Bristol Temple Meads is the oldest and largest railway station in Bristol, England. It is located 118 miles 31 chains away from London Paddington. It is an important transport hub for public transport in the city; there are bus services to many parts of the city and surrounding districts, with a ferry to the city centre. Bristol's other major station, Bristol Parkway, is a more recent station on the northern outskirts of the conurbation.

Brentford is a suburban town in West London, England and part of the London Borough of Hounslow. It lies at the confluence of the River Brent and the Thames, 8 miles (13 km) west of Charing Cross.

Paddington is an area in the City of Westminster, in central London, England. A medieval parish then a metropolitan borough, it was integrated with Westminster and Greater London in 1965. Paddington station, designed by the engineer Isambard Kingdom Brunel opened in 1847. It is also the site of St Mary's Hospital and the former Paddington Green Police Station.

The Royal Albert Bridge is a railway bridge which spans the River Tamar in England between Plymouth, Devon and Saltash, Cornwall. Its unique design consists of two 455-foot (138.7 m) lenticular iron trusses 100 feet (30.5 m) above the water, with conventional plate-girder approach spans. This gives it a total length of 2,187.5 feet (666.8 m). It carries the Cornish Main Line railway in and out of Cornwall. It is adjacent to the Tamar Bridge which opened in 1961 to carry the A38 road.

The Hertford Union Canal or Duckett's Cut, just over 1 mile (1.6 km) long, connects the Regent's Canal to the Lee Navigation in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in East London. It was opened in 1830 but quickly proved to be a commercial failure. It was acquired by the Regents Canal Company in 1857, and became part of the Grand Union Canal in 1927.

The Colne is a river and a tributary of the River Thames in England. Just over half its course is in south Hertfordshire. Downstream, it forms the boundary between Buckinghamshire and the London Borough of Hillingdon. The confluence with the River Thames is on the Staines reach at Staines-upon-Thames.

Bishop's Bridge, sometimes known as Paddington Bridge, is a road bridge in the Paddington district of London which carries Bishop's Bridge Road across the rail approaches to Paddington station and across the adjacent Paddington Arm of the Grand Union Canal. The original Isambard Kingdom Brunel built bridge was replaced in 2006. The name Bishop's Bridge Road comes from the manor of Paddington which was granted to the Bishop of London, Nicholas Ridley, by Edward VI in the mid 16th Century.
The Grand Junction Canal is a canal in England from Braunston in Northamptonshire to the River Thames at Brentford, with a number of branches. The mainline was built between 1793 and 1805, to improve the route from the Midlands to London, by-passing the upper reaches of the River Thames near Oxford, thus shortening the journey.

Maidenhead Railway Bridge, also known as Maidenhead Viaduct and The Sounding Arch, carries the Great Western Main Line (GWML) over the River Thames between Maidenhead, Berkshire and Taplow, Buckinghamshire, England. It is a single structure of two tall wide red brick arches buttressed by two over-land smaller arches. It crosses the river on the Maidenhead-Bray Reach which is between Boulter's Lock and Bray Lock and is near-centrally rooted in the downstream end of a very small island.

Burscough is a town and civil parish in the district of West Lancashire, Lancashire, England. The town is located approximately 13.5 miles (21.7 km) north-northeast of Liverpool and 13 miles (21 km) southwest of Preston. Its northern part is called Burscough Bridge, and was originally a separate settlement.

Bath Spa railway station is the principal station serving the city of Bath in South West England. It is on the Great Western Main Line, 106 miles 71 chains down the line from the zero point at London Paddington between Chippenham to the east and Oldfield Park to the west. Its three-letter station code is BTH.

Norwood Green is a place in the London Borough of Ealing in London, England, that forms the southern part of Southall. It is a suburban development centred 10.7 miles (17.2 km) west of Charing Cross and 4 miles (6.4 km) ENE of Heathrow Airport.

Isambard Kingdom Brunel was a British civil engineer and mechanical engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history", "one of the 19th-century engineering giants", and "one of the greatest figures of the Industrial Revolution, [who] changed the face of the English landscape with his groundbreaking designs and ingenious constructions". Brunel built dockyards, the Great Western Railway (GWR), a series of steamships including the first purpose-built transatlantic steamship, and numerous important bridges and tunnels. His designs revolutionised public transport and modern engineering.

The Store Street Aqueduct in central Manchester, England, was built in 1798 by Benjamin Outram on the Ashton Canal. A Grade II* listed building, it is built on a skew of 40° across Store Street, and is believed to be the first major aqueduct of its kind in Great Britain and the oldest still in use today.

The Westport Canal was built in the late 1830s to link Westport and Langport in Somerset, England. It was part of a larger scheme involving improvements to the River Parrett above Burrow Bridge. Langport is the point at which the River Yeo joins the River Parrett and the intention was to enable trade via the port at Bridgwater. It remained in use until the 1870s, but closed when the Somerset Drainage Commissioners took over control of the River Parrett. Despite a petition against closure by local people, the Commissioners ruled that navigation of the canal must cease due to their interpretation of the Act which gave them control of it, leaving the canal to serve as a drainage channel since 1878.
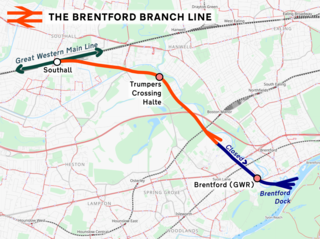
The Brentford branch line, also known as the Brentford Dock Line, is a freight-only branch railway line in west London, England. The route, which opened in 1859, was backed by the Great Western Railway and built by the Great Western & Brentford Railway Company. It ran 4 mi (6.4 km) from Southall to Brentford Dock. In 1964, the line to the wharves was closed. The branch now runs from the Great Western Main Line to a goods yard and waste transfer station in Brentford.

A balloon flange girder or (colloquially) balloon topper is a form of vertical I-beam wrought iron plate girder, where the top flange, instead of being a simple flat plate, is extended into a hollow tube. When a girder is subjected to a positive bending moment the top flange acts in compression making a flat plate flange more susceptible to local buckling than the balloon flange is.

A bronze statue of Isambard Kingdom Brunel, also known as Brunel Monument or the Isambard Brunel Monument, by Carlo Marochetti, stands on the Victoria Embankment in London, England, at the west end of Temple Place. The statue rests on a Portland stone pedestal, with flanking screens and benches, by the architect Richard Norman Shaw.

A bronze statue of Robert Stephenson by Carlo Marochetti usually stands on a red granite plinth in the forecourt of Euston railway station in London, England. Erected in 1871, it is one of few surviving elements of the original station after it was redeveloped in the 1960s, and it became a Grade II listed building in 1974. It was temporarily removed in 2020 to allow the station to be remodelled to accommodate the new High Speed 2 (HS2) railway line.