
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it is convenient for areas in frequent communication to keep the same time.

Japan Standard Time, or Japan Central Standard Time, is the standard time zone in Japan, 9 hours ahead of UTC (UTC+09:00). Japan does not observe daylight saving time, though its introduction has been debated on several occasions. During World War II, the time zone was often referred to as Tokyo Standard Time.
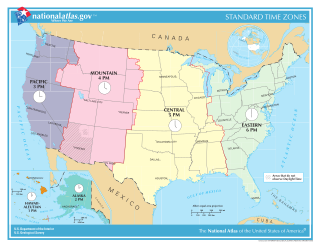
In the United States, time is divided into nine standard time zones covering the states, territories and other US possessions, with most of the country observing daylight saving time (DST) for approximately the spring, summer, and fall months. The time zone boundaries and DST observance are regulated by the Department of Transportation, but no single map of those existed until the agency announced intentions to make one in September 2022. Official and highly precise timekeeping services (clocks) are provided by two federal agencies: the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) ; and the United States Naval Observatory (USNO). The clocks run by these services are kept synchronized with each other as well as with those of other international timekeeping organizations.

Eastern European Time (EET) is one of the names of UTC+02:00 time zone, 2 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. The zone uses daylight saving time, so that it uses UTC+03:00 during the summer.

The Atlantic Time Zone is a geographical region that keeps standard time—called Atlantic Standard Time (AST)—by subtracting four hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), resulting in UTC−04:00. AST is observed in parts of North America including several Caribbean islands. During part of the year, some portions of the zone observe daylight saving time, referred to as Atlantic Daylight Time (ADT), by moving their clocks forward one hour to UTC−03:00. The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time of the 60th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory.

Moscow Time is the time zone for the city of Moscow, Russia, and most of western Russia, including Saint Petersburg. It is the second-westernmost of the eleven time zones of Russia. It has been set to UTC+03:00 without DST since 26 October 2014; before that date it had been set to UTC+04:00 year-round on 27 March 2011.

UTC+10:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +10:00. This time is used in:

UTC+08:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +08:00.

UTC+11:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +11:00. This time is used in:

UTC+09:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +09:00.

UTC+07:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +07:00. In ISO 8601 the associated time would be written as 2024-12-27T09:01:41+07:00. It is 7 hours ahead of UTC, meaning that when the time in UTC areas is midnight (00:00), the time in UTC+07:00 areas would be 7:00 in the morning.

UTC+06:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +06:00. This time is used in:

Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Eastern Standard Time, Australian Central Standard Time and Australian Western Standard Time.
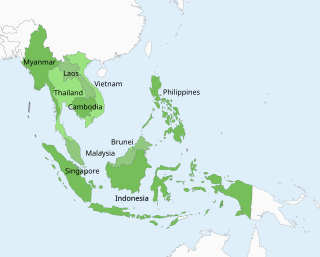
The ASEAN Common Time (ACT) is a proposal to adopt a standard time for all Association of Southeast Asian Nations member states. It was proposed in 1995 by Singapore, and in 2004 and 2015 by Malaysia to make business across countries easier. The proposal failed because of opposition in Thailand and Cambodia: Thais and Cambodians argued that UTC+08:00 was not better than UTC+07:00, which is the current time zone of their countries.
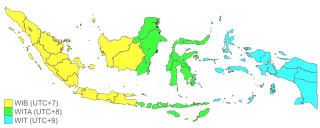
The Republic of Indonesia, a country located in Southeast Asia has three time zones. Western Indonesia Time is seven hours ahead (UTC+07:00) of the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), used in the islands of Sumatra, Java, and the western half of Kalimantan. Central Indonesia Time is eight hours ahead (UTC+08:00), used in the eastern half of Kalimantan, as well as all of Bali, the Lesser Sunda Islands, and Sulawesi. Eastern Indonesia Time is nine hours ahead (UTC+09:00), used in the Maluku Islands and Western New Guinea.

Central Africa Time or CAT, is a time zone used in central and southern Africa. Central Africa Time is two hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC+02:00), which is the same as the adjacent South Africa Standard Time, Egypt Standard Time, Eastern European Time, Kaliningrad Time and Central European Summer Time.

East Africa Time, or EAT, is a time zone used in eastern Africa. The time zone is three hours ahead of UTC (UTC+03:00), which is the same as Moscow Time, Arabia Standard Time, Further-eastern European Time and Eastern European Summer Time.
South Korea has one time zone, Korea Standard Time (UTC+9), which is abbreviated KST. South Korea currently does not observe daylight saving time.
Reunified Vietnam follows Indochina Time (ICT), which is seven hours ahead of UTC, ICT is used all year round as Vietnam does not observe daylight saving time. Vietnam shares the same time zone with Thailand, Cambodia, Christmas Island, Laos, and Western Indonesia.
Time in Palau is given by Palau Time. Palau does not have an associated daylight saving time.















