frequency for human ears, such as those made by small mammals. It also secretes and perceives pheromones.

Felidae is the family of mammals in the order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats. A member of this family is also called a felid. The term "cat" refers both to felids in general and specifically to the domestic cat.

Sex is the biological trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing organism produces male or female gametes. Male organisms produce small mobile gametes, while female organisms produce larger, non-mobile gametes. Organisms that produce both types of gametes are called hermaphrodites. During sexual reproduction, male and female gametes fuse to form zygotes, which develop into offspring that inherit traits from each parent.

Balaenidae is a family of whales of the parvorder Mysticeti that contains mostly fossil taxa and two living genera: the right whale, and the closely related bowhead whale.
The Catalogue of Life is an online database that provides an index of known species of animals, plants, fungi, and microorganisms. It was created in 2001 as a partnership between the global Species 2000 and the American Integrated Taxonomic Information System. The Catalogue is used by research scientists, citizen scientists, educators, and policy makers. The Catalogue is also used by the Biodiversity Heritage Library, the Barcode of Life Data System, Encyclopedia of Life, and the Global Biodiversity Information Facility. The Catalogue currently compiles data from 165 peer-reviewed taxonomic databases that are maintained by specialist institutions around the world. As of September 2022, the COL Checklist lists 2,067,951 of the world's 2.2m extant species known to taxonomists on the planet at present time.
The Ethiopian long-eared bat or Ethiopian big-eared bat is a species of long-eared bat in the family Vespertilionidae.

The tree bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae and the only species in the genus Ardops. It is found in Dominica, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Montserrat, Saint Lucia, Saba, Saint Martin, Sint Eustatius, Saint Kitts, Nevis, Grenada and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.

Ichthyodectiformes is an extinct order of marine stem-teleost ray-finned fish. The order is named after the genus Ichthyodectes, established by Edward Drinker Cope in 1870. Ichthyodectiforms are usually considered to be some of the closest relatives of the teleost crown group.

The Thyatirinae, or false owlet moths, are a subfamily of the moth family Drepanidae with about 200 species described. Until recently, most classifications treated this group as a separate family called Thyatiridae.
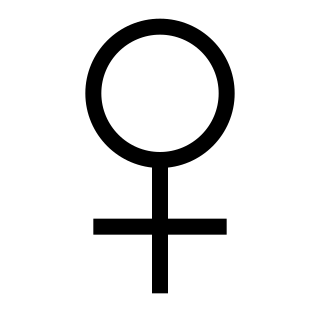
An organism's sex is female if it produces the ovum, the type of gamete that fuses with the male gamete during sexual reproduction.
The Reptile Database is a scientific database that collects taxonomic information on all living reptile species. The database focuses on species and has entries for all currently recognized ~13,000 species and their subspecies, although there is usually a lag time of up to a few months before newly described species become available online. The database collects scientific and common names, synonyms, literature references, distribution information, type information, etymology, and other taxonomically relevant information.
Permutotetraviridae is a family of viruses. Lepidopteran insects serve as natural hosts. The family contains one genus that has two species. Diseases associated with this family include: infection outcome varies from unapparent to lethal.
Pyrgacris is a small genus of grasshoppers in the monotypic family Pyrgacrididae. The two species in the genus Pyrgacris are found only on Reunion Island.
AmphibiaWeb is an American non-profit website that provides information about amphibians. It is run by a group of universities working with the California Academy of Sciences: San Francisco State University, the University of California at Berkeley, University of Florida at Gainesville, and University of Texas at Austin.
Aphendala recta is a moth of the family Limacodidae first described by George Hampson in 1893. It is found in Sri Lanka.
Thosea aperiens, the stinging caterpillar, is a moth of the family Limacodidae. The species was first described by Francis Walker in 1865. It is found in Sri Lanka and India.
Thosea cervina is a moth of the family Limacodidae first described by Frederic Moore in 1877. It is found in Sri Lanka and India.








